Gummel plot
From HandWiki
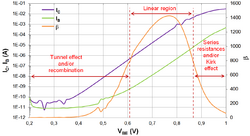
In electronics, the Gummel plot is the combined plot of the base and collector electric currents, and , of a bipolar transistor vs. the base–emitter voltage, , on a semi-logarithmic scale. This plot is very useful in device characterization because it reflects on the quality of the emitter–base junction while the base–collector bias, , is kept constant.
A number of other device parameters can be garnered either quantitatively or qualitatively directly from the Gummel plot:[1]
- The common-emitter current gain, , and the common-base current gain, ,
- Base and collector ideality factors, ,
- Series resistances and leakage currents.
Sometimes the DC current gain, , is plotted on the same figure as well.
See also
- Hermann Gummel
- Bipolar junction transistor
- Gummel–Poon model
References
- ↑ A. S. Zoolfakar et N. A. Shahrol, «Modelling of NPN Bipolar Junction Transistor Characteristics Using Gummel Plot Technique», in 2010 International Conference on Intelligent Systems, Modelling and Simulation (ISMS), 2010, p. 396–400.
 |
