Earth:Volcanism of New Zealand

The volcanism of New Zealand has been responsible for many of the country's geographical features, especially in the North Island and the country's outlying islands.
While the land's volcanism dates back to before the Zealandia microcontinent rifted away from Gondwana 60–130 million years ago, activity continues today with minor eruptions occurring every few years. This recent activity is primarily due to the country's position on the boundary between the Indo-Australian and Pacific Plates, a part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, and particularly the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Indo-Australian Plate.
New Zealand's rocks record examples of almost every kind of volcanism observed on Earth, including some of the world's largest eruptions in geologically recent times.
None of the South Island's volcanoes are active. <mapframe text="Map of selected surface volcanic features in the northern North Island which includes features from volcanic activity in recorded historic times in New Zealand. {{Wikipedia:Map data/Northern North Island Volcanics/key}}" zoom="6" align="right" longitude="175.1" height="350" class="no-icon" latitude="-37.2" width="350">{{Wikipedia:Map data/Northern North Island Volcanics}}</mapframe>
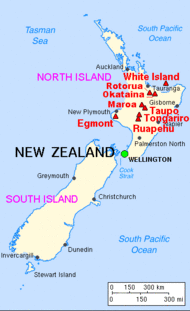
Major eruptions
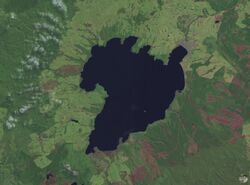
New Zealand has been the site of many large explosive eruptions during the last two million years, including several of supervolcano size.[1] These include eruptions from Macauley Island and the Taupō, Whakamaru, Mangakino, Reporoa, Rotorua, and Haroharo calderas.
Two relatively recent eruptions from the Taupō Volcano are perhaps the best known. Its Oruanui eruption was the world's largest known eruption in the past 70,000 years, with a Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) of 8. It occurred around 26,500 years ago and deposited approximately 1,200 km³ of material.[2][3] Tephra from the eruption covered much of the central North Island with ignimbrite up to 200 metres (650 feet) deep, and most of New Zealand was affected by ash fall, with even an 18 cm (7 inch) ash layer left on the Chatham Islands, 1,000 km (620 mi) away. Later erosion and sedimentation had long-lasting effects on the landscape, causing the Waikato River to shift from the Hauraki Plains to its current course through the Waikato to the Tasman Sea.[4] New Zealand's largest lake, Lake Taupō, fills the caldera formed in this eruption.
Taupō's most recent major eruption, the Taupō or Hatepe eruption, took place around 232 CE, and is New Zealand's largest eruption since Oruanui.[5] It ejected some 120 km³ of material (rating 7 on the VEI scale),[6] with around 30 km³ ejected in just a few minutes. It is believed that the eruption column was 50 kilometres (31 mi) high, twice as high as the eruption column from Mount St. Helens in 1980. This makes it one of the most violent eruptions in the last 5000 years (alongside the Tianchi eruption of Baekdu at around 1000 and the 1815 eruption of Tambora). The resulting ash turned the sky red over Rome and China.[7]
Mount Tarawera's eruption around 1310 CE, while not nearly as large, was still substantial, producing 2.5 km³ of lava and 5 km³ of tephra (VEI 5).[8] Because its deposits, stretching from Gisborne to the Bay of Islands, were emplaced around the time that Māori permanently settled New Zealand, they have provided a useful archaeological marker. Tarawera erupted again on 10 June 1886, spewing ash and debris over 16,000 km2 (6,200 sq mi), destroying the Pink and White Terraces and three villages, including Te Wairoa, and claiming the lives of perhaps 120 people.[9] Approximately 2 km³ of tephra was erupted (VEI 5).[8]
Hazards
As well as the direct effects of explosions, lava, and pyroclastic flows, volcanoes pose various hazards to the New Zealand populace. These include tsunamis, break-out floods and lahars from volcanically dammed lakes, ashfall, and other far field effects.

For instance, the Tangiwai disaster occurred on 24 December 1953 when the Tangiwai railway bridge across the Whangaehu River collapsed from a lahar in full flood, just before an express train was about to cross it. The train could not stop in time, and 151 people died. This was ultimately caused by Ruapehu's 1945 eruption, which had emptied the crater lake and dammed the outlet with tephra.
An eruption of the Whakaari / White Island stratovolcano occurred on 8 December 2019 while there was a group of 47 visitors on the island. Twenty-two people died, either in the explosion or from injuries sustained, including two whose bodies were never found and were later declared dead. A further 25 people suffered injuries, with the majority needing intensive care for severe burns.[10]
Effects can be widespread even for eruptions of only moderate size. Ash plumes from Ruapehu's 1996 eruption forced the closure of eleven airports, including Auckland International Airport.[11]
Insurance against volcanic damage (along with other natural disasters) is provided by the country's Earthquake Commission.
Cultural references
The Māori had many myths and legends regarding the land's volcanic mountains. Perhaps the most well known regards the relative locations of Taranaki, Tongariro and Pihanga. It holds that the two first-named volcanoes competed for the love of the beautiful Pihanga and, after Tongariro succeeded, the defeated Taranaki moved to its lonely location near New Plymouth.

Another legend recounts the exploits of Ngātoro-i-rangi, a tohunga (priest) who arrived from the ancestral Māori homeland, Hawaiki, on the Arawa waka (canoe). Travelling inland and then looking southward from Lake Taupō, he decided to climb the mountains he saw there. He reached and began to climb the first mountain along with his slave Ngāuruhoe, who had been travelling with him, and named the mountain Tongariro (the name literally means 'looking south'), whereupon the two were overcome by a blizzard carried by the cold south wind. Near death, Ngātoro-i-rangi called back to his two sisters, Kuiwai and Haungaroa, who had also come from Hawaiki but remained on Whakaari / White Island, to send him sacred fire, which they had brought from Hawaiki. This they did, sending the fire in the form of two taniwha (powerful spirits) named Te Pupu and Te Haeata by a subterranean passage to the top of Tongariro. The tracks of these two taniwha formed the line of geothermal fire that extends from the Pacific Ocean and beneath the Taupō Volcanic Zone, and is seen in the many volcanoes and hot springs extending from Whakaari to Tokaanu and up to the Tongariro massif. The fire arrived just in time to save Ngātoro-i-rangi from freezing to death, but Ngāuruhoe had already died by the time Ngātoro-i-rangi turned to give him the fire. For this reason the hole through which the fire ascended, the active cone of Tongariro, is now called Ngauruhoe.
Eruptions in the North Island, such as the Kaharoa eruption of Mt Tarawera in 1314, have been used to help determine the approximate date of arrival of the early Polynesian colonists to about 1280. Fossilized footprints of perhaps second- or third-generation Polynesian colonists have been found in volcanic ash on islands in the Hauraki Gulf.
Geology
Please see the main articles above because as already mentioned almost every kind of volcanism observed on Earth is found in New Zealand. For historic intrusive volcanism please see the section on older volcanism below. There is good evidence for continued intrusive volcanism activity in the central North Island.[12][13][5] A quite recent, large dioritic pluton of the order of 550,000 years old has been dated from drill cores there.[14]
Volcanic areas
While there are remnants of volcanic activity throughout most of New Zealand, there are several areas where they are more obvious, and somewhere activity continues. Since Taranaki's last activity in 1854, all eruptions have been in the Taupō Volcanic Zone or the Kermadec Arc.[15]

Kermadec Arc
The Kermadec Islands are an active volcanic island arc stretching north-northeast from New Zealand's North Island towards Tonga. While only a few volcanoes in the arc are tall enough to form islands, it includes about 30 sizeable submarine volcanoes with many in the South Kermadec Ridge Seamounts at the New Zealand end of the chain. The largest island, Raoul Island, produced a large eruption around 2200 years ago with a VEI of 6.[16] Its activity has continued intermittently since, with its latest eruption occurring in 2006.[17] {{#section-h:North Island surface volcanism|Volcanic areas}}
Chatham Islands
The higher portions of the Chatham Islands are formed from volcanic rock that is up to 81 million years old, although lava flows on the northern shore of Chatham Island date back only about five million years.[18] {{#section-h:South Island surface volcanism|Volcanic areas}}

Solander Islands
The Solander Islands, a small chain of uninhabited islets close to the western end of the Foveaux Strait, are the emergent portions of a large extinct andesitic volcano that last erupted around 50,000 to 150,000 years ago.[19] Caused by the subduction of the Australian Plate beneath the Pacific Plate, it is the only volcano associated with this subduction zone that protrudes above the sea.[20][21]
Subantarctic islands
The majority of New Zealand's widely separated subantarctic islands are primarily volcanic in origin, including Auckland Island, Campbell Island / Motu Ihupuku, and Antipodes Island.[18] These are mainly Miocene intraplate volcanoes with ages decreasing towards the northeast, although Antipodes Island may have been active during the last 20,000 years.
Older volcanism

Older remnants of volcanism are also found in several places around New Zealand. These were generally formed either when New Zealand still formed part of the Gondwana supercontinent, or while Zealandia was rifting away from the rest of Gondwana, although some have been emplaced in their current setting more recently. (New Zealand is the main part of the submerged microcontinent of Zealandia that currently emerges above the sea.)
A band of granitic intrusions covering over 10,000 km2, the Median Batholith, stretches from Stewart Island / Rakiura through Fiordland, and again through the West Coast and Nelson after interruption by the Alpine Fault. This was produced between 375 and 105 million years ago in the course of subduction-related volcanism in a long mountain range along the Gondwanan coast somewhat like today's Andes. Two more batholiths, the Karamea-Paparoa and Hohonu Batholiths, are also found on the West Coast.
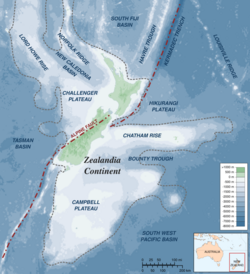
Basaltic lava flows, dikes, and tuff from fissure eruptions between 100 million and 66 million years ago, during Zealandia's separation from Gondwana, are found in Marlborough, the West Coast and offshore further west. Ultramafic intrusions are found in Marlborough and north Canterbury, including at the summit of Tapuae-o-Uenuku, the country's highest mountain outside the Southern Alps.[22] The Mount Somers volcanics that erupted from 100 to 80 million years ago extend to Banks Peninsula but are mostly buried there by more recent volcanism.
Rhyolitic ignimbrite[23] and tuff deposits found in Otago at Shag Point / Matakaea and in the Kakanui Mountains that were originally dated in the range 107 to 101 million years ago[24] are now both dated to 112 ± 0.2 million years ago and so likely come from a large singe event.[25]
The Hikurangi Plateau is an oceanic plateau on the Pacific Plate that attached to the Chatham Ridge after being partially subducted under it, and is now subducting under the North Island. It likely formed in one of the world's largest volcanic outpourings, the greater Ontong Java event.
Ophiolites, volcanic deposits from the ocean floor, have been incorporated into the continental basement of New Zealand in the Dun Mountain Ophiolite Belt, found at both ends of the South Island, and in Northland.
See also
File:Mud pool near Waiotapu 256x192.ogv
- North Island surface volcanism (for more geology details)
- South Island surface volcanism (for more geology details)
- Geothermal areas in New Zealand
- List of disasters in New Zealand by death toll
- List of earthquakes in New Zealand
- List of volcanoes in Antarctica (for volcanoes in New Zealand's Ross Dependency)
- List of volcanoes in New Zealand
Notes
- ↑ Heather Catchpole. Islands of fire , Cosmos Magazine.
- ↑ "The 26.5 ka Oruanui eruption, New Zealand: an introduction and overview". Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 112 (1–4): 133–174. 2001. doi:10.1016/S0377-0273(01)00239-6. Bibcode: 2001JVGR..112..133W.
- ↑ Wilson, Colin J. N. (2006). "The 26.5 ka Oruanui Eruption, Taupo Volcano, New Zealand: Development, Characteristics and Evacuation of a Large Rhyolitic Magma Body". Journal of Petrology 47 (1): 35–69. doi:10.1093/petrology/egi066.
- ↑ Manville, Vern; Wilson, Colin J. N. (2004). "The 26.5 ka Oruanui eruption, New Zealand: a review of the roles of volcanism and climate in the post-eruptive sedimentary response". New Zealand Journal of Geology & Geophysics 47 (3): 525–547. doi:10.1080/00288306.2004.9515074.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Illsley-Kemp, Finnigan; Barker, Simon J.; Wilson, Colin J. N.; Chamberlain, Calum J.; Hreinsdóttir, Sigrún; Ellis, Susan; Hamling, Ian J.; Savage, Martha K. et al. (1 June 2021). "Volcanic Unrest at Taupō Volcano in 2019: Causes, Mechanisms and Implications". Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems 22 (6): 1–27. doi:10.1029/2021GC009803. Bibcode: 2021GGG....2209803I.
- ↑ "Taupo – Eruptive History". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution. http://www.volcano.si.edu/world/volcano.cfm?vnum=0401-07=&volpage=erupt.
- ↑ Wilson, C. J. N.; Ambraseys, N. N.; Bradley, J.; Walker, G. P. L. (1980). "A new date for the Taupo eruption, New Zealand". Nature 288 (5788): 252–253. doi:10.1038/288252a0. Bibcode: 1980Natur.288..252W.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Okataina: Eruptive History". Smithsonian Institution. https://volcano.si.edu/volcano.cfm?vn=241050.
- ↑ Dench, p 114.
- ↑ "New Zealand volcano: Divers deployed to find last two missing bodies". 13 December 2019. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-50768761.
- ↑ Mass aircraft grounding possible in NZ too scientists say , media release, GNS Science, 19 April 2010.
- ↑ Gómez-Vasconcelos, Martha Gabriela; Villamor, Pilar; Cronin, Shane; Procter, Jon; Palmer, Alan; Townsend, Dougal; Leonard, Graham (2017). "Crustal extension in the Tongariro graben, New Zealand: Insights into volcano-tectonic interactions and active deformation in a young continental rift". GSA Bulletin 129 (9–10): 1085–1099. doi:10.1130/B31657.1. Bibcode: 2017GSAB..129.1085G.
- ↑ Benson, Thomas W.; Illsley-Kemp, Finnigan; Elms, Hannah C.; Hamling, Ian J.; Savage, Martha K.; Wilson, Colin J. N.; Mestel, Eleanor R. H.; Barker, Simon J. (2021). "Earthquake Analysis Suggests Dyke Intrusion in 2019 Near Tarawera Volcano, New Zealand". Frontiers in Earth Science 8: 604. doi:10.3389/feart.2020.606992. ISSN 2296-6463. Bibcode: 2021FrEaS...8..604B.
- ↑ Arehart, G.B; Christenson, B.W; Wood, C.P; Foland, K.A; Browne, P.R.L (2002). "Timing of volcanic, plutonic and geothermal activity at Ngatamariki, New Zealand". Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 116 (3–4): 201–214. doi:10.1016/S0377-0273(01)00315-8. ISSN 0377-0273. Bibcode: 2002JVGR..116..201A. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0377027301003158.
- ↑ Volcanoes of New Zealand to Fiji, Global Volcanism Program, Smithsonian Institution.
- ↑ "Smithsonian Global Volcanic Program:Raoul Island". https://volcano.si.edu/volcano.cfm?vn=242030.
- ↑ "Raoul Island". Smithsonian Institution. https://volcano.si.edu/volcano.cfm?vn=242030.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 K. S. Panter, J. Blusztajn, S. R. Hart, P. R. Kyle, R. Esser, W. C. McIntosh (2006). The Origin of HIMU in the SW Pacific: Evidence from Intraplate Volcanism in Southern New Zealand and Subantarctic Islands
- ↑ Mortimer, N.; Gans, P.B.; Foley, F. V.; Turner, M. B.; Daczko, N.; Robertson, M.; Turnbull, I. M. (2013). "Geology and Age of Solander Volcano, Fiordland, New Zealand". Journal of Geology 121 (5): 475-487. doi:10.1086/671397.
- ↑ Keith Lewis, Scott D. Nodder and Lionel Carter. 'Sea floor geology – Solander Island', Te Ara – the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Updated 2 March 2009. Accessed 18 April 2010.
- ↑ Mortimer, N.; Gans, P.B.; Mildenhall, D.C. (2008). "A middle-late Quaternary age for the adakitic arc volcanics of Hautere (Solander Island), Southern Ocean". Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research 178 (4): 701–707. doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2008.09.003. ISSN 0377-0273. Bibcode: 2008JVGR..178..701M. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S037702730800468X.
- ↑ Baker, I. A.; Gamble, J. A.; Graham, I. J. (1994). "The age, geology, and geochemistry of the Tapuaenuku Igneous Complex, Marlborough, New Zealand". New Zealand Journal of Geology & Geophysics 37 (3): 249–268. doi:10.1080/00288306.1994.9514620.
- ↑ Steiner, A.; Brown, D. A.; White, A. J. R. (1959). "Occurrence of ignimbrite in the Shag Valley, North-east Otago". New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics 2 (2): 380–384. doi:10.1080/00288306.1959.10417656. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/epdf/10.1080/00288306.1959.10417656.
- ↑ Adams, C.J.; Raine, J.I. (1988). "Age of Cretaceous silicic volcanism at Kyeburn, Central Otago, and Palmerston, eastern Otago, South Island, New Zealand". New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics 31 (4): 471–475. doi:10.1080/00288306.1988.10422144. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/epdf/10.1080/00288306.1988.10422144.
- ↑ Tulloch, AJ; Ramezani, J; Mortimer, N; Mortensen; J; van den Bogaard, P; Maas, R (2009). "Cretaceous felsic volcanism in New Zealand and Lord Howe Rise (Zealandia) as a precursor to final Gondwana break-up". Geological Society, London, Special Publications 321 (1): 89–118. doi:10.1144/SP321.5. Bibcode: 2009GSLSP.321...89T.
References
- Dench, Alison; Essential Dates: A Timeline of New Zealand History, Auckland: Random House, 2005 ISBN:1-86941-689-9
External links
- Geonet: NZ's geological hazard monitoring system
- GNS Science: NZ Government research site
- Earthquake Commission
 |



