Earth:Eibenstock
Eibenstock | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Coordinates: [ ⚑ ] : 50°29′44″N 12°35′51″E / 50.49556°N 12.5975°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Saxony |
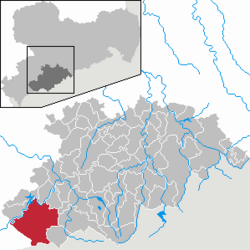
| District | Erzgebirgskreis |
| Subdivisions | 13 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2022–29) | Uwe Staab[1] (CDU) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 112.35 km2 (43.38 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 650 m (2,130 ft) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 08309 |
| Dialling codes | 037752 |
| Vehicle registration | ERZ, ANA, ASZ, AU, MAB, MEK, STL, SZB, ZP |
| Website | www.eibenstock.de |
Eibenstock is a town in the Erzgebirgskreis, Saxony, Germany . It is situated in the western Ore Mountains, near the river Mulde.
Geography
Eibenstock has the following constituent communities: Eibenstock, Blauenthal, Wolfsgrün, Neidhardtsthal, Wildenthal, Oberwildenthal, Carlsfeld, Blechhammer, Neues Wiesenhaus, Sosa, Stabhammer, Wilzschmühle and Weitersglashütte.
History
Middle Ages
Owing to its elevation of more than 600 m, Eibenstock would not have been one of the first farming villages in the Ore Mountains, but rather a longstanding settlement in the form of a radial forest homestead village, founded at the earliest sometime in the thirteenth century in what later became the Barony of Schwarzenberg. About 1.5 km from the edge of town, not far from where the Steinbächel empties into the Große Bockau, a ringwall was unearthed.
The first two documentary mentions as Ybenstok and Ibenstok both date from the year 1378. At that time, an Alte Seife (“Old Placer”) was named, hinting that the village's development was also spurred by mining. Placer mines were being worked in the Eibenstock area even as late as the 19th century, although at the same time, iron ore and tin were also being mined from harder deposits. In 1560 Eibenstock became the official seat of a Bergamt ("mining office") and thereafter called itself freie Bergstadt ("free mining town").
In 1453, Elector Friedrich of Saxony fiefed the Brothers Leonhart und Nickel von Tannenberg auf Plohn with, among other things, the villages of Eibenstock, Sosa and Burkhardtsgrün. These were not under the new ownership for very long, as Wilhelm von Tannenberg had to give up Eibenstock by 1456 to the Hereditary Marshal of Saxony, Hans Löser. In 1464, Eibenstock passed to the lordly estate of Schwarzenberg and hence to the Saxon Amt of Schwarzenberg in 1533.
In 1532, the community was described as a market town, and in 1555 as a small town. The town was only granted market rights in 1639. In 1734, for the first time, a fish market was held at which fresh fish brought in from Hamburg was sold.
19th Century to Present
Clara Angermann brought Tambourieren to the town in 1775, a kind of artistic lace embroidery.[2] She taught this to the women until 1780, and thereafter embroidery began to blossom. By 1850 there were 6 successful embroidering businesses and in 1858, the first embroidery machine went into operation. The work was famous worldwide, so much so that from 1891 to 1908, the United States even maintained a consulate in town to foster their business relationships.
After three great fires (1856, 1862 and 1892), to which whole neighbourhoods fell victim, reconstruction was undertaken in such a way as to give the buildings a more contemporary look. Between 1864 and 1868, the neo-Romanesque church was built, and in 1906 and 1907 a new art nouveau town hall.
With the First World War (1914–1918), the embroidery industry collapsed and could only establish itself once again after the Second World War. However, it never again achieved the level of fame that it had enjoyed before 1914.
From 1952 to 1990, Eibenstock was part of the Bezirk Karl-Marx-Stadt of East Germany. Small embroidery businesses merged into collectives such as the Produktionsgenossenschaften des Handwerks (PGH) Sticktex or the Eibenstocker Buntstickerei, but then in 1972, these were converted into a Volkseigener Betrieb (“nationally owned business”, a kind of enterprise found in the former East Germany)
Between 1974 and 1979 the second biggest dam project in East Germany was realized. A basin with 77 million cubic metres of storage and 350 ha in area was created and now supplies roughly a million people with drinking water.
After the political and economic changes of 1989 and 1990, Eibenstock's economy suffered, like that of much of the former East Germany, which had its ramifications for the administration of small communities. It became impossible to run them independently, and for this reason came on 1 January 1994 the amalgamation of Blauenthal, Neidhardtsthal, Wolfsgrün, Wildenthal and Oberwildenthal with Eibenstock, and likewise on 1 April 1997 of Carlsfeld and Weitersglashütte.
In 2005 Eibenstock celebrated 850 years of existence.
Climate
Script error: No such module "weather box".
Population development
- 1875 = 6,553
- 1913 = 9,899
- 1959 = 9,500
- 1998 = 7,410
- 2004 = 6,708
- 2007 = 6,339
- 2010 = 8,168
- 2012 = 7,838
- 2013 = 7,736
- Source as of 1998: Statistisches Landesamt des Freistaates Sachsen
Local council
The elections in May 2014 showed the following results:
- CDU: 11 Seats
- SPD: 4 Seats
- The Left: 1 Seat
- Gewerbeverein (Trade association): 1 Seat
- FWG (Free voters): 1 Seat
Culture and sightseeing
- Neo-Romanesque church
- Replica of an Electorate of Saxony postal milestone at the Postplatz
- Restored Kingdom of Saxony station stone near the former postal station
- Eibenstock was once well known for its great Freier Deutscher Gewerkschaftsbund (FDGB) holiday home at the Eibenstock Reservoir. Today, the complex has been restored and is run as a hotel, beside which a waterpark has been built. Owing to the hotel's conspicuous blue paintwork, it has borne, since the restoration, the name Das Blaue Wunder (“The Blue Wonder”). The building was originally meant as lodging for the dam builders.
- South of town is the 778-m-high Adlerfels (a crag), from near which, on a clear day, there is a wonderful panoramic view of Eibenstock. On the mountain ridge are found an all-weather bobsleigh run and a skilift.
Economy and infrastructure
From the 14th to 18th centuries there was tin and iron ore mining in the region. After a great famine in 1771-1773, this industry was largely displaced by the embroidery industry.
Notable people
- Paul Drews (1858–1912), theologian and university lecturer
- Werner Ehrig (1897-1981), an officer, most recently a general lieutenant in the Second World War
- Wolfgang Unger (1948-2004), choral conductor and academic in Leipzig
Honorary citizens
- 1895: Otto von Bismarck, Imperial Chancellor
References
This article needs additional citations for verification. (August 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
- ↑ Gewählte Bürgermeisterinnen und Bürgermeister im Freistaat Sachsen, Stand: 17. Juli 2022, Statistisches Landesamt des Freistaates Sachsen.
- ↑ Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). "Eibenstock". Encyclopædia Britannica. 9 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 131.
- ↑ "Carlsfeld Climate Normals 1991–2020". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. https://www.nodc.noaa.gov/archive/arc0216/0253808/1.1/data/0-data/Region-6-WMO-Normals-9120/Germany/CSV/Carlsfeld_10574.csv.
External links
 |