Engineering:Degree of reaction
In turbomachinery, degree of reaction or reaction ratio (denoted R) is defined as the ratio of the change in static pressure in the rotating blades of a compressor or turbine, to the static pressure change in the compressor or turbine stage. Alternatively it is the ratio of static enthalpy change in the rotor to the static enthalpy change in the stage.
Various definitions exist in terms of enthalpies, pressures or flow geometry of the device. In case of turbines, both impulse and reaction machines, degree of reaction is defined as the ratio of energy transfer by the change in static head to the total energy transfer in the rotor:[1]
For a gas turbine or compressor it is defined as the ratio of isentropic heat drop in the moving blades (the rotor) to the sum of the isentropic heat drops in both the fixed blades (the stator) and the moving blades:
In pumps, degree of reaction deals in static and dynamic head. Degree of reaction is defined as the fraction of energy transfer by change in static head to the total energy transfer in the rotor:
Relation
Most turbo machines are efficient to a certain degree and can be approximated to undergo isentropic process in the stage. Hence from
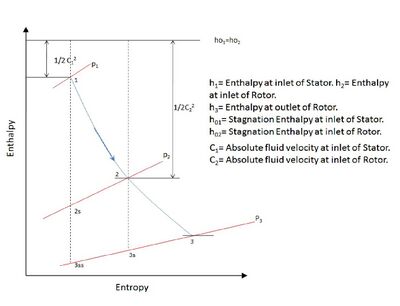
it is easy to see that for isentropic process ∆H ≃ ∆P. Hence it can be implied The same can be expressed mathematically as:[2]
Where 1 to 3ss in Figure 1 represents the isentropic process beginning from stator inlet at 1 to rotor outlet at 3. And 2 to 3s is the isentropic process from rotor inlet at 2 to rotor outlet at 3. The velocity triangle[2] (Figure 2.) for the flow process within the stage represents the change in fluid velocity as it flows first in the stator or the fixed blades and then through the rotor or the moving blades. Due to the change in velocities there is a corresponding pressure change.
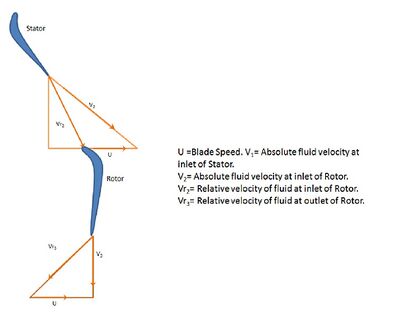
Another useful definition used commonly uses stage velocities as:[2] is the enthalpy drop in the rotor and[2] is the total enthalpy drop. The degree of reaction is then expressed as[3]
For axial machines , then[3] The degree of reaction can also be written in terms of the geometry of the turbomachine as obtained by[2] where β3 is the vane angle of rotor outlet and β2 is the vane angle of stator outlet. In practice is substituted as φ and [2] as giving The degree of reaction now depends only on φ and which again depend on geometrical parameters β3 and β2 i.e. the vane angles of stator outlet and rotor outlet. Using the velocity triangles degree of reaction can be derived as:[3] This relation is again very useful when the rotor blade angle and rotor vane angle are defined for the given geometry.
Choice of reaction (R) and effect on efficiency

The Figure 3[4] alongside shows the variation of total-to-static efficiency at different blade loading coefficient with the degree of reaction. The governing equation is written as
where is the stage loading factor. The diagram shows the optimization of total - to - static efficiency at a given stage loading factor, by a suitable choice of reaction. It is evident from the diagram that for a fixed stage loading factor that there is a relatively small change in total-to-static efficiency for a wide range of designs.
50% reaction
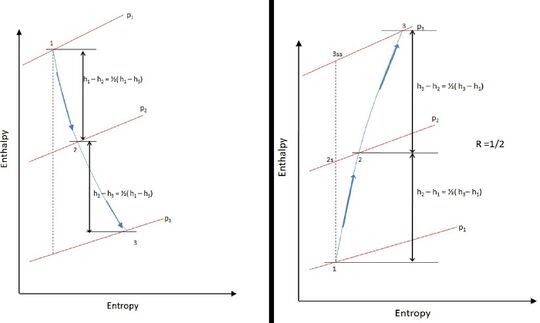
The degree of reaction contributes to the stage efficiency and thus used as a design parameter. Stages having 50% degree of reaction are used where the pressure drop is equally shared by the stator and the rotor for a turbine.
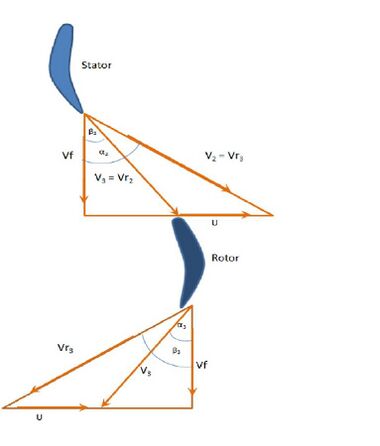
This reduces the tendency of boundary layer separation from the blade surface avoiding large stagnation pressure losses.
If R= 1⁄2 then from the relation of degree of reaction,|| α2 = β3 and the velocity triangle (Figure 4.) is symmetric. The stage enthalpy gets equally distributed in the stage (Figure 5.) . In addition the whirl components are also the same at the inlet of rotor and diffuser.

Reaction less than 50%
Stage having reaction less than half suggest that pressure drop or enthalpy drop in the rotor is less than the pressure drop in the stator for the turbine. The same follows for a pump or compressor as shown in Figure 6. From the relation for degree of reaction, || α2 > β3.
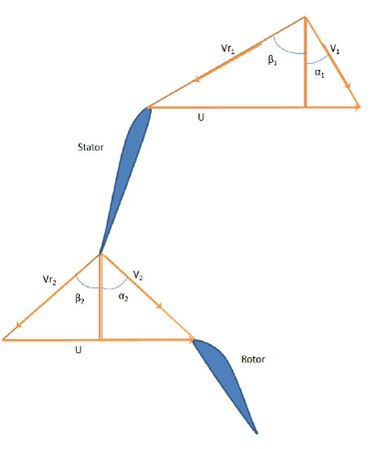
Reaction more than 50%
Stage having reaction more than half suggest that pressure drop or enthalpy drop in the rotor is more than the pressure drop in the stator for the turbine. The same follows for a pump or compressor. From the relation for degree of reaction,|| α2 < β3 which is also shown in corresponding Figure 7.
Reaction = zero
This is special case used for impulse turbine which suggest that entire pressure drop in the turbine is obtained in the stator. The stator performs a nozzle action converting pressure head to velocity head. It is difficult to achieve adiabatic expansion in the impulse stage, i.e. expansion only in the nozzle, due to irreversibility involved, in actual practice. Figure 8 shows the corresponding enthalpy drop for the reaction = 0 case.

References
- ↑ Peng, William W., Fundamentals of turbomachinery, John Wiley, 2008
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 S.M, Yahya, Turbines, Compressors and Fans, 4th ed. McGraw,2011
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Dixon, S. L., Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics of Turbo-machinery, 5th ed. Elsevier,2011.
- ↑ Shapiro, A. H., Soderberg, C. R., Stenning, A. H., Taylor, E. S. and Horlock, J. H. (1957). Notes on Turbomachinery. Department of Mechanical Engineering, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Further reading and works referred to
- Gopalakrishnan, G. and Prithvi Raj, D., A Treatise on Turbomachines, Scitech, Chennai, India, 2012
- Venkanna, B.K. (July 2011). Fundamentals of Turbomachinery. New Delhi: PHI Learning Private Limited. ISBN 978-81-203-3775-6.
- Shepherd, D.G., Principles of Turbomachinery, Ninth Printing, Macmillan, 1969
- Wisclicenus, G.F., Fluid Mechanics of Turbomachinery, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1947
- Thomson, W.R., Preliminary Design of Gas Turbines, Emmott and CO. Ltd., London, 1963
- Traupel, W., Thermische Turbomachinen, 3rd Edn, Springer Verlag, Berlin, 1978
- Ainley, D. G. and Mathieson, G. C. R. (1951). A method of performance estimation for axial flow turbines. ARC R. and M.
- Dunham, J. and Panton, J. (1973). Experiments on the design of a small axial turbine. Conference Publication 3, Instn. Mech. Engrs.
- Horlock, J. H. (1960). Losses and efficiencies in axial-flow turbines. Int. J. Mech. Sci.,
- Kim, T. H., Takao, M., Setoguchi, T., Kaneko, K. and Inoue, M. (2001). Performance comparison of turbines for wave power conversion. Int. J. Therm. Sci.,
- http://www.physicsforums.com/archive/index.php/t-243219.html
- https://www.scribd.com/doc/55453233/18/Degree-of-reaction
 |
