Medicine:Biliary sludge
| Biliary sludge | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Gallbladder sludge, Microcrystalline disease, Biliary sediment, Thick bile, Biliary sand |
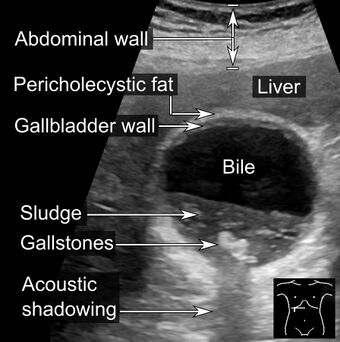 | |
| Abdominal ultrasonography showing biliary sludge and gallstones | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology |
Biliary sludge refers to a viscous mixture of small particles derived from bile.[1][2] These sediments consist of cholesterol crystals, calcium salts, calcium bilirubinate, mucin, and other materials.[1][2][3]
Signs and symptoms
Complications
Biliary sludge may cause complications such as biliary colic, acute cholecystitis, acute cholangitis, and acute pancreatitis.[1][2]
Cause
Biliary sludge has been associated with pregnancy, rapid weight loss, total parenteral nutrition, drugs such as ceftriaxone and octreotide, solid organ transplantation, and gastric surgery.[1][2] In many of these conditions, it is thought that the impairment in the contractility of the gallbladder leads to the formation of the sludge.[2]
Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of biliary sludge formation is likely related to gallbladder dysmotility.[2] It is presumed that because the gallbladder is unable to effectively empty, the biliary sludge can start to accumulate.[2]
Diagnosis
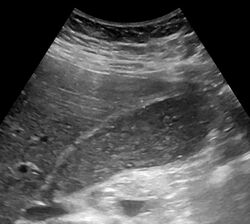
Biliary sludge is typically diagnosed by CT scan or transabdominal ultrasonography.[1][2] Endoscopic ultrasonography is another more sensitive option. However, the gold standard is considered to be direct microscopy of aspirated gallbladder bile.[1][2] This method is much more sensitive, although it is less practical.[2]
Treatment
For patients without symptoms, no treatment is recommended. If patients become symptomatic and/or develop complications, cholecystectomy is indicated.[1] For those who are poor surgical candidates, endoscopic sphincterotomy may be performed to reduce the risk of developing pancreatitis.[1]
Prognosis
The clinical course of biliary sludge can do one of three things: (1) it can resolve completely, (2) wax and wane, or (3) progress to gallstones.[1][2][3] If the biliary sludge has a cause (e.g. pregnancy), it oftentimes is resolved when the underlying cause is removed.[3]
Epidemiology
The prevalence of biliary sludge is low in the general population.[2] It has been reported that the prevalence ranges from 0-0.20% in men and 0.18-0.27% in women.[2] However, in patients with certain conditions, the prevalence may be higher.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Shaffer, E. A. (2001). "Gallbladder sludge: What is its clinical significance?". Current Gastroenterology Reports 3 (2): 166–73. doi:10.1007/s11894-001-0015-6. PMID 11276386.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 Pazzi, P; Gamberini, S; Buldrini, P; Gullini, S (2003). "Biliary sludge: The sluggish gallbladder". Digestive and Liver Disease 35 Suppl 3: S39-45. doi:10.1016/s1590-8658(03)00093-8. PMID 12974509.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Gallbladder and Bile Duct Disorders". Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc. http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/hepatic_and_biliary_disorders/gallbladder_and_bile_duct_disorders/cholelithiasis.html. Retrieved 15 January 2015.
External links
| Classification |
|---|
 |
