Engineering:Explorer S-45A (satellite)
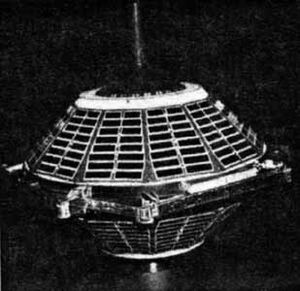 Explorer S-45A satellite before launch | |
| Names | S-45A NASA S-45A |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Ionosphere research |
| Operator | NASA |
| COSPAR ID | EXS-451 |
| Mission duration | Failed to orbit |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Explorer S-45A |
| Spacecraft type | Science Explorer |
| Bus | S-45 |
| Manufacturer | Goddard Space Flight Center |
| Launch mass | 33.6 kg (74 lb) |
| Power | Solar cells and batteries |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 24 May 1961, 19:48:05 GMT |
| Rocket | Juno II (AM-19G) |
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral, LC-26B |
| Contractor | Army Ballistic Missile Agency |
| End of mission | |
| Destroyed | Failed to orbit |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric orbit (planned) |
| Regime | Highly elliptical orbit |
| Perigee altitude | 221 km (137 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 181,100 km (112,500 mi) |
| Inclination | 33.0° |
| Period | 5013.90 minutes |
| Instruments | |
| Beacon | |
Explorer program | |
Explorer S-45A was a NASA satellite, which was lost in a launch failure in 1961. The satellite was intended to operate in a highly elliptical orbit, from which it was to have provided data on the shape of the ionosphere,[1] and on the Earth's magnetic field.[2] It was part of the Explorer program and would have been designated Explorer 12 had it reached orbit. It was the second of two identical satellites to be launched; the first, Explorer S-45, had also been lost in a launch failure, earlier in the year.[2]
Launch
Explorer S-45A was launched aboard a Juno II launch vehicle, serial number AM-19G. It was the final flight of the Juno II.[3] The launch took place from LC-26B at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) at 19:48:05 GMT on 24 May 1961.[3] The system which was intended to ignite the second stage malfunctioned, and as a result that stage failed to ignite.[4] The launch vehicle failed to achieve orbit.[5]
See also
- Explorer program
References
- ↑ "Explorer S-45A". NASA. 28 October 2021. https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/display.action?id=EXS-452.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Wade, Mark. "P-14". Encyclopedia Astronautica. http://www.astronautix.com/craft/p14.htm.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 McDowell, Jonathan (21 July 2021). "Launch Log". Jonathan's Space Page. http://planet4589.org/space/log/launchlog.txt.
- ↑ Krebs, Gunter. "Explorer: S-45". Gunter's Space Page. http://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/explorer_s45.htm.
- ↑ "Explorer Program". Mission and Spacecraft Library. NASA. http://msl.jpl.nasa.gov/Programs/explorer.html.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
 |


