Engineering:VEF I-16
| VEF I-16 | |
|---|---|

| |
| Role | fighter |
| Manufacturer | Valsts Elektrotechniska Fabrika (VEF), Riga, Latvia |
| Designer | Kārlis Irbītis |
| First flight | 1940 |
| Retired | 1942 |
| Number built | 1 (in some sources 3) |
The VEF I-16 was a prototype Latvian fighter aircraft designed by Kārlis Irbītis and produced by VEF in 1939. Development was halted by the Soviet occupation of Latvia in 1940 and subsequent purges of VEF personnel.
Description
The I-16 was of conventional monoplane layout with a Walter Sagitta supercharged air-cooled V12 engine of Czechoslovak origin, a two-bladed propeller and a low set wing with rounded wingtips. The prototype had fixed undercarriage with aerodynamic fairings, but production models were to have retractable landing gear. The cockpit seat and controls were designed as one unit - they could be assembled totally separately from the rest of the aircraft and then installed as a unit with only six bolts.
While the prototype was unarmed, there were provisions for two machine guns in the fuselage, along with the ability to carry one additional gun under each wing.[citation needed]
Operational history
In the spring of 1940 Latvian Air Force pilots made the first test flights of the VEF I-16 prototype. After the occupation of Latvia in June 1940, the Soviet authorities ordered that all VEF aircraft be removed from Spilve Airport and, a few weeks later, all parts fabrication and assembly work was ordered suspended pending further instructions from Moscow. In March 1941, the I-16's designer Kārlis Irbītis received orders to prepare one example each of the VEF I-12, VEF I-15a and I-15b, I-16, VEF I-17 (two variants) and VEF I-18 to be shipped to Moscow for evaluation. The I-16 still had engine problems and needed further testing, so was left behind and stayed in Riga. Following the German invasion of the Soviet Union, the I-16 managed to make several test flights from an aerodrome in Kalnciems but soon the single example was captured by German forces and tested by the Luftwaffe. The VEF I-16 was used as training aircraft at an aviation school in Torun until 1942.[citation needed]
Specifications (I-16)
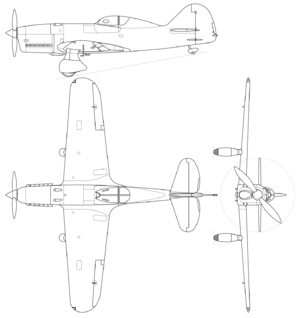
Data from Latvia's Little Hawk,[1]and EF I-16 : LATVIA : Single-engine light fighter aircraft.[2]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 7.3 m (23 ft 11 in)
- Wingspan: 8.23 m (27 ft 0 in)
- Height: 2.7 m (8 ft 10 in)
- Wing area: 11.43 m2 (123.0 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 1,100 kg (2,425 lb)
- Gross weight: 1,540–1,550 kg (3,395–3,417 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Walter Sagitta I-SR V-12 inverted air-cooled piston engine, 399 kW (535 hp) at 2,500 rpm at 3,800 m (12,500 ft)
- Propellers: 2-bladed Schwarz wooden fixed-pitch propeller
Performance
- Maximum speed: 483 km/h (300 mph, 261 kn) at 7,900 m (25,900 ft)
- Range: 805 km (500 mi, 435 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 8,100 m (26,600 ft)
- Wing loading: 136 kg/m2 (28 lb/sq ft)
- Power/mass: 0.220 kW/kg (0.134 hp/lb)
Armament
- Guns: 2x 7.9 mm Browning machine guns
References
- ↑ Davis, Chuck (December 1992). "Latvia's Little Hawk". Air Enthusiast (48): 58–64. ISSN 0143-5450.
- ↑ "VEF I-16 : LATVIA : Single-engine light fighter aircraft." (in pl). http://www.samoloty.ow.pl/str071.htm.
External links
- VEF IRBITIS I-16 at LatvianAviation.com
- I-16 at airwar.ru
- VEF I-16; The Latvian Lightweight, by Ed Nash's Military Matters, on youtbe.com
 |
