Line–line intersection
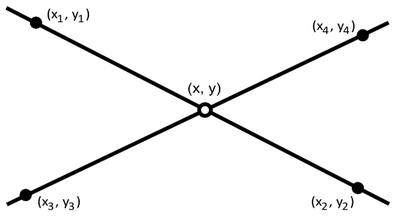
In Euclidean geometry, the intersection of a line and a line can be the empty set, a point, or another line. Distinguishing these cases and finding the intersection have uses, for example, in computer graphics, motion planning, and collision detection.
In three-dimensional Euclidean geometry, if two lines are not in the same plane, they have no point of intersection [citation needed] and are called skew lines. If they are in the same plane, however, there are three possibilities: if they coincide (are not distinct lines), they have an infinitude of points in common (namely all of the points on either of them); if they are distinct but have the same slope, they are said to be parallel and have no points in common; otherwise, they have a single point of intersection.
The distinguishing features of non-Euclidean geometry are the number and locations of possible intersections between two lines and the number of possible lines with no intersections (parallel lines) with a given line.[further explanation needed]
Formulas
A necessary condition for two lines to intersect is that they are in the same plane—that is, are not skew lines. Satisfaction of this condition is equivalent to the tetrahedron with vertices at two of the points on one line and two of the points on the other line being degenerate in the sense of having zero volume. For the algebraic form of this condition, see Skew lines § Testing for skewness.
Given two points on each line
First we consider the intersection of two lines L1 and L2 in two-dimensional space, with line L1 being defined by two distinct points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2), and line L2 being defined by two distinct points (x3, y3) and (x4, y4).[1]
The intersection P of line L1 and L2 can be defined using determinants.
The determinants can be written out as:
When the two lines are parallel or coincident, the denominator is zero.
Given two points on each line segment
The intersection point above is for the infinitely long lines defined by the points, rather than the line segments between the points, and can produce an intersection point not contained in either of the two line segments. In order to find the position of the intersection in respect to the line segments, we can define lines L1 and L2 in terms of first degree Bézier parameters:
(where t and u are real numbers). The intersection point of the lines is found with one of the following values of t or u, where
and
with
There will be an intersection if 0 ≤ t ≤ 1 and 0 ≤ u ≤ 1. The intersection point falls within the first line segment if 0 ≤ t ≤ 1, and it falls within the second line segment if 0 ≤ u ≤ 1. These inequalities can be tested without the need for division, allowing rapid determination of the existence of any line segment intersection before calculating its exact point.[2]
Given two line equations
The x and y coordinates of the point of intersection of two non-vertical lines can easily be found using the following substitutions and rearrangements.
Suppose that two lines have the equations y = ax + c and y = bx + d where a and b are the slopes (gradients) of the lines and where c and d are the y-intercepts of the lines. At the point where the two lines intersect (if they do), both y coordinates will be the same, hence the following equality:
We can rearrange this expression in order to extract the value of x,
and so,
To find the y coordinate, all we need to do is substitute the value of x into either one of the two line equations, for example, into the first:
Hence, the point of intersection is
Note if a = b then the two lines are parallel. If c ≠ d as well, the lines are different and there is no intersection, otherwise the two lines are identical and intersect at every point.
Using homogeneous coordinates
By using homogeneous coordinates, the intersection point of two implicitly defined lines can be determined quite easily. In 2D, every point can be defined as a projection of a 3D point, given as the ordered triple (x, y, w). The mapping from 3D to 2D coordinates is (x′, y′) = (x/w, y/w). We can convert 2D points to homogeneous coordinates by defining them as (x, y, 1).
Assume that we want to find intersection of two infinite lines in 2-dimensional space, defined as a1x + b1y + c1 = 0 and a2x + b2y + c2 = 0. We can represent these two lines in line coordinates as U1 = (a1, b1, c1) and U2 = (a2, b2, c2). The intersection P′ of two lines is then simply given by[3]
If cp = 0, the lines do not intersect.
More than two lines
The intersection of two lines can be generalized to involve additional lines. The existence of and expression for the n-line intersection problem are as follows.
In two dimensions
In two dimensions, more than two lines almost certainly do not intersect at a single point. To determine if they do and, if so, to find the intersection point, write the ith equation (i = 1, …, n) as
and stack these equations into matrix form as
where the ith row of the n × 2 matrix A is [ai1, ai2], w is the 2 × 1 vector [xy], and the ith element of the column vector b is bi. If A has independent columns, its rank is 2. Then if and only if the rank of the augmented matrix [A | b] is also 2, there exists a solution of the matrix equation and thus an intersection point of the n lines. The intersection point, if it exists, is given by
where Ag is the Moore–Penrose generalized inverse of A (which has the form shown because A has full column rank). Alternatively, the solution can be found by jointly solving any two independent equations. But if the rank of A is only 1, then if the rank of the augmented matrix is 2 there is no solution but if its rank is 1 then all of the lines coincide with each other.
In three dimensions
The above approach can be readily extended to three dimensions. In three or more dimensions, even two lines almost certainly do not intersect; pairs of non-parallel lines that do not intersect are called skew lines. But if an intersection does exist it can be found, as follows.
In three dimensions a line is represented by the intersection of two planes, each of which has an equation of the form
Thus a set of n lines can be represented by 2n equations in the 3-dimensional coordinate vector w:
where now A is 2n × 3 and b is 2n × 1. As before there is a unique intersection point if and only if A has full column rank and the augmented matrix [A | b] does not, and the unique intersection if it exists is given by
Nearest points to skew lines
In two or more dimensions, we can usually find a point that is mutually closest to two or more lines in a least-squares sense.
In two dimensions
In the two-dimensional case, first, represent line i as a point pi on the line and a unit normal vector n̂i, perpendicular to that line. That is, if x1 and x2 are points on line 1, then let p1 = x1 and let
which is the unit vector along the line, rotated by a right angle.
The distance from a point x to the line (p, n̂) is given by
And so the squared distance from a point x to a line is
The sum of squared distances to many lines is the cost function:
This can be rearranged:
To find the minimum, we differentiate with respect to x and set the result equal to the zero vector:
so
and so
In more than two dimensions
While n̂i is not well-defined in more than two dimensions, this can be generalized to any number of dimensions by noting that n̂i n̂iT is simply the symmetric matrix with all eigenvalues unity except for a zero eigenvalue in the direction along the line providing a seminorm on the distance between pi and another point giving the distance to the line. In any number of dimensions, if v̂i is a unit vector along the ith line, then
- becomes
where I is the identity matrix, and so[4]
General derivation
In order to find the intersection point of a set of lines, we calculate the point with minimum distance to them. Each line is defined by an origin ai and a unit direction vector n̂i. The square of the distance from a point p to one of the lines is given from Pythagoras:
where (p − ai)T n̂i is the projection of p − ai on line i. The sum of distances to the square to all lines is
To minimize this expression, we differentiate it with respect to p.
which results in
where I is the identity matrix. This is a matrix Sp = C, with solution p = S+C, where S+ is the pseudo-inverse of S.
Non-Euclidean geometry
In spherical geometry, any two lines intersect.[5]
In hyperbolic geometry, given any line and any point, there are infinitely many lines through that point that do not intersect the given line.[5]
See also
- Line segment intersection
- Line intersection in projective space
- Distance between two parallel lines
- Distance from a point to a line
- Line–plane intersection
- Parallel postulate
- Triangulation (computer vision)
- Intersection (Euclidean geometry) § Two line segments
References
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W.. "Line-Line Intersection". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Line-LineIntersection.html.
- ↑ Antonio, Franklin (1992). "Chapter IV.6: Faster Line Segment Intersection". in Kirk, David. Graphics Gems III. Academic Press, Inc.. pp. 199–202. ISBN 0-12-059756-X.
- ↑ Birchfield, Stanley (1998-04-23). "Homogeneous coordinates". http://robotics.stanford.edu/~birch/projective/node4.html. Retrieved 2015-08-18.
- ↑ Traa, Johannes (2013). "Least-Squares Intersection of Lines". http://cal.cs.illinois.edu/~johannes/research/LS_line_intersect.pdf. Retrieved 2018-08-30.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Exploring Hyperbolic Space". https://math.berkeley.edu/~kpmann/Hyperbolic%20and%20Spherical%20geometries.pdf.
External links
- Distance between Lines and Segments with their Closest Point of Approach, applicable to two, three, or more dimensions.
 |
