Inverse gamma function
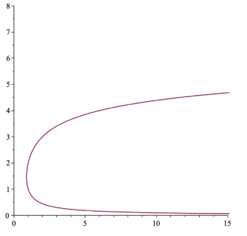
In mathematics, the inverse gamma function is the inverse function of the gamma function. In other words, whenever . For example, .[1] Usually, the inverse gamma function refers to the principal branch with domain on the real interval and image on the real interval , where [2] is the minimum value of the gamma function on the positive real axis and [3] is the location of that minimum.[4]
Definition
The inverse gamma function may be defined by the following integral representation[5] where is a Borel measure such that and and are real numbers with .
Approximation
To compute the branches of the inverse gamma function one can first compute the Taylor series of near . The series can then be truncated and inverted, which yields successively better approximations to . For instance, we have the quadratic approximation:[6]
where is the trigamma function. The inverse gamma function also has the following asymptotic formula[7] where is the Lambert W function. The formula is found by inverting the Stirling approximation, and so can also be expanded into an asymptotic series.
Series expansion
To obtain a series expansion of the inverse gamma function one can first compute the series expansion of the reciprocal gamma function near the poles at the negative integers, and then invert the series.
Setting then yields, for the n th branch of the inverse gamma function ()[8] where is the polygamma function.
References
- ↑ Borwein, Jonathan M.; Corless, Robert M. (2017). "Gamma and Factorial in the Monthly". The American Mathematical Monthly 125 (5): 400–424. doi:10.1080/00029890.2018.1420983.
- ↑ OEIS: A030171
- ↑ OEIS: A030169
- ↑ Uchiyama, Mitsuru (April 2012). "The principal inverse of the gamma function". Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society 140 (4): 1347. doi:10.1090/S0002-9939-2011-11023-2.
- ↑ Pedersen, Henrik (9 September 2013). ""Inverses of gamma functions"". Constructive Approximation 7 (2): 251–267. doi:10.1007/s00365-014-9239-1. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00365-014-9239-1.
- ↑ Corless, Robert M.; Amenyou, Folitse Komla; Jeffrey, David (2017). "Properties and Computation of the Functional Inverse of Gamma". International Symposium on Symbolic and Numeric Algorithms for Scientific Computing (SYNASC). pp. 65. doi:10.1109/SYNASC.2017.00020. ISBN 978-1-5386-2626-9.
- ↑ Amenyou, Folitse Komla; Jeffrey, David (2018). "Properties and Computation of the inverse of the Gamma Function" (MS). p. 28.
- ↑ Couto, Ana Carolina Camargos; Jeffrey, David; Corless, Robert (November 2020). "The Inverse Gamma Function and its Numerical Evaluation". Maple Conference Proceedings: Section 8. https://www.maplesoft.com/mapleconference/2020/highlights.aspx.
 |