Hyper-Wiener index
In chemical graph theory, the hyper-Wiener index or hyper-Wiener number is a topological index of a molecule, used in biochemistry. The hyper-Wiener index is a generalization introduced by Milan Randić [1] of the concept of the Wiener index, introduced by Harry Wiener. The hyper-Wiener index of a connected graph G is defined by
where d(u,v) is the distance between vertex u and v. Hyper-Wiener index as topological index assigned to G = (V,E) is based on the distance function which is invariant under the action of the automorphism group of G.
Hyper-Wiener index can be used for the representation of computer networks and enhancing lattice hardware security. Hyper-Wiener indices used to limit the structure of a particle into a solitary number which signifies the sub-atomic stretching and electronic structures.
Example
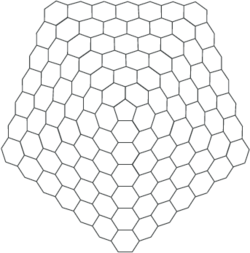
One-pentagonal carbon nanocone which is an infinite symmetric graph, consists of one pentagon as its core surrounded by layers of hexagons. If there are n layers, then the graph of the molecules is denoted by Gn. we have the following explicit formula for hyper-Wiener index of one-pentagonal carbon nanocone,[2]
References
- ↑ Randic, M. (1993), "Novel molecular descriptor for structure—property studies", Chemical Physics Letters 211 (10): 478–483, doi:10.1016/0009-2614(93)87094-J, Bibcode: 1993CPL...211..478R.
- ↑ Darafsheh, M. R.; Khalifeh, M. H.; Jolany, H. (2013), "The Hyper-Wiener Index of One-pentagonal Carbon Nanocone", Current Nanoscience 9 (4): 557–560, doi:10.2174/15734137113090990061.
 |
