Chemistry:Tabimorelin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
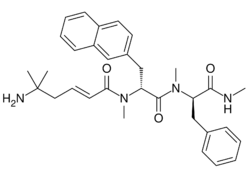
| Other names | ((2E)-5-amino-5-methylhex-2-enoic acid N-methyl-N-((1R)-1-(N-methyl-N-((1R)-1-(methylcarbamoyl)-2-phenylethyl)carbamoyl)-2-(2-naphthyl)ethyl)amide) |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C32H40N4O3 |
| Molar mass | 528.697 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Tabimorelin (INN) (developmental code name NN-703) is a drug which acts as a potent, orally-active agonist of the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR) and growth hormone secretagogue, mimicking the effects of the endogenous peptide agonist ghrelin as a stimulator of growth hormone (GH) release. It was one of the first GH secretagogues developed and is largely a modified polypeptide, but it is nevertheless orally-active in vivo.[1] Tabimorelin produced sustained increases in levels of GH and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), along with smaller transient increases in levels of other hormones such as adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), cortisol, and prolactin.[2][3] However actual clinical effects in adults with growth hormone deficiency were limited, with only the most severely GH-deficient patients showing significant benefit,[4] and tabimorelin was also found to act as a CYP3A4 inhibitor which could cause it to have undesirable interactions with other drugs.[5]
See also
- List of growth hormone secretagogues
References
- ↑ "Pharmacological characterisation of a new oral GH secretagogue, NN703". European Journal of Endocrinology 141 (2): 180–9. August 1999. doi:10.1530/eje.0.1410180. PMID 10427162.
- ↑ "The pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety and tolerability of a single dose of NN703, a novel orally active growth hormone secretagogue in healthy male volunteers". Growth Hormone & IGF Research 10 (4): 193–8. August 2000. doi:10.1054/ghir.2000.0152. PMID 11032702.
- ↑ "The pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety and tolerability following 7 days daily oral treatment with NN703 in healthy male subjects". Growth Hormone & IGF Research 11 (1): 41–8. February 2001. doi:10.1054/ghir.2000.0188. PMID 11437473.
- ↑ "Oral administration of the growth hormone secretagogue NN703 in adult patients with growth hormone deficiency". Clinical Endocrinology 58 (5): 572–80. May 2003. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2265.2003.01754.x. PMID 12699438.
- ↑ "A clinical study investigating the pharmacokinetic interaction between NN703 (tabimorelin), a potential inhibitor of CYP3A4 activity, and midazolam, a CYP3A4 substrate". European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 58 (10): 683–8. February 2003. doi:10.1007/s00228-002-0539-1. PMID 12610745.
 |

