Chemistry:Thiocoraline
From HandWiki
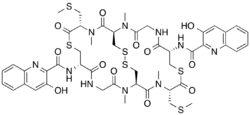
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N,N′-{(1R,7S,11S,14R,20S,24S)-2,12,15,25-Tetramethyl-11,24-bis[(methylsulfanyl)methyl]-3,6,10,13,16,19,23,26-octaoxo-9,22,28,29-tetrathia-2,5,12,15,18,25-hexaazabicyclo[12.12.4]triacontane-7,20-diyl}bis(3-hydroxy-2-quinolinecarboxamide)
| |
| Other names
Thiocoraline A
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C48H56N10O12S6 | |
| Molar mass | 1157.39 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Thiocoraline is a microbial natural product of the depsipeptide class. Thiocoraline was isolated from the mycelium cake of a marine actinomycete strain L-13-ACM2-092.[1] In vitro, thiocoraline causes an arrest in G1 phase of the cell cycle and decreases the rate of S phase progression towards G2/M phase.[2] Thiocoraline is likely to be a DNA replication inhibitor. Thiocoraline is produced on a nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) assembly line.[3]
References
- ↑ "Thiocoraline, a new depsipeptide with antitumor activity produced by a marine Micromonospora. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation, and biological activities". The Journal of Antibiotics 50 (9): 734–7. September 1997. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.50.734. PMID 9360617.
- ↑ "Mode of action of thiocoraline, a natural marine compound with anti-tumour activity". British Journal of Cancer 80 (7): 971–80. June 1999. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6690451. PMID 10362104.
- ↑ "Deciphering the biosynthesis pathway of the antitumor thiocoraline from a marine actinomycete and its expression in two Streptomyces species". ChemBioChem 7 (2): 366–76. February 2006. doi:10.1002/cbic.200500325. PMID 16408310.
 |

