Medicine:Cauliflower ear
| Cauliflower ear | |
|---|---|
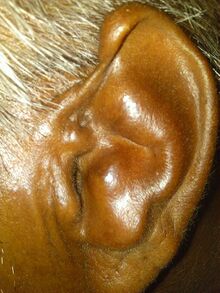 | |
| Cauliflower ear | |
| Specialty | Otorhinolaryngology |
Cauliflower ear is an irreversible condition that occurs when the external portion of the ear is hit and develops a blood clot or other collection of fluid under the perichondrium. This separates the cartilage from the overlying perichondrium that supplies its nutrients, causing it to die and resulting in the formation of fibrous tissue in the overlying skin. As a result, the outer ear becomes permanently swollen and deformed, resembling a cauliflower.
The condition is common in martial arts such as boxing, mixed martial arts or wrestling, and in full-contact sports such as Rugby union and Rugby league.
Cause
The cause is bleeding within the external portion of the ear, a condition known as hematoma auris, perichondrial hematoma, or traumatic auricular hematoma.[1]
Prevention

Headgear called a "scrum cap" in rugby, or simply "headgear" or earguard in wrestling and other martial arts, that protects the ears is worn to help prevent this condition. For some athletes, however, a cauliflower ear is considered a badge of courage or experience.[2]
Treatment
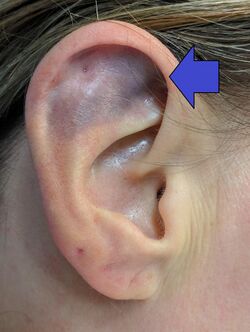
Because an acute hematoma can lead to cauliflower ear, prompt evacuation of the blood is needed to prevent permanent deformity.[3] The outer ear is prone to infections, so antibiotics are usually prescribed. Pressure is applied by bandaging, helping the skin and the cartilage to reconnect. Without medical intervention the ear can suffer serious damage. Disruption of the ear canal is possible. The outer ear may wrinkle, and can become slightly pale due to reduced blood flow; hence the common term "cauliflower ear".[4] Cosmetic procedures are available that can possibly improve the appearance of the ear.[5]
History
Historically, the condition has usually been seen with wrestlers.[6] Statues with ears resembling cauliflower ear date as far back as ancient Rome and Greece.
References
- ↑ Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L.; Rapini, Ronald P. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.[page needed]
- ↑ Williams, Preston (2008-03-06). "For Wrestlers a Swelled Sense of Pride". The Washington Post: p. PG14. https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2008/03/04/AR2008030402360.html. Retrieved 2008-04-02.
- ↑ Auricular Hematoma Drainage. 2018-09-04. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/82793-overview.
- ↑ "Cauliflower Ear Article". Nationwide Children's Hospital: Sports Med Articles. http://www.nationwidechildrens.org/cauliflower-ear-article. Retrieved 23 December 2011.
- ↑ Lukash, Frederick (21 August 2013). The Safe and Sane Guide to Teenage Plastic Surgery. BenBella Books, Inc.. p. 103. ISBN 978-1-935618-63-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=oYYXt60L9LkC&pg=PT103.
- ↑ "Cauliflower ear". http://kidshealth.org/kid/talk/qa/cauliflower_ear.html.
External links
| Classification |
|---|
