Engineering:Kosmos 135
 | |
| Mission type | Micrometeoroid research |
|---|---|
| COSPAR ID | 1966-112A |
| SATCAT no. | 02612 |
| Mission duration | 121 days |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft type | DS-U2-MP |
| Manufacturer | Yuzhnoye |
| Launch mass | 355 kg[1] |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 12 December 1966 20:37:59 GMT[2] |
| Rocket | Kosmos-2I 63SM |
| Launch site | Kapustin Yar, Site 86/1 |
| Contractor | Yuzhnoye |
| End of mission | |
| Decay date | 12 April 1967 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric[2] |
| Regime | Low Earth |
| Perigee altitude | 253 km |
| Apogee altitude | 649 km |
| Inclination | 48.5° |
| Period | 93.5 minutes |
| Epoch | 12 December 1966 |
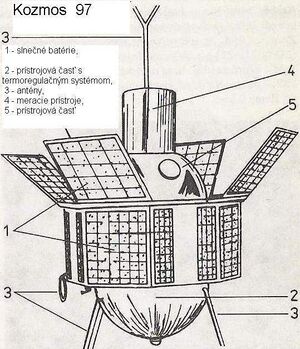
Kosmos 135 (Russian: Космос 135 meaning Cosmos 135), also known as DS-U2-MP No.1, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1966 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 355 kilograms (783 lb) spacecraft,[1] which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Office, and was used to investigate micrometeoroids and particles of dust in space.[3]
A Kosmos-2I 63SM carrier rocket was used to launch Kosmos 135 into low Earth orbit. The launch took place from Site 86/1 at Kapustin Yar.[4] The launch occurred at 20:37:59 GMT on 12 December 1966, and resulted in the successful insertion of the satellite into orbit.[5] Upon reaching orbit, the satellite was assigned its Kosmos designation, and received the International Designator 1966-112A. The North American Air Defense Command assigned it the catalogue number 02612.[1]
Kosmos 135 was the first of two DS-U2-MP satellites to be launched, the other being Kosmos 163 (5 June 1967).[3][6] It was operated in an orbit with a perigee of 253 kilometres (157 mi), an apogee of 649 kilometres (403 mi), an inclination of 48.5°, and an orbital period of 93.5 minutes.[2] It decayed from its orbit and reentered in the atmosphere on 12 April 1967.[7]
See also
- 1966 in spaceflight
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Cosmos 135: Display 1966-112A". NASA. 27 February 2020. https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/display.action?id=1966-112A.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Cosmos 135:Trajectory 1966-112A". NASA. 27 February 2020. https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/displayTrajectory.action?id=1966-112A.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Wade, Mark. "DS-U2-MP". Encyclopedia Astronautica. http://www.astronautix.com/craft/dsu2mp.htm.
- ↑ McDowell, Jonathan. "Launch Log". Jonathan's Space Page. http://planet4589.org/space/log/launchlog.txt.
- ↑ Wade, Mark. "Kosmos 2". Encyclopedia Astronautica. http://www.astronautix.com/lvs/kosmos2.htm.
- ↑ Krebs, Gunter. "DS-U2-MP". Gunter's Space Page. http://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/ds-u2-mp.htm.
- ↑ McDowell, Jonathan. "Satellite Catalog". Jonathan's Space Page. http://www.planet4589.org/space/log/satcat.txt.
 |
