Engineering:IAI Harpy
| Harpy | |
|---|---|

| |
| IAI Harpy at Paris Air Show 2007 | |
| Role | Loitering Munition |
| National origin | Israel |
| Manufacturer | IAI |
| First flight | 1989 |
| Variants | IAI Harop |
The IAI Harpy is a loitering munition missile produced by Israel Aerospace Industries. The Harpy is designed to attack radar systems and is optimised for the suppression of enemy air defences (SEAD) role. It carries a high explosive warhead. The Harpy has been sold to several foreign nations, including South Korea , Turkey and China .
Design and development
In the late 1980s, Kentron sold the designs for its ARD-10 loitering drone to IAI. IAI then used those designs to develop the Harpy which was first tested in 1989.[1]
In 2004, the Harpy became the focus of the effort by the United States to restrict arms transfers and the sales of advanced military technology to China. Sold to China in 1994 for around US$55 million, the loitering munitions were returned to Israel in 2004 under contract to be upgraded. The United States, fearing that the Harpy would pose a threat to Taiwanese and American forces in the case of a war with China,[2] demanded that Israel seize the loitering munitions and nullify the contract. According to Israel, the Harpy is an indigenously designed loitering munition, and does not contain any US-produced sub-systems.[3] In 2005, the loitering munitions were returned to China without being upgraded. This incident chilled relations between the United States and Israel, with Israel being suspended from its status as Security Cooperative Participant in the Joint Strike Fighter program. However, on 6 November 2005, Israel stated that it has been re-admitted into the program.[4]
Specifications
Harpy
General characteristics
- Length: 2.7 m (8 ft 10 in)
- Wingspan: 2.1 m (6 ft 11 in)
- Gross weight: 135 kg (298 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × UEL AR731 Wankel rotary engine, 28 kW (38 hp)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 185 km/h (115 mph, 100 kn)
- Range: 600 km (370 mi, 320 nmi)
Armament
- 1 × 32 kg (70 lb) high-explosive warhead
Mini Harpy
General characteristics
- Length: 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in)
- Wingspan: 2.9 m (9 ft 6 in)
- Gross weight: 41 kg (90 lb)
- Loitering speed: 55–85 kn (102–157 km/h; 63–98 mph)
- Operational altitude: 304–1,524 m (997–5,000 ft)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 370 km/h (230 mph, 200 kn)
- Range: 200 km (120 mi, 110 nmi)
- Endurance: 2 hours
Armament
- Warhead: up to 17 lb (7.7 kg)
- CEP: <1 m (3 ft 3 in)
Dual-homing capabilities - utilizing anti-radiation and electro-optical seekers
Operators
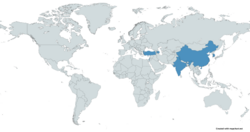
 Azerbaijan[8]
Azerbaijan[8] China
China India
India Israel
Israel South Korea
South Korea Turkey
Turkey
See also
- WB Electronics Warmate
- Shahed 131
- Raad 85 (UAV)
- NCSIST Chien Hsiang
- AeroVironment Switchblade
References
- ↑ "South African heritage". Air Forces Monthly: 23. December 2022.
- ↑ Federman, Josef (12 June 2005). "Report: U.S. imposes sanctions against Israeli arms". Associated Press. http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1P1-109882603.html.
- ↑ "USA and Israel in crisis over China Harpy deal". 4 January 2005. http://www.flightglobal.com/news/articles/usa-and-israel-in-crisis-over-china-harpy-deal-191940.
- ↑ Schiff, Ze'ev (22 December 2004). "Don't Return Drones to China, U.S. Tells Israel". Haaretz. http://www.haaretz.com/print-edition/news/don-t-return-drones-to-china-u-s-tells-israel-1.144880.
- ↑ "Mini Harpy Multi-Purpose Tactical Loitering Munition". https://www.iai.co.il/drupal/sites/default/files/2019-05/Mini%20HARPY%20Brochure.pdf.
- ↑ "Mini Harpy Multi-Purpose Tactical Loitering Munition". https://www.iai.co.il/p/mini-harpy.
- ↑ "Loitering Munitions - Meeting the Challenge of Time-Sensitive Targets". https://aviationweek.com/defense-space/loitering-munitions-meeting-challenge-time-sensitive-targets.
- ↑ Missiles, rockets and drones define Azerbaijan-Armenia conflict, Seth J. Frantzman, The Jerusalem Post, October 4, 2020
External links
- HARPY - Autonomous Weapon for All Weather. IAI website
 |
