Earth:Trincheras Formation
| Trincheras Formation Stratigraphic range: Early Aptian ~120–115 Ma | |
|---|---|
| Type | Geological formation |
| Unit of | Villeta Group |
| Sub-units | Anapoima Mb., El Tigre Mb. |
| Underlies | Socotá Fm., El Peñón Fm. |
| Overlies | Murca Fm., La Naveta Fm., Útica Fm. |
| Thickness | up to 1,260 m (4,130 ft) |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Shale |
| Other | Sandstone, limestone |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | [ ⚑ ] : 4°30′13″N 74°36′22″W / 4.50361°N 74.60611°W |
| Region | Altiplano Cundiboyacense Eastern Ranges, Andes |
| Country | |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Quebrada Trincheras |
| Named by | Cáceres & Etayo |
| Location | Apulo |
| Year defined | 1969 |
| Coordinates | [ ⚑ ] 4°30′13″N 74°36′22″W / 4.50361°N 74.60611°W |
| Region | Cundinamarca |
| Country | |
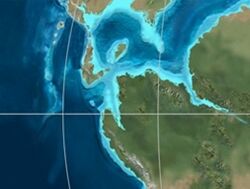 Paleogeography of Northern South America 120 Ma, by Ron Blakey | |
The Trincheras Formation (Spanish: Formación Trincheras, Kitr) is a geological formation of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The formation consisting of a lower unit of calcareous shales and an upper sequence of shales dates to the Early Cretaceous period; Early Aptian epoch and has a maximum thickness of 1,260 metres (4,130 ft). The formation, deposited in a marine platform environment, part of a transgressive cycle, hosts ammonite, bryozoan, mollusc and echinoid fossils.
Etymology
The formation was defined and named in 1969 by Cáceres and Etayo after Quebrada Trincheras, Apulo, Cundinamarca.[1]
Description
Lithologies
The Trincheras Formation has a maximum thickness of 1,260 metres (4,130 ft),[2] and is characterised by a sequence of claystones with intercalated limestones and sandstones. Fossils of the ammonites Heinzia sp., Pseudohaploceras sp., Heminautilus etheringtoni, Cheloniceras sp. and bryozoans, molluscs and echinoids have been found in the Trincheras Formation.[3]
Stratigraphy and depositional environment
The Trincheras Formation is the lowermost unit of the Villeta Group,[4] and conformably overlies the Murca, La Naveta and Útica Formations. The formation is overlain in a transitional pattern by the Socotá and El Peñón Formations.[2] The Trincheras Formation is subdivided into the El Tigre and Anapoima Members. The age has been estimated to be Early Aptian. Stratigraphically, the formation is time equivalent with the fossiliferous Paja Formation of Boyacá and the Las Juntas Formation.[5] The formation has been deposited in a marine well oxygenated platform environment.[3] In terms of sequence stratigraphy, this phase was transgressional.[5]
Outcrops
Lua error in Module:Location_map at line 522: Unable to find the specified location map definition: "Module:Location map/data/Bogotá savanna" does not exist. The Trincheras Formation is apart from its type locality in Apulo, found near La Mesa and Anapoima,[3] in the Villeta Anticlinal, the Murca-Guayabal-Nimaima Anticlinal and along the roads between Pacho and La Palma and Útica-La Peña.[2] The formation also crops out around San Joaquín east of La Mesa,[6] and on the right bank of the Bogotá River near Apulo.[7]
The reverse Bituima Fault thrusts the Trincheras Formation on top of the Güagüaquí Group,[6] while the Bogotá River Fault laterally displaces the formation near Anapoima.[7]
Regional correlations
See also
 Geology of the Eastern Hills
Geology of the Eastern Hills Geology of the Ocetá Páramo
Geology of the Ocetá Páramo Geology of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense
Geology of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense
References
- ↑ Acosta & Ulloa, 2002, p.39
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 Acosta & Ulloa, 2001, p.23
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 3.2 Acosta & Ulloa, 2002, p.40
- ↑ Acosta & Ulloa, 2001, p.22
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.0 5.1 Villamil, 2012, p.168
- ↑ Jump up to: 6.0 6.1 Plancha 227, 1998
- ↑ Jump up to: 7.0 7.1 Plancha 246, 1998
Bibliography
- Acosta Garay, Jorge E., and Carlos E. Ulloa Melo. 2002. Mapa Geológico del Departamento de Cundinamarca - 1:250,000 - Memoria explicativa, 1–108. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-05.
- Acosta Garay, Jorge, and Carlos E. Ulloa Melo. 2001. Geología de la Plancha 208 Villeta - 1:100,000, 1-84. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-05.
- Villamil, Tomas. 2012. Chronology Relative Sea Level History and a New Sequence Stratigraphic Model for Basinal Cretaceous Facies of Colombia, 161–216. Society for Sedimentary Geology (SEPM).
Maps
- Ulloa, Carlos, and Jorge Acosta. 1998. Plancha 208 - Villeta - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Ulloa, Carlos E; Erasmo Rodríguez, and Jorge E. Acosta. 1998. Plancha 227 - La Mesa - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Acosta, Jorge E., and Carlos E. Ulloa. 1998. Plancha 246 - Fusagasugá - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
External links
- Gómez, J.; N.E. Montes; Á. Nivia, and H. Diederix. 2015. Plancha 5-09 del Atlas Geológico de Colombia 2015 – escala 1:500,000, 1. Servicio Geológico Colombiano. Accessed 2017-03-16.
 |

