Frobenius algebra
In mathematics, especially in the fields of representation theory and module theory, a Frobenius algebra is a finite-dimensional unital associative algebra with a special kind of bilinear form which gives the algebras particularly nice duality theories. Frobenius algebras began to be studied in the 1930s by Richard Brauer and Cecil Nesbitt and were named after Georg Frobenius. Tadashi Nakayama discovered the beginnings of a rich duality theory (Nakayama 1939), (Nakayama 1941). Jean Dieudonné used this to characterize Frobenius algebras (Dieudonné 1958). Frobenius algebras were generalized to quasi-Frobenius rings, those Noetherian rings whose right regular representation is injective. In recent times, interest has been renewed in Frobenius algebras due to connections to topological quantum field theory.
Definition
A finite-dimensional, unital, associative algebra A defined over a field k is said to be a Frobenius algebra if A is equipped with a nondegenerate bilinear form σ : A × A → k that satisfies the following equation: σ(a·b, c) = σ(a, b·c). This bilinear form is called the Frobenius form of the algebra.
Equivalently, one may equip A with a linear functional λ : A → k such that the kernel of λ contains no nonzero left ideal of A.
A Frobenius algebra is called symmetric if σ is symmetric, or equivalently λ satisfies λ(a·b) = λ(b·a).
There is also a different, mostly unrelated notion of the symmetric algebra of a vector space.
Nakayama automorphism
For a Frobenius algebra A with σ as above, the automorphism ν of A such that σ(a, b) = σ(ν(b), a) is Nakayama automorphism associated to A and σ.
Examples
- Any matrix algebra defined over a field k is a Frobenius algebra with Frobenius form σ(a,b)=tr(a·b) where tr denotes the trace.
- Any finite-dimensional unital associative algebra A has a natural homomorphism to its own endomorphism ring End(A). A bilinear form can be defined on A in the sense of the previous example. If this bilinear form is nondegenerate, then it equips A with the structure of a Frobenius algebra.
- Every group ring k[G] of a finite group G over a field k is a symmetric Frobenius algebra, with Frobenius form σ(a,b) given by the coefficient of the identity element in a·b.
- For a field k, the four-dimensional k-algebra k[x,y]/ (x2, y2) is a Frobenius algebra. This follows from the characterization of commutative local Frobenius rings below, since this ring is a local ring with its maximal ideal generated by x and y, and unique minimal ideal generated by xy.
- For a field k, the three-dimensional k-algebra A=k[x,y]/ (x, y)2 is not a Frobenius algebra. The A homomorphism from xA into A induced by x ↦ y cannot be extended to an A homomorphism from A into A, showing that the ring is not self-injective, thus not Frobenius.
- Any finite-dimensional Hopf algebra, by a 1969 theorem of Larson-Sweedler on Hopf modules and integrals.
Properties
- The direct product and tensor product of Frobenius algebras are Frobenius algebras.
- A finite-dimensional commutative local algebra over a field is Frobenius if and only if the right regular module is injective, if and only if the algebra has a unique minimal ideal.
- Commutative, local Frobenius algebras are precisely the zero-dimensional local Gorenstein rings containing their residue field and finite-dimensional over it.
- Frobenius algebras are quasi-Frobenius rings, and in particular, they are left and right Artinian and left and right self-injective.
- For a field k, a finite-dimensional, unital, associative algebra is Frobenius if and only if the injective right A-module Homk(A,k) is isomorphic to the right regular representation of A.
- For an infinite field k, a finite-dimensional, unital, associative k-algebra is a Frobenius algebra if it has only finitely many minimal right ideals.
- If F is a finite-dimensional extension field of k, then a finite-dimensional F-algebra is naturally a finite-dimensional k-algebra via restriction of scalars, and is a Frobenius F-algebra if and only if it is a Frobenius k-algebra. In other words, the Frobenius property does not depend on the field, as long as the algebra remains a finite-dimensional algebra.
- Similarly, if F is a finite-dimensional extension field of k, then every k-algebra A gives rise naturally to a F algebra, F ⊗k A, and A is a Frobenius k-algebra if and only if F ⊗k A is a Frobenius F-algebra.
- Amongst those finite-dimensional, unital, associative algebras whose right regular representation is injective, the Frobenius algebras A are precisely those whose simple modules M have the same dimension as their A-duals, HomA(M,A). Amongst these algebras, the A-duals of simple modules are always simple.
- A finite-dimensional bi-Frobenius algebra or strict double Frobenius algebra is a k-vector-space A with two multiplication structures as unital Frobenius algebras (A, • , 1) and (A, , ): there must be multiplicative homomorphisms and of A into k with and non-degenerate, and a k-isomorphism S of A onto itself which is an anti-automorphism for both structures, such that This is the case precisely when A is a finite-dimensional Hopf algebra over k and S is its antipode. The group algebra of a finite group gives an example.[1][2][3][4]
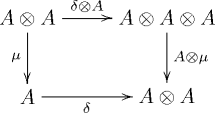
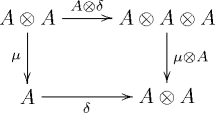
Category-theoretical definition
In category theory, the notion of Frobenius object is an abstract definition of a Frobenius algebra in a category. A Frobenius object in a monoidal category consists of an object A of C together with four morphisms
such that
- is a monoid object in C,
- is a comonoid object in C,
- the diagrams
and
commute (for simplicity the diagrams are given here in the case where the monoidal category C is strict) and are known as Frobenius conditions.[5]
More compactly, a Frobenius algebra in C is a so-called Frobenius monoidal functor A:1 → C, where 1 is the category consisting of one object and one arrow.
A Frobenius algebra is called isometric or special if .
Applications
Frobenius algebras originally were studied as part of an investigation into the representation theory of finite groups, and have contributed to the study of number theory, algebraic geometry, and combinatorics. They have been used to study Hopf algebras, coding theory, and cohomology rings of compact oriented manifolds.
Topological quantum field theories
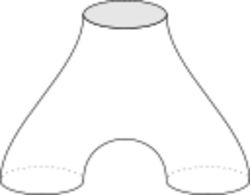
Recently, it has been seen that they play an important role in the algebraic treatment and axiomatic foundation of topological quantum field theory. A commutative Frobenius algebra determines uniquely (up to isomorphism) a (1+1)-dimensional TQFT. More precisely, the category of commutative Frobenius -algebras is equivalent to the category of symmetric strong monoidal functors from - (the category of 2-dimensional cobordisms between 1-dimensional manifolds) to (the category of vector spaces over ).
The correspondence between TQFTs and Frobenius algebras is given as follows:
- 1-dimensional manifolds are disjoint unions of circles: a TQFT associates a vector space with a circle, and the tensor product of vector spaces with a disjoint union of circles,
- a TQFT associates (functorially) to each cobordism between manifolds a map between vector spaces,
- the map associated with a pair of pants (a cobordism between 1 circle and 2 circles) gives a product map or a coproduct map , depending on how the boundary components are grouped – which is commutative or cocommutative, and
- the map associated with a disk gives a counit (trace) or unit (scalars), depending on grouping of boundary.
This relation between Frobenius algebras and (1+1)-dimensional TQFTs can be used to explain Khovanov's categorification of the Jones polynomial.[6][7]
Generalizations
Frobenius extensions
Let B be a subring sharing the identity element of a unital associative ring A. This is also known as ring extension A | B. Such a ring extension is called Frobenius if
- There is a linear mapping E: A → B satisfying the bimodule condition E(bac) = bE(a)c for all b,c ∈ B and a ∈ A.
- There are elements in A denoted and such that for all a ∈ A we have:
The map E is sometimes referred to as a Frobenius homomorphism and the elements as dual bases. (As an exercise it is possible to give an equivalent definition of Frobenius extension as a Frobenius algebra-coalgebra object in the category of B-B-bimodules, where the equations just given become the counit equations for the counit E.)
For example, a Frobenius algebra A over a commutative ring K, with associative nondegenerate bilinear form (-,-) and projective K-bases is a Frobenius extension A | K with E(a) = (a,1). Other examples of Frobenius extensions are pairs of group algebras associated to a subgroup of finite index, Hopf subalgebras of a semisimple Hopf algebra, Galois extensions and certain von Neumann algebra subfactors of finite index. Another source of examples of Frobenius extensions (and twisted versions) are certain subalgebra pairs of Frobenius algebras, where the subalgebra is stabilized by the symmetrizing automorphism of the overalgebra.
The details of the group ring example are the following application of elementary notions in group theory. Let G be a group and H a subgroup of finite index n in G; let g1, ..., gn. be left coset representatives, so that G is a disjoint union of the cosets g1H, ..., gnH. Over any commutative base ring k define the group algebras A = k[G] and B = k[H], so B is a subalgebra of A. Define a Frobenius homomorphism E: A → B by letting E(h) = h for all h in H, and E(g) = 0 for g not in H : extend this linearly from the basis group elements to all of A, so one obtains the B-B-bimodule projection
(The orthonormality condition follows.) The dual base is given by , since
The other dual base equation may be derived from the observation that G is also a disjoint union of the right cosets .
Also Hopf-Galois extensions are Frobenius extensions by a theorem of Kreimer and Takeuchi from 1989. A simple example of this is a finite group G acting by automorphisms on an algebra A with subalgebra of invariants:
By DeMeyer's criterion A is G-Galois over B if there are elements in A satisfying:
whence also
Then A is a Frobenius extension of B with E: A → B defined by
which satisfies
(Furthermore, an example of a separable algebra extension since is a separability element satisfying ea = ae for all a in A as well as . Also an example of a depth two subring (B in A) since
where
for each g in G and a in A.)
Frobenius extensions have a well-developed theory of induced representations investigated in papers by Kasch and Pareigis, Nakayama and Tzuzuku in the 1950s and 1960s. For example, for each B-module M, the induced module A ⊗B M (if M is a left module) and co-induced module HomB(A, M) are naturally isomorphic as A-modules (as an exercise one defines the isomorphism given E and dual bases). The endomorphism ring theorem of Kasch from 1960 states that if A | B is a Frobenius extension, then so is A → End(AB) where the mapping is given by a ↦ λa(x) and λa(x) = ax for each a,x ∈ A. Endomorphism ring theorems and converses were investigated later by Mueller, Morita, Onodera and others.
Frobenius adjunctions
As already hinted at in the previous paragraph, Frobenius extensions have an equivalent categorical formulation. Namely, given a ring extension , the induced induction functor from the category of, say, left S-modules to the category of left R-modules has both a left and a right adjoint, called co-restriction and restriction, respecitvely. The ring extension is then called Frobenius if and only if the left and the right adjoint are naturally isomorphic.
This leads to the obvious abstraction to ordinary category theory: An adjunction is called a Frobenius adjunction iff also . A functor F is a Frobenius functor if it is part of a Frobenius adjunction, i.e. if it has isomorphic left and right adjoints.
See also
- Bialgebra
- Frobenius category
- Frobenius norm
- Frobenius inner product
- Hopf algebra
- Quasi-Frobenius Lie algebra
- Dagger compact category
References
- ↑ Haim, Mariana (2007). "Group-like algebras and Hadamard matrices". J. Algebra 308 (1): 215–235. doi:10.1016/j.jalgebra.2006.06.005.
- ↑ Koppinen, M. (1996). "On algebras with two multiplications, including Hopf algebras and Bose-Mesner algebras". J. Algebra 182 (1): 256–273. doi:10.1006/jabr.1996.0170. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/81959376.pdf.
- ↑ Wang, Zhihua; Li, Libin (2018). "Double Frobenius algebras". Front. Math. China 13 (2): 399–415. doi:10.1007/s11464-018-0682-3.
- ↑ Doi, Yukio; Takeuchi, Mitsuhiro (2000). "Bi-Frobenius algebras". New trends in Hopf algebra theory (La Falda, 1999). Contemp. Math.. 267. American Mathematical Society. pp. 67–97. ISBN 0-8218-2126-1.
- ↑ Pavlovic, Dusko (2013), "Monoidal computer I: Basic computability by string diagrams", Information and Computation 226: 94–116, doi:10.1016/j.ic.2013.03.007
- ↑ Bar-Natan, Dror (2005), "Khovanov's homology for tangles and cobordisms", Geom. Topol. 9 (3): 1443–1499, doi:10.2140/gt.2005.9.1443, Bibcode: 2004math.....10495B
- ↑ Paul Turner (2006), Five Lectures on Khovanov Homology, Bibcode: 2006math......6464T
- Brauer, R.; Nesbitt, C. (1937), "On the regular representations of algebras.", Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 23 (4): 236–240, doi:10.1073/pnas.23.4.236, PMID 16588158, Bibcode: 1937PNAS...23..236B
- DeMeyer, F., Ingraham, E. (1971), Separable Algebras over Commutative Rings, Lect. Notes Math, 181, Springer
- Dieudonné, Jean (1958), "Remarks on quasi-Frobenius rings", Illinois Journal of Mathematics 2 (3): 346–354, doi:10.1215/ijm/1255454538, ISSN 0019-2082
- Frobenius, Ferdinand Georg (1903), "Theorie der hyperkomplexen Größen I" (in German), Sitzungsberichte der Preussischen Akademie der Wissenschaften: 504–537
- Kock, Joachim (2003), Frobenius Algebras and 2D Topological Quantum Field Theories, London Mathematical Society student texts, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-83267-0
- Lam, T. Y. (1999), Lectures on modules and rings, Graduate Texts in Mathematics, 189, Springer, ISBN 978-0-387-98428-5
- Lurie, Jacob (2009), On the Classification of Topological Field Theories, http://www-math.mit.edu/~lurie/papers/cobordism.pdf
- Nakayama, Tadasi (1939), "On Frobeniusean algebras. I", Annals of Mathematics, Second Series (Annals of Mathematics) 40 (3): 611–633, doi:10.2307/1968946, Bibcode: 1939AnMat..40..611N
- Nakayama, Tadasi (1941), "On Frobeniusean algebras. II", Annals of Mathematics, Second Series (Annals of Mathematics) 42 (1): 1–21, doi:10.2307/1968984
- Nesbitt, C. (1938), "On the regular representations of algebras", Annals of Mathematics, Second Series 39 (3): 634–658, doi:10.2307/1968639, ISSN 0003-486X, PMID 16588158
- Onodera, T. (1964), "Some studies on projective Frobenius extensions", Hokkaido Mathematical Journal 18 (1–2): 89–107, doi:10.14492/hokmj/1530691549
External links
- Street, Ross (2004). "Frobenius algebras and monoidal categories". Annual Meeting Aust. Math. Soc. http://www.maths.mq.edu.au/~street/FAMC.pdf.
 |