Engineering:Carburetor icing
In engine design, carburetor icing is an icing condition which can affect carburetors under certain atmospheric conditions. The problem is most notable in aviation engines using float-type carburetors.
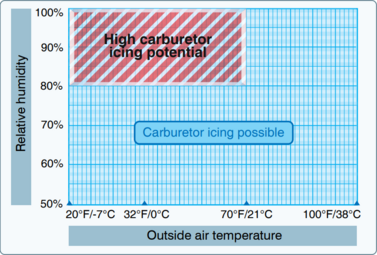
Carburetor icing is caused by the temperature drop in the carburetor, as an effect of fuel vaporization, and the temperature drop associated with the pressure drop in the venturi.[2] If the temperature drops below freezing, water vapor will freeze onto the throttle valve, and other internal surfaces of the carburetor. The venturi effect can reduce the air temperature by 39 K; 39 °C (70 °F). In other words, air at an outside temperature of 38 °C (100 °F), can drop to −1 °C (30 °F) in the carburetor. Carburetor icing most often occurs when the outside air temperature is below 21 °C (70 °F) and the relative humidity is above 80 percent.[1] The risk of carburettor icing is significantly increased at partial power settings (such as when power is reduced during descent), due to the cooling effect of the partly-closed throttle.[2]
The high ambient temperature at which it can occur often causes aircraft pilots to overlook the possibility of carb icing. The ice will form on the surfaces of the carburetor throat, further restricting it. This may increase the venturi effect initially, but eventually restricts airflow, perhaps even causing a complete blockage of air to the carburetor. The engine begins to run more rich as ice formation increases. Without intervention (such as carburetor heating or manually adjusting the air–fuel ratio) this can continue until the air–fuel ratio is outside the correct range for proper operation of the engine. Icing may also cause jamming of the mechanical parts of the carburetor, such as the throttle, typically a butterfly valve.
While it can affect any carburetor, carburetor icing is of particular concern in piston-powered aircraft, especially small, single-engine, light aircraft. Aircraft powered by carbureted engines are equipped with carburetor heating systems to counter icing. In road vehicles, carburetor icing can occasionally be a nuisance, although some engine designs are more susceptible to it than others. The inlet manifold and parts of the carburetor often have warm water from the cooling system or exhaust gas circulating through them to combat this problem. Air-cooled engines may be more prone to icing, due to the absence of warm coolant circulating through the engine.
See also
- Atmospheric icing
- Carburetor heat
- Convair B-36
- Dew point
- Fog
- Fuel injection
- Fuel system icing inhibitor
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Chapter 7: Aircraft Systems". Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge, FAA-H-8083-25B. US Dept. of Transportation, FAA. 2016. pp. 7-8 - 7-10. https://www.faa.gov/regulations_policies/handbooks_manuals/aviation/phak/media/09_phak_ch7.pdf. Retrieved 2023-02-25. "As mentioned earlier, one disadvantage of the float-type carburetor is its icing tendency."
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 (in EN) Visual Flight Rules Guide (Version 7.2 ed.). Canberra: Australian Government. 2023. pp. 96-97. https://www.casa.gov.au/resources-and-education/publications-and-resources/industry-guides-and-publications/pilot-guides/visual-flight-rules-guide.
 |