Engineering:Socket A
 | |
| Type | PGA-ZIF |
|---|---|
| Chip form factors | Ceramic Pin Grid Array (CPGA) Organic Pin Grid Array (OPGA) |
| Contacts | 462 |
| FSB protocol | EV6 |
| FSB frequency | 200 MT/s, 266 MT/s, 333 MT/s, 400 MT/s |
| Voltage range | 1.0–2.05 V |
| Processors | AMD Athlon (650 MHz – 1400 MHz) AMD Athlon XP (1500+ – 3200+) AMD Duron (600 MHz – 1800 MHz) AMD Sempron (2000+ – 3300+) AMD Athlon MP (1000 MHz – 3000+) AMD Geode NX (667 MHz – 2200 MHz) |
| Predecessor | Slot A |
| Successor | Socket 754 Socket 939 Socket 940 |
This article is part of the CPU socket series | |
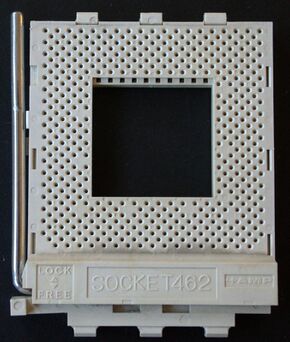
Socket A (also known as Socket 462) is the CPU socket used for AMD processors ranging from the Athlon Thunderbird to the Athlon XP/MP 3200+, and AMD budget processors including the Duron and Sempron. Socket A also supports AMD Geode NX embedded processors (derived from the Mobile Athlon XP). The socket is a zero insertion force pin grid array type with 462 pins (nine pins are blocked in the socket to prevent accidental insertion of Socket 370 CPUs, hence the number 462). The front-side bus frequencies supported for the AMD Athlon XP and Sempron are 133 MHz, 166 MHz, and 200 MHz. Socket A supports 32-bit CPUs only.
Socket A was replaced by Socket 754 and Socket 939 during 2003 and 2004 respectively, except for its use with Geode NX processors.
Chipsets
| Model | Code name | Released | CPU support | FSB/HT (MHz) | Southbridge | Features / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMD-750 chipset | AMD-751 | August 1999[1] | Athlon, Duron (Slot A, Socket A), Alpha 21264 | 100 (FSB) | AMD-756, VIA-VT82C686A | AGP 2×, SDRAM Irongate chipset family; early steppings had issues with AGP 2×; drivers often limited support to AGP 1×; later fixed with "super bypass" memory access adjustment.[2] |
| AMD-760 chipset | AMD-761 | Nov 2000 | Athlon, Athlon XP, Duron (Socket A), Alpha 21264 | 133 (FSB) | AMD-766, VIA-VT82C686B | AGP 4×, DDR SDRAM |
In practice third party chipsets were heavily favoured by motherboard manufacturers. Stability problems and compatibility quirks abounded from manufacturers not following chipset designers' guidelines which in turn caused lasting damage to AMD's reputation despite AMD having nothing to do with the poorly realised hardware.
Technical specifications
- Support of processor clock-speeds between 600 MHz (Duron) to 2333 MHz (Athlon XP 3200+)[3]
- Double data rate 100, 133, 166 and 200 MHz front-side bus on Duron, XP and Sempron processors, based on the Alpha 21264 EV6 bus.

Initially launched with 100 MHz FSB support in the earliest chipsets it evolved stepwise to faster 200 MHz FSB while maintaining pin compatibility throughout its lifetime. However, clock, timing, BIOS and voltage differences restrict compatibility between older chipsets and later processors.[4]
Socket dimensions are 5.59 cm (5.24 cm without lever) x 6.55 cm or 2.2" (2.06" without lever) x 2.58".
Socket A mechanical load limits
AMD recommends that the mass of a Socket A CPU cooler to not exceed 300 grams (10.6 ounces). Heavier coolers may result in damage to the die when the system is not properly handled.
All socket A processors (Athlon, Sempron, Duron and Geode NX) have the following mechanical maximum load limits[5] which should not be exceeded during heatsink assembly, shipping conditions, or standard use. Load above those limits may crack the processor die and make it unusable.
| Location | Dynamic | Static |
|---|---|---|
| Die Surface | 445 N(100 lbf) | 133 N(30 lbf) |
| Die Edge | 44 N(10 lbf) | 44 N(10 lbf) |
Those load limits are quite small compared to the load limits of Socket 478 processors. Indeed, they were so small that many users ended up with cracked processors while trying to remove or attach heatsinks to their fragile processor core. This made installing non-standard or non-certified heatsink solutions a risky business. [citation needed] OEM aluminium heatsinks typically provided small thermal tolerances so the improper application or absence of a thermal pad or thermal grease, or operation in high room temperatures, could lead to some Socket A CPUs overheating and crashing.
Heatsink
Heatsinks were commonly attached directly to the CPU socket, but some motherboards also had 4 holes for fastening bigger heatsinks to the motherboard. Those holes are placed in a rectangle with lateral lengths of 35 mm and 65 mm.
See also
References
- ↑ "AMD-750 Chipset Overview". amd.com. http://www.datasheetcatalog.org/datasheet/AdvancedMicroDevices/mXvvyt.pdf. Retrieved 2001-08-01.
- ↑ AMD's Super Bypass - AMD Improves their 750 Chipset : Tom's Hardware
- ↑ "CPU Sockets Chart". users.erols.com. http://pclinks.xtreemhost.com/sockets.htm. Retrieved 2009-04-04.
- ↑ "CTechnology Evolution". amd.com. https://www.amd.com/us-en/Processors/ProductInformation/0,,30_118_9331_12851,00.html. Retrieved 2009-04-04.
- ↑ "AMD Athlon Processor Model 4 Data Sheet". amd.com. Archived from the original on April 7, 2005. https://web.archive.org/web/20050407201323/http://www.amd.com/us-en/assets/content_type/white_papers_and_tech_docs/23792.pdf. Retrieved 2001-11-08.
