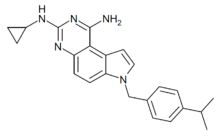
Chemistry:SCH-79797
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H25N5 |
| Molar mass | 371.488 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
SCH-79797 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist of the thrombin receptor proteinase activated receptor 1 (PAR1).[1] It has anticoagulant, anticonvulsant and antiinflammatory effects and has been researched as a treatment for heart attack and stroke, though never developed for medical use.[2][3][4][5] It also shows antibiotic actions which are not shared with other PAR1 antagonists such as vorapaxar, so may be mediated through a different target than PAR1.[6][7]
References
- ↑ "Inhibition of cellular action of thrombin by N3-cyclopropyl-7-{[4-(1-methylethyl)phenyl]methyl}-7H-pyrrolo[3,2-f]quinazoline-1,3-diamine (SCH 79797), a nonpeptide thrombin receptor antagonist". Biochemical Pharmacology 60 (10): 1425–34. November 2000. doi:10.1016/s0006-2952(00)00460-3. PMID 11020444.
- ↑ "A protease-activated receptor 1 antagonist protects against global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury after asphyxial cardiac arrest in rabbits". Neural Regeneration Research 12 (2): 242–249. February 2017. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.199011. PMID 28400806.
- ↑ "Inhibition of protease-activated receptor 1 ameliorates behavioral deficits and restores hippocampal synaptic plasticity in a rat model of status epilepticus". Neuroscience Letters 692: 64–68. January 2019. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2018.10.058. PMID 30391321.
- ↑ "Fibrinolysis protease receptors promote activation of astrocytes to express pro-inflammatory cytokines". Journal of Neuroinflammation 16 (1): 257. December 2019. doi:10.1186/s12974-019-1657-3. PMID 31810478.
- ↑ "Blockade of PAR-1 Signaling Attenuates Cardiac Hypertrophy and Fibrosis in Renin-Overexpressing Hypertensive Mice". Journal of the American Heart Association 9 (12): e015616. June 2020. doi:10.1161/JAHA.119.015616. PMID 32495720.
- ↑ "SCH79797 improves outcomes in experimental bacterial pneumonia by boosting neutrophil killing and direct antibiotic activity". The Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 73 (6): 1586–1594. June 2018. doi:10.1093/jac/dky033. PMID 29514266.
- ↑ "A Dual-Mechanism Antibiotic Kills Gram-Negative Bacteria and Avoids Drug Resistance". Cell 181 (7): 1518–1532.e14. May 2020. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.005. PMID 32497502.
 |

