Glissette
From HandWiki
In geometry, a glissette is a curve determined by either the locus of any point, or the envelope of any line or curve, that is attached to a curve that slides against or along two other fixed curves.
Examples
Ellipse
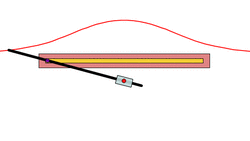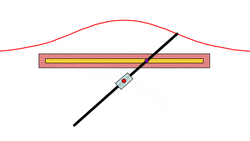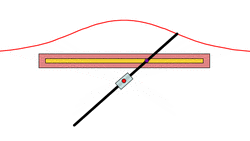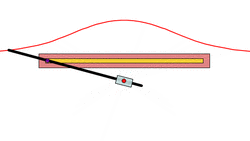
A basic example is that of a line segment of which the endpoints slide along two perpendicular lines. The glissette of any point on the line forms an ellipse.[1]

Astroid
Similarly, the envelope glissette of the line segment in the example above is an astroid.[2]

Conchoid
Any conchoid may be regarded as a glissette, with a line and one of its points sliding along a given line and fixed point.[3]
References
- ↑ Besant, William (1890). Notes on Roulettes and Glissettes. Deighton, Bell. p. 51. https://archive.org/details/notesonroulette00besagoog. Retrieved 6 April 2017.
- ↑ Yates, Robert C. (1947). A Handbook on Curves and their Properties. Ann Arbor, MI: Edwards Bros.. p. 109. https://archive.org/details/YatesHandbookCurves1947. Retrieved 6 April 2017.
- ↑ Lockwood, E. H. (1961). A Book of Curves. Cambridge University Press. p. 162. http://www.aproged.pt/biblioteca/ABookofCurvesLockwood.pdf. Retrieved 6 April 2017.
External links
 |
