Koszul complex
This article provides insufficient context for those unfamiliar with the subject. (November 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
This article may be too technical for most readers to understand. Please help improve it to make it understandable to non-experts, without removing the technical details. (November 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
In mathematics, the Koszul complex was first introduced to define a cohomology theory for Lie algebras, by Jean-Louis Koszul (see Lie algebra cohomology). It turned out to be a useful general construction in homological algebra. As a tool, its homology can be used to tell when a set of elements of a (local) ring is an M-regular sequence, and hence it can be used to prove basic facts about the depth of a module or ideal which is an algebraic notion of dimension that is related to but different from the geometric notion of Krull dimension. Moreover, in certain circumstances, the complex is the complex of syzygies, that is, it tells you the relations between generators of a module, the relations between these relations, and so forth.
Definition
Let A be a commutative ring and s: Ar → A an A-linear map. Its Koszul complex Ks is
where the maps send
where means the term is omitted and means the wedge product. One may replace with any A-module.
Motivating example
Let M be a manifold, variety, scheme, ..., and A be the ring of functions on it, denoted .
The map corresponds to picking r functions . When r = 1, the Koszul complex is
whose cokernel is the ring of functions on the zero locus f = 0. In general, the Koszul complex is
The cokernel of the last map is again functions on the zero locus . It is the tensor product of the r many Koszul complexes for , so its dimensions are given by binomial coefficients.
In pictures: given functions , how do we define the locus where they all vanish?
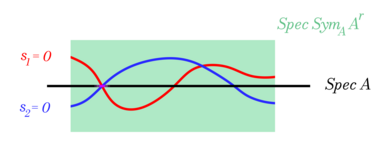
In algebraic geometry, the ring of functions of the zero locus is . In derived algebraic geometry, the dg ring of functions is the Koszul complex. If the loci intersect transversely, these are equivalent.
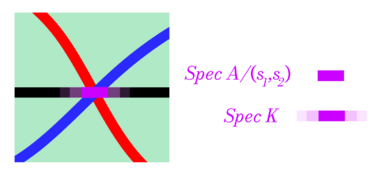
Thus: Koszul complexes are derived intersections of zero loci.
Properties
Algebra structure
First, the Koszul complex Ks of (A,s) is a chain complex: the composition of any two maps is zero. Second, the map
makes it into a dg algebra.[1]
As a tensor product
The Koszul complex is a tensor product: if , then
where denotes the derived tensor product of chain complexes of A-modules.[2]
Vanishing in regular case
When form a regular sequence, the map is a quasi-isomorphism, i.e.
and as for any s, .
History
The Koszul complex was first introduced to define a cohomology theory for Lie algebras, by Jean-Louis Koszul (see Lie algebra cohomology). It turned out to be a useful general construction in homological algebra. As a tool, its homology can be used to tell when a set of elements of a (local) ring is an M-regular sequence, and hence it can be used to prove basic facts about the depth of a module or ideal which is an algebraic notion of dimension that is related to but different from the geometric notion of Krull dimension. Moreover, in certain circumstances, the complex is the complex of syzygies, that is, it tells you the relations between generators of a module, the relations between these relations, and so forth.
Detailed Definition
Let R be a commutative ring and E a free module of finite rank r over R. We write for the i-th exterior power of E. Then, given an R-linear map , the Koszul complex associated to s is the chain complex of R-modules:
- ,
where the differential is given by: for any in E,
- .
The superscript means the term is omitted. To show that , use the self-duality of a Koszul complex.
Note that and . Note also that ; this isomorphism is not canonical (for example, a choice of a volume form in differential geometry provides an example of such an isomorphism).
If (i.e., an ordered basis is chosen), then, giving an R-linear map amounts to giving a finite sequence of elements in R (namely, a row vector) and then one sets
If M is a finitely generated R-module, then one sets:
- ,
which is again a chain complex with the induced differential .
The i-th homology of the Koszul complex
is called the i-th Koszul homology. For example, if and is a row vector with entries in R, then is
and so
Similarly,
Koszul complexes in low dimensions
Given a commutative ring R, an element x in R, and an R-module M, the multiplication by x yields a homomorphism of R-modules,
Considering this as a chain complex (by putting them in degree 1 and 0, and adding zeros elsewhere), it is denoted by . By construction, the homologies are
the annihilator of x in M. Thus, the Koszul complex and its homology encode fundamental properties of the multiplication by x. This chain complex is called the Koszul complex of R with respect to x, as in #Definition.
The Koszul complex for a pair is
with the matrices and given by
- and
Note that is applied on the right. The cycles in degree 1 are then exactly the linear relations on the elements x and y, while the boundaries are the trivial relations. The first Koszul homology therefore measures exactly the relations mod the trivial relations. With more elements the higher-dimensional Koszul homologies measure the higher-level versions of this.
In the case that the elements form a regular sequence, the higher homology modules of the Koszul complex are all zero.
Example
If k is a field and are indeterminates and R is the polynomial ring , the Koszul complex on the 's forms a concrete free R-resolution of k.
Properties of a Koszul homology
Let E be a finite-rank free module over R, let be an R-linear map, and let t be an element of R. Let be the Koszul complex of .
Using , there is the exact sequence of complexes:
- ,
where signifies the degree shift by and . One notes:[3] for in ,
In the language of homological algebra, the above means that is the mapping cone of .
Taking the long exact sequence of homologies, we obtain:
Here, the connecting homomorphism
is computed as follows. By definition, where y is an element of that maps to x. Since is a direct sum, we can simply take y to be (0, x). Then the early formula for gives .
The above exact sequence can be used to prove the following.
Theorem — [4] Let R be a ring and M a module over it. If a sequence of elements of R is a regular sequence on M, then
for all . In particular, when M = R, this is to say
is exact; i.e., is an R-free resolution of .
Proof by induction on r. If , then . Next, assume the assertion is true for r - 1. Then, using the above exact sequence, one sees for any . The vanishing is also valid for , since is a nonzerodivisor on
Corollary — [5] Let R, M be as above and a sequence of elements of R. Suppose there are a ring S, an S-regular sequence in S and a ring homomorphism S → R that maps to . (For example, one can take .) Then
where Tor denotes the Tor functor and M is an S-module through .
Proof: By the theorem applied to S and S as an S-module, we see that is an S-free resolution of . So, by definition, the i-th homology of is the right-hand side of the above. On the other hand, by the definition of the S-module structure on M.
Corollary — [6] Let R, M be as above and a sequence of elements of R. Then both the ideal and the annihilator of M annihilate
for all i.
Proof: Let S = R[y1, ..., yn]. Turn M into an S-module through the ring homomorphism S → R, yi → xi and R an S-module through yi → 0. By the preceding corollary, and then
For a local ring, the converse of the theorem holds. More generally,
Theorem — [7] Let R be a ring and M a nonzero finitely generated module over R . If are elements of the Jacobson radical of R, then the following are equivalent:
- The sequence is a regular sequence on M,
- ,
- for all i ≥ 1.
Proof: We only need to show 2. implies 1., the rest of the cycle of implications being clear. We argue by induction on r. The case r = 1 is already known. Let x' denote x1, ..., xr-1. Consider
Since the first is surjective, with . By Nakayama's lemma, and so x' is a regular sequence by the inductive hypothesis. Since the second is injective (i.e., is a nonzerodivisor), is a regular sequence. (Note: by Nakayama's lemma, the requirement is automatic.)
Tensor products of Koszul complexes
In general, if C, D are chain complexes, then their tensor product is the chain complex given by
with the differential: for any homogeneous elements x, y,
where |x| is the degree of x.
This construction applies in particular to Koszul complexes. Let E, F be finite-rank free modules, and let and be two R-linear maps. Let be the Koszul complex of the linear map . Then, as complexes,
To see this, it is more convenient to work with an exterior algebra (as opposed to exterior powers). Define the graded derivation of degree
by requiring: for any homogeneous elements x, y in ΛE,
- when
One easily sees that (induction on degree) and that the action of on homogeneous elements agrees with the differentials in #Definition.
Now, we have as graded R-modules. Also, by the definition of a tensor product mentioned in the beginning,
Since and are derivations of the same type, this implies
Note, in particular,
- .
The next proposition shows how the Koszul complex of elements encodes some information about sequences in the ideal generated by them.
Proposition — Let R be a ring and I = (x1, ..., xn) an ideal generated by some n-elements. Then, for any R-module M and any elements y1, ..., yr in I,
where is viewed as a complex with zero differential. (In fact, the decomposition holds on the chain-level).
Proof: (Easy but omitted for now)
As an application, we can show the depth-sensitivity of a Koszul homology. Given a finitely generated module M over a ring R, by (one) definition, the depth of M with respect to an ideal I is the supremum of the lengths of all regular sequences of elements of I on M. It is denoted by . Recall that an M-regular sequence x1, ..., xn in an ideal I is maximal if I contains no nonzerodivisor on .
The Koszul homology gives a very useful characterization of a depth.
Theorem (depth-sensitivity) — Let R be a Noetherian ring, x1, ..., xn elements of R and I = (x1, ..., xn) the ideal generated by them. For a finitely generated module M over R, if, for some integer m,
- for all i > m,
while
then every maximal M-regular sequence in I has length n - m (in particular, they all have the same length). As a consequence,
- .
Proof: To lighten the notations, we write H(-) for H(K(-)). Let y1, ..., ys be a maximal M-regular sequence in the ideal I; we denote this sequence by . First we show, by induction on , the claim that is if and is zero if . The basic case is clear from #Properties of a Koszul homology. From the long exact sequence of Koszul homologies and the inductive hypothesis,
- ,
which is Also, by the same argument, the vanishing holds for . This completes the proof of the claim.
Now, it follows from the claim and the early proposition that for all i > n - s. To conclude n - s = m, it remains to show that it is nonzero if i = n - s. Since is a maximal M-regular sequence in I, the ideal I is contained in the set of all zerodivisors on , the finite union of the associated primes of the module. Thus, by prime avoidance, there is some nonzero v in such that , which is to say,
Self-duality
There is an approach to a Koszul complex that uses a cochain complex instead of a chain complex. As it turns out, this results essentially in the same complex (the fact known as the self-duality of a Koszul complex).
Let E be a free module of finite rank r over a ring R. Then each element e of E gives rise to the exterior left-multiplication by e:
Since , we have: ; that is,
is a cochain complex of free modules. This complex, also called a Koszul complex, is a complex used in (Eisenbud 1995). Taking the dual, there is the complex:
- .
Using an isomorphism , the complex coincides with the Koszul complex in the definition.
Use
The Koszul complex is essential in defining the joint spectrum of a tuple of commuting bounded linear operators in a Banach space.[citation needed]
See also
- Koszul–Tate complex
- Syzygy (mathematics)
Notes
- ↑ The Stacks Project, section 0601
- ↑ The Stacks Project, section 0601, Lemma 15.28.12
- ↑ Indeed, by linearity, we can assume where . Then
- ,
- ↑ Matsumura 1989, Theorem 16.5. (i)
- ↑ Eisenbud 1995, Exercise 17.10.
- ↑ Serre 1975, Ch IV, A § 2, Proposition 4.
- ↑ Matsumura 1989, Theorem 16.5. (ii)
References
- Eisenbud, David (1995). Commutative algebra: with a view toward algebraic geometry. Graduate Texts in Mathematics. 150. New York: Springer. ISBN 0-387-94268-8.
- William Fulton (1998), Intersection theory, Ergebnisse der Mathematik und ihrer Grenzgebiete. 3. Folge., 2 (2nd ed.), Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag, ISBN 978-3-540-62046-4
- Matsumura, Hideyuki (1989), Commutative Ring Theory, Cambridge Studies in Advanced Mathematics (2nd ed.), Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-36764-6
- Serre, Jean-Pierre (1975) (in French), Algèbre locale, Multiplicités, Cours au Collège de France, 1957–1958, rédigé par Pierre Gabriel. Troisième édition, 1975. Lecture Notes in Mathematics, 11, Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag
- The Stacks Project, section 0601
External links
- Melvin Hochster, Math 711: Lecture of October 3, 2007 (especially the very last part).
 |
