History:15th century BC
From HandWiki
The 15th century BC was the century that lasted from 1500 BC to 1401 BC.
Events

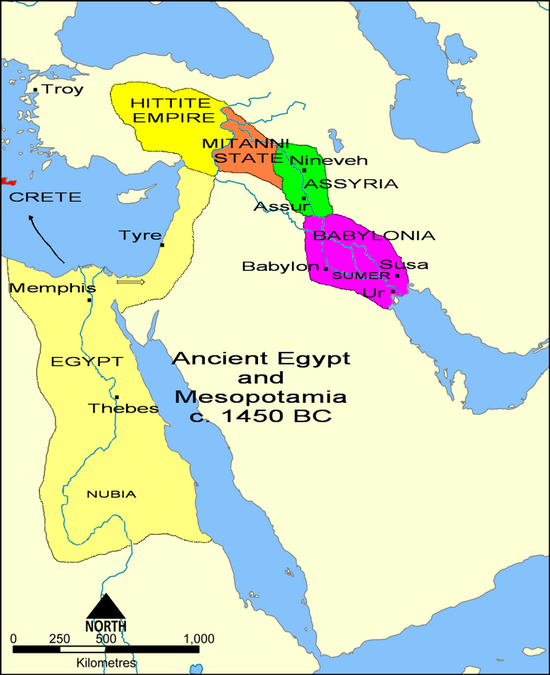
- 1504 BC – 1492 BC: Egypt conquers Nubia and the Levant.[1]
- 1500 BC – 1400 BC: The Battle of the Ten Kings took place around this time.[2]
- 1500 BC: Coalescence of a number of cultural traits including undecorated pottery, megalithic burials, and millet-bean-rice agriculture indicate the beginning of the Mumun Pottery Period on the Korean peninsula.[3]
- c. 1490 BC: Cranaus, legendary King of Athens, is deposed after a reign of 10 years by his son-in-law Amphictyon of Thessaly, son of Deucalion and Pyrrha.[citation needed]
- 1487 BC: Amphictyon, son of Deucalion and Pyrrha and legendary King of Athens, dies after a reign of 10 years and is succeeded by Erichthonius I of Athens, a grandson of Cranaus.[4]
- c. 1480 BC: Queen Hatshepsut succeeded by her stepson and nephew Thutmosis III. Period of greatest Egyptian expansion (4th Nile cataract to the Euphrates).[5]
- c. 1469 BC: In the Battle of Megiddo, Egypt defeats Canaan (Low Chronology).[6]
- c. 1460 BC: The Kassites overrun Babylonia and found a dynasty there that lasts for 576 years and nine months.[7][8][9][10]
- 1437 BC: Legendary King Erichthonius I of Athens dies after a reign of 50 years and is succeeded by his son Pandion I.[citation needed]
- 1430 BC – 1178 BC: Beginning of Hittite empire.[11]
- c. 1420 BC: Crete conquered by Mycenae—start of the Mycenaean period. First Linear B tablets.[citation needed]
- 1400 BC: In Crete the use of bronze helmets (discovery at Knossos).[12]
- 1400 BC: Palace of Minos destroyed by fire.[13]
- c. 1400 BC: Linear A reaches its peak of popularity.[citation needed]
- c. 1400 BC: The height of the Canaanite town of Ugarit. Royal Palace of Ugarit is built.[14]
- Myceneans conquers Greece and border of Anatolia.
- The Tumulus culture flourishes.[citation needed]
- Earliest traces of Olmec civilization.[15]
Inventions, discoveries, introductions
- The Shang dynasty Chinese capital city at Ao[further explanation needed] had massive defensive walls of 20 metres (66 ft) in width at the base and enclosed an area of some 2,100 square yards (1,800 m2).
Sovereign states
See: List of sovereign states in the 15th century BC.
References
- ↑ (in en) The Encyclopedia of Ancient Civilizations of the Near East and Mediterranean. Sharpe Reference. 1997. ISBN 978-1-56324-799-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=1DEOAQAAMAAJ&q=:+Egypt+conquered+Nubia+and+the+Levant.+1504%5D.
- ↑ "Dasarajna: Battle of the Ten Kings from Rig Veda" (in en-US). 2015-02-15. https://www.sanskritimagazine.com/indian-religions/hinduism/dasarajna-battle-ten-kings-rig-veda/.
- ↑ Bale, Martin T. (2001). "Archaeology of Early Agriculture in Korea: An Update on Recent Developments". Bulletin of the Indo-Pacific Prehistory Association 21 (5): 77–84. http://journals.lib.washington.edu/index.php/BIPPA/article/view/11765/10394.
- ↑ Newton, Isaac (2009-02-20) (in en). Newton's Revised History of Ancient Kingdoms: A Complete Chronology. New Leaf Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-89051-556-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=DdWIhzBknP4C&q=%2C+a+grandson+of+Cranaus&pg=PA55.
- ↑ Egypt experienced its greatest territ . expansion( from the Euphrates to the 4th Cataract of the Nile ) .
- ↑ Meistrich, Ira (12 June 2006). "Military History: The Birthplace of War". The Quarterly Journal of Military History (Spring 2005). http://www.historynet.com/military-history-the-birthplace-of-war.htm. Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- ↑ Sayce, Archibald Henry (1894) (in en). The "higher Criticism" and the Verdict of the Monuments. Society for promoting Christian knowledge. https://books.google.com/books?id=ZlgXAAAAYAAJ&q=The+Kassites+gave+a+dynasty+to+Babylonia+which+lasted+for+576+years&pg=PA148.
- ↑ Williams, Henry Smith (in en). The Historians' History of the World Vol.1 (of 25) (Illustrations): Prolegomena; Egypt, Mesopotamia. THE TROW PRESS. https://books.google.com/books?id=TVNVDwAAQBAJ&q=The+Kassites+gave+a+dynasty+to+Babylonia+which+lasted+for+576+years&pg=PT174.
- ↑ Larned, Josephus Nelson (1894) (in en). Nicea-Tunis. C. A. Nichols Company. https://books.google.com/books?id=Yf5PAAAAYAAJ&q=The+Kassites+gave+a+dynasty+to+Babylonia+which+lasted+for+576+years&pg=PA2890.
- ↑ (in en) The Historians' History of the World in Twenty-Five Volumes: Prolegomena; Egypt, Mesopotamia. Library of Alexandria. 2020-09-28. ISBN 978-1-4656-0802-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=RPJADAAAQBAJ&q=The+Kassites+gave+a+dynasty+to+Babylonia+which+lasted+for+576+years&pg=PT576.
- ↑ "Old Hittite Kingdom and Hittite Empire (1600 BC - 1200 BC) – Ancient Civilizations". https://anciv.info/mesopotamia/old-hittite-kingdom-and-hittite-empire.html.
- ↑ Hencken, Hugh (1965). "ARCHEOLOGY: Early Greek Armour and Weapons from the End of the Bronze Age to 600 B.C. ANTHONY SNODGRASS" (in en). American Anthropologist 67 (4): 1054–1055. doi:10.1525/aa.1965.67.4.02a00450. ISSN 1548-1433.
- ↑ Sacks, David; Murray, Oswyn (1995) (in en). A Dictionary of the Ancient Greek World. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-511206-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=KeEjUjSaDA0C&q=Palace+of+Minos+destroyed+by+fire&pg=PA146.
- ↑ Gates, Charles (2011). Ancient Cities: The Archaeology of Urban Life in the Ancient Near East and Egypt, Greece, and Rome (2nd ed.). Abingdon, Oxon: Routledge. pp. 160. ISBN 9780415498647.
- ↑ Diehl, Richard A. (2004). The Olmecs : America's First Civilization. London: Thames and Hudson. pp. 9–25. ISBN 0500285039.
 |
