Engineering:Side platform
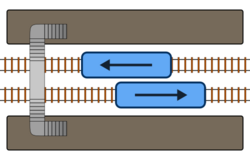
A side platform (also known as a marginal platform[1] or a single-face platform) is a platform positioned to the side of one or more railway tracks or guideways at a railway station, tram stop, transitway, or Rapid transit.[2] A station having dual side platforms, one for each direction of travel, is the basic design used for double-track railway lines (as opposed to, for instance, the island platform where a single platform lies between the tracks). Side platforms may result in a wider overall footprint for the station compared with an island platform, where a single width of platform can be shared by riders using either track.[3][4]
In some stations, the two side platforms are connected by a footbridge or tunnel to allow safe access to the alternate platform.[3] While a pair of side platforms is often provided on a dual-track line, a single side platform is usually sufficient (trains are usually only boarded from one side) for a single-track line.
Layout
Template:Routemap Where the station is close to a level crossing (grade crossing) the platforms may either be on the same side of the crossing road or alternatively may be staggered in one of two ways. With the 'near-side platforms' configuration, each platform appears before the intersection and with 'far-side platforms' they are positioned after the intersection.[5][6]
In some situations, a single side platform can be served by multiple vehicles simultaneously with a scissors crossing provided to allow access mid-way along its length.[7]
Larger stations may have two side platforms with several island platforms in between. Some are in a Spanish solution format, with two side platforms and an island platform in between, serving two tracks.
In some situations, a single side platform may be in use with the other one (side platform) disused like with Ryde Esplanade.[8]
-
Lysaghts railway station, in Australia, with two side platforms and a footbridge connecting them
-
Cambronne station on Line 6 of the Paris Métro. An example of an elevated station with side platforms.
-
View of Katase-Shirata Station (Japan), an example where the line is mainly a single track, but it is possible for trains to cross each other at the station
-
Ryde Esplanade railway station, with one platform in use and another out of use. Ryde, Isle of Wight, Hampshire, England.
-
Xinzhuang Fuduxin metro station on the Taoyuan Airport MRT (Taiwan). Many stations on the Taoyuan Airport MRT use side platforms rather than an island platform to better accommodate large numbers of passengers.
-
Dover MRT station (Singapore) with two platforms in use. The station is an infill station built along an existing line; thus, it takes a side platform structure.
See also
References
- ↑ Longhurst, Derek (2008). 48 months, 48 minutes : building the Perth to Mandurah railway. West Perth, Western Australia: Rawlhouse Publishing. p. 303. ISBN 9780958740685. https://catalogue.nla.gov.au/Record/4300108.
- ↑ Parkinson, Tom; Fisher, Ian (1996). Rail Transit Capacity. Transportation Research Board. p. 24. ISBN 978-0-309-05718-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=NbYqQSQcE2MC&pg=PA24.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Railway Station Design". Railway Technical Web Pages. http://www.railway-technical.com/stations.shtml.
- ↑ "Railway Platform and Types". Railwaysysyem.net. http://www.railsystem.net/railway-platform-and-types/.
- ↑ "Railway Platform and Types |". http://www.railsystem.net/railway-platform-and-types/.
- ↑ "Stations | the Railway Technical Website | PRC Rail Consulting Ltd". http://www.railway-technical.com/infrastructure/stations.html.
- ↑ "The Layout of the Station". https://www.railwayarchive.org.uk/the-layout-of-the-station.
- ↑ "Delivering a better railway for a better Britain – Route Specifications 2016 Wessex". March 2016. https://www.networkrail.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Route-Specification-2016-Wessex-1.pdf.
ja:プラットホーム#相対式ホーム
 |






