Chemistry:SIB-1893
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
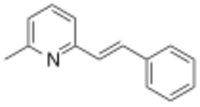
| Formula | C14H13N |
| Molar mass | 195.265 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
SIB-1893 is a drug used in scientific research which was one of the first compounds developed that acts as a selective antagonist for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5.[1] It has anticonvulsant and neuroprotective effects,[2] and reduces glutamate release.[3] It has also been found to act as a positive allosteric modulator of mGluR4.[4]
References
- ↑ "SIB-1757 and SIB-1893: selective, noncompetitive antagonists of metabotropic glutamate receptor type 5". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 290 (1): 170–81. July 1999. PMID 10381773.
- ↑ "Anticonvulsant activity of two metabotropic glutamate group I antagonists selective for the mGlu5 receptor: 2-methyl-6-(phenylethynyl)-pyridine (MPEP), and (E)-6-methyl-2-styryl-pyridine (SIB 1893)". Neuropharmacology 39 (9): 1567–74. July 2000. doi:10.1016/S0028-3908(99)00242-7. PMID 10854901.
- ↑ "Noncompetitive metabotropic glutamate5 receptor antagonist (E)-2-methyl-6-styryl-pyridine (SIB1893) depresses glutamate release through inhibition of voltage-dependent Ca2+ entry in rat cerebrocortical nerve terminals (synaptosomes)". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 309 (3): 951–8. June 2004. doi:10.1124/jpet.103.064881. PMID 14982967.
- ↑ "Positive allosteric modulation of the human metabotropic glutamate receptor 4 (hmGluR4) by SIB-1893 and MPEP". British Journal of Pharmacology 138 (6): 1026–30. March 2003. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0705159. PMID 12684257.
 |
