Earth:Filicudi
 Filicudi as seen from Alicudi | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Tyrrhenian Sea |
| Coordinates | [ ⚑ ] : 38°34′17″N 14°33′45″E / 38.57139°N 14.5625°E |
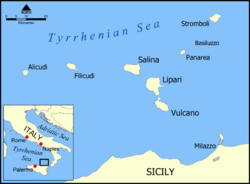
| Archipelago | Aeolian Islands |
| Area | 9.49 km2 (3.66 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 774 m (2539 ft) |
| Highest point | Fossa Felci |
| Administration | |
Italy | |
| Region | Sicily |
| Province | Messina |
| Comune | Lipari |
| Demographics | |
| Demonym | Filicudari |
| Population | 235 (2001) |
| Pop. density | 25/km2 (65/sq mi)[1] |
| Additional information | |
| Official website | comunelipari.gov.it |
Filicudi (Italian pronunciation: [filiˈkuːdi]) is one of eight islands that make up the Aeolian archipelago, situated 56 km (35 mi) northeast of the island of Sicily, southern Italy. It is a frazione of the comune of Lipari.
Geography
Its total area is 9.5 km2 (3.7 sq mi). There are several small villages on the island, which include Pecorini Mare and Valdichiesa. Filicudi's lands are capable of producing wine, olive oil, grain, and vegetables. In 1997, three quarters, approximately 7 km2 (2.7 sq mi) of Filicudi was turned into a Natural Reserve.
The highest point is Monte Fossa Felci at 774 m (2,539 ft). Other points include Monte Montagnola at 349 m (1,145 ft) and Monte Terrione at 278 m (912 ft). At Capo Graziano are the remains of a Bronze Age village dating back to the second millennium BCE. Off the coast, the volcanic finger-like rock of La Canna rises about 74 metres (243 ft) above the sea.
History

The modern name of "Filicudi" is a corruption of the ancient Greek name for the island, Phoenicusa (Phoenician island). The island, like the other Aeolian Islands, was settled since the Neolithic Age, around 3000 BCE. As evidenced by archaeological findings, the island was occupied by a new people during the Bronze Age. The island was uninhabited for many centuries until occupied by the Greeks. Roman and Byzantine remains can also be found on the island.
By 1971, the island had 270 residents. Roughly one-third of them left, however, after May 26 of that year, when Italian police used Filicudi as a place of exile for 18 reputed leaders of the Italian Mafia who were awaiting trial for on charges of organized crime. [2] By May 31, the remaining residents left in protest, with the exception of the exiles and the police guarding them. [3]
Since the 1970s Filicudi was rediscovered and populated by photographers and artists such as Sergio Libiszewsky, Ettore Sottsass, novelist Roland Zoss, and editor Giulio Einaudi. Their perceptions brought the island into the focus of modern tourism.
People
- John Bonica (born 1917), anesthesiologist and professional wrestler
- Roland Zoss (born 1951), novelist and composer
See also
- List of volcanoes in Italy
- List of islands of Italy
References
- ↑ "14th General Population Census and General Housing Census (2001)". DaWinci. http://dawinci.istat.it/daWinci/jsp/MD/dawinciMD.jsp?a1=m60G0c0i0&a2=m0a02048f8&n=1UH90009OG0&v=1UH08207TL5000000.
- ↑ "Many Quit Island as Reputed Mafiosi Begin Exile", The New York Times, May 29, 1971, p. 3
- ↑ "Last of Islanders Leaving in Protest", The New York Times, June 1, 1971, p. 16
External links
- Private page of a novelist living on Filicudi
- A commercial touristic website about Filicudi
- Info about the island
- Filicudi Society of Waltham Massachusetts
- "Filicudi". Smithsonian Institution. https://volcano.si.edu/volcano.cfm?vn=211817.