Engineering:Chebyshev's Lambda Mechanism
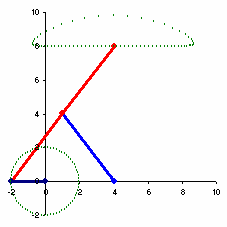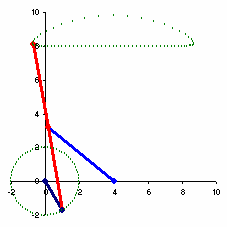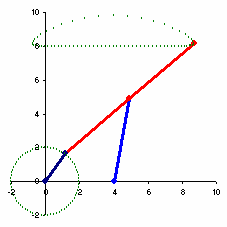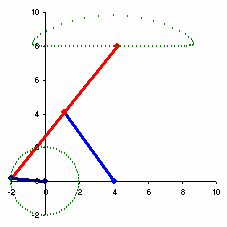

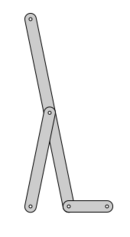
The Chebyshev's Lambda Mechanism[1] is a four-bar mechanism that converts rotational motion to approximate straight-line motion with approximate constant velocity.[2] The precise design trades off straightness, lack of acceleration, and the proportion of the driving rotation that is spent in the linear portion of the full curve.[3]
The example to the right spends over half of the cycle in the near straight portion. Coupler point stays within 1% positional tolerance with intersecting the ideal straight line 6 times.
The Chebyshev's Lambda Mechanism is a cognate linkage of the Chebyshev linkage.
The linkage was first shown in Paris on the Exposition Universelle (1878) as "The Plantigrade Machine".[4][5]
The Chebyshev's Lambda Mechanism is so-named because it looks like a lowercase Greek letter lambda.[5]
Chebyshev's Lambda Mechanism used in vehicle suspension mechanisms, walking robots and rover wheel mechanisms. In 2004, a study completed as a Master of Science Thesis at Izmir Institute of Technology, a new mechanism design introduced by combining two symmetrical Lambda Mechanism to distribute the force evenly on to ground with providing the straight vertical wheel motion.[6]
Double Lambda Chebyshev Mechanism rover suspension design manufactured and tested in Earth Rover Project of Los Angeles City College Electronics Club[7]
See also
- Straight line mechanism
- Peaucellier–Lipkin linkage (an 8-bar linkage)
- Chebyshev linkage
- Four-bar linkage
- Hoeckens linkage
- Leg mechanism
References
- ↑ http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/ChebyshevsLambdaMechanism/
- ↑ Design of Machinery. 2011. http://www.designofmachinery.com/DOM/.
- ↑ DOM p134 Hoecken linkage. http://www.designofmachinery.com/DOM/Chap_03_3ed_p134.pdf.
- ↑ http://mech.spbstu.ru/Dzenushko_Dainis:_Walking_mechanisms_survey#The_Chebyshev_Walking_Mechanism
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Tchebyshev’s plantigrade machine — Mathematical Etudes". Archived from the original on 2017-07-28. https://web.archive.org/web/20170728024836/http://www.etudes.ru/en/etudes/chebyshev-plantigrade-machine. Retrieved 2014-11-16.
- ↑ Barlas, Fırat (June 2004). "Design of a Mars Rover suspension mechanism". Izmir Institute of Technology. https://openaccess.iyte.edu.tr/xmlui/handle/11147/3449.
- ↑ https://vimeo.com/117774490 Video of The Earth Rover Moxie
External links
- Hoeckens approximate straight-line mechanism (diagram and table of lengths)
- Hoeckens straight line linkage (Homemade example)
- Video of computer simulation of Tchebychev walking machine (Стопоход Чебышева).
- alexdenouden.nl - Rectilinear motion after "Tchebychev"
- A simulation using the Molecular Workbench software
- How does a Hoecken's Linkage Work? (Interactive Flash Animation)
