Engineering:Reactances of synchronous machines
The reactances of synchronous machines comprise a set of characteristic constants used in the theory of synchronous machines.[1] Technically, these constants are specified in units of the electrical reactance (ohms), although they are typically expressed in the per-unit system and thus dimensionless. Since for practically all (except for the tiniest) machines the resistance of the coils is negligibly small in comparison to the reactance, the latter can be used instead of (complex) electrical impedance, simplifying the calculations.[2]
Two reactions theory
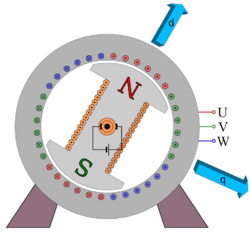
The air gap of the machines with a salient pole rotor is quite different along the pole axis (so called direct axis) and in the orthogonal direction (so called quadrature axis). Andre Blondel in 1899 proposed in his paper "Empirical Theory of Synchronous Generators" the two reactions theory that divided the armature magnetomotive force (MMF) into two components: the direct axis component and the quadrature axis component. The direct axis component is aligned with the magnetic axis of the rotor, while the quadrature (or transverse) axis component is perpendicular to the direct axis.[3] The relative strengths of these two components depend on the design of the machine and the operating conditions. Since the equations naturally split into direct and quadrature components, many reactances come in pairs, one for the direct axis (with the index d), one for the quadrature axis (with the index q). Direct-quadrature-zero transformation is often used.
In machines with a cylindrical rotor the air gap is uniform, the reactances along the d and q axes are equal,[4] and d/q indices are frequently dropped.
States of the generator
The flux linkages of the generator vary with its state. Usually applied for transients after a short circuit current. Three states are considered:[5]
- the steady-state is the normal operating condition with the armature magnetic flux going through the rotor;
- the sub-transient state () is the one the generator enters immediately after the fault (short circuit). In this state the armature flux is pushed completely out of the rotor. The state is very brief, as the current in the damper winding quickly decays allowing the armature flux to enter the rotor poles only. The generator goes into transient state;
- in the transient state () the flux is still out of the field winding of the rotor. The transient state decays to steady-state in few cycles.[6]
The sub-transient () and transient () states are characterized by significantly smaller reactances.
Leakage reactances
The nature of magnetic flux makes it inevitable that part of the flux deviates from the intended "useful" path. In most designs, the productive flux links the rotor and stator; the flux that links just the stator (or the rotor) to itself is useless for energy conversion and thus is considered to be wasted leakage flux (stray flux). The corresponding inductance is called leakage inductance. Due to the presence of air gap, the role of the leakage flux is more important in a synchronous machine in comparison to a transformer. [7]
Synchronous reactances
The synchronous reactances are exhibited by the armature in the steady-state operation of the machine.[8] The three-phase system is viewed as a superposition of two: the direct one, where the maximum of the phase current is reached when the pole is oriented towards the winding and the quadrature one, that is 90° offset.[9]
The per-phase reactance can be determined in a mental experiment where the rotor poles are perfectly aligned with a specific angle of the phase field in the armature (0° for , 90° for the ). In this case, the reactance X will be related with the flux linkage and the phase current I as , where is the circular frequency. [10] The conditions for this mental experiment are hard to recreate in practice, but:
- when the armature is short-circuited, the flowing current is practically all reactive (as the coil resistance is negligible), thus under the short-circuit condition the poles of the rotor are aligned with the armature magnetomotive force;
- when the armature is left open-circuit, the voltage on the terminals is also aligned with the same phase and is equal to . If saturation is neglected, the flux linkage is the same.
Therefore, the direct synchronous reactance can be determined as a ratio of the voltage in open condition to short-circuit current : . These current and voltage values can be obtained from the open-circuit saturation curve and the synchronous impedance curve.[11]
The synchronous reactance is a sum of the leakage reactance and the reactance of the armature itself (): .[12]
Sequence network reactances
When analyzing unbalanced three-phase systems it is common to describe a system of symmetrical components. This models the machine by three components, each with a positive sequence reactance , a negative sequence reactance and a zero sequence reactance .
List of reactances
Das[13] identifies the following reactances:
- leakage reactance . Potier reactance is an estimate of the armature leakage reactance;
- synchronous reactance (also [2]);
- transient reactance ;
- subtransient reactance ;
- quadrature axis reactances , , , counterparts to , , ;
- negative sequence reactance ;
- zero sequence reactance .
References
- ↑ Park & Robertson 1928, p. 514.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Klempner & Kerszenbaum 2004, p. 144.
- ↑ Gieras & Shen 2022, p. 211.
- ↑ Deshpande 2011, p. 315.
- ↑ Machowski, Bialek & Bumby 1997, pp. 102–103.
- ↑ Ramar & Kuruseelan 2013, p. 20.
- ↑ Lipo 2017, p. 67.
- ↑ Das 2017, p. 181.
- ↑ Park & Robertson 1928, p. 515.
- ↑ Prentice 1937, p. 7.
- ↑ Prentice 1937, p. 8.
- ↑ Machowski, Bialek & Bumby 1997, p. 104.
- ↑ Das 2017, pp. 180–182.
Sources
- Park, R. H.; Robertson, B. L. (1928). "The Reactances of Synchronous Machines". Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)) 47 (2): 514–535. doi:10.1109/t-aiee.1928.5055010. ISSN 0096-3860.
- Prentice, B. R. (1937). "Fundamental Concepts of Synchronous Machine Reactances". Transactions of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)) 56 (12): 1–21. doi:10.1109/t-aiee.1937.5057505. ISSN 0096-3860.
- Heydt, G.; Kalsi, S.; Kyriakides, E. (2003). "A Short Course on Synchronous Machines and Synchronous Condensers". Arizona State University, American Superconductor. https://documents.pserc.wisc.edu/documents/general_information/presentations/presentations_by_pserc_university_members/heydt_synchronous_mach_sep03.pdf.
- El-Serafi, A.M.; Abdallah, A.S. (1992). "Saturated synchronous reactances of synchronous machines". IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)) 7 (3): 570–579. doi:10.1109/60.148580. ISSN 0885-8969.
- Das, J. C. (2017). Short-Circuits in AC and DC Systems: ANSI, IEEE, and IEC Standards. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4987-4542-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=PjwPEAAAQBAJ&pg=PA180. Retrieved 2023-07-02.
- Gieras, J.F.; Shen, J.X. (2022). Modern Permanent Magnet Electric Machines: Theory and Control. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-000-77700-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=KvGaEAAAQBAJ&pg=PA211. Retrieved 2023-07-03.
- Deshpande, M.V. (2011). Electrical Machines. Prentice Hall India Pvt., Limited. ISBN 978-81-203-4026-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=JKsH_3AzYMMC&pg=PA315. Retrieved 2023-07-03.
- Klempner, Geoff; Kerszenbaum, Isidor (2004) (in en). Operation and Maintenance of Large Turbo-Generators. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-471-61447-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=DPdkLp_crLAC&pg=PA144.
- Machowski, J.; Bialek, J.; Bumby, J.R. (1997). Power System Dynamics and Stability. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-95643-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=L7o4TitajRIC&pg=PA104. Retrieved 2023-07-04.
- Ramar, S.; Kuruseelan, S. (2013). Power System Analysis. PHI Learning. ISBN 978-81-203-4733-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=ahntULiMFgwC&pg=PA19. Retrieved 2023-07-04.
Template:Characteristics of synchronous machines
- Lipo, T.A. (2017). Analysis of Synchronous Machines. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-351-83272-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=AglEDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA67. Retrieved 2024-09-16.
 |
