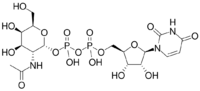
Chemistry:Uridine diphosphate N-acetylgalactosamine
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Uridine 5′-(2-acetamido-2-deoxy-α-D-galactopyranosyl dihydrogen diphosphate)
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
O1-[(2R,3R,4R,5R,6R)-3-Acetamido-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl] O3-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl} dihydrogen diphosphate | |
| Other names
UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine; UDP-GalNAc
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H27N3O17P2 | |
| Molar mass | 607.355 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Uridine diphosphate N-acetylgalactosamine or UDP-GalNAc is a nucleotide sugar composed of uridine diphosphate (UDP) and N-acetyl galactosamine (GalNAc). It is used by glycosyltransferases to transfer N-acetylgalactosamine residues to substrates.[1] UDP-GalNAc is an important building block for the production of glycoproteins and glycolipids in the body. It also serves as a precursor for the synthesis of mucin-type O-glycans, which are important components of mucus and play important roles in biological processes such as cell signaling, immune defense, and lubrication of the digestive tract.
See also
References
 |

