Medicine:Coarse facial features
From HandWiki
Coarse facial features (coarse facies) is a constellation of facial features that are present in many inborn errors of metabolism.[1]
| Coarse facies | |
|---|---|
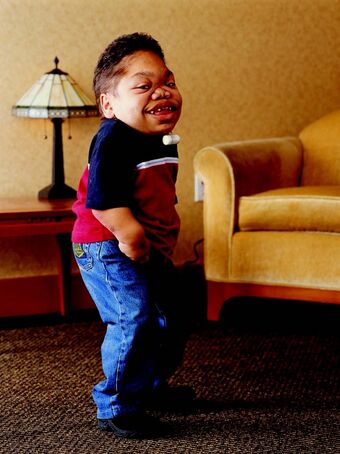 | |
| A 16 year old with Mucopolysaccharidosis showing coarse facial features. | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
Features include:[1]
- large, bulging head
- prominent scalp veins
- "saddle-like, flat bridged nose with broad, fleshy tip"
- large lips and tongue
- small, widely spaced and/or malformed teeth
- hypertrophic alveolar ridges and/or gums
The head tends to be longer than normal from front to back, with a bulging forehead. This is because of the premature fusion of skull bones in the affected person.
Causes
Several conditions are associated with coarse facial features.[2]
- Acromegaly
- Alpha-mannosidosis type II
- Aspartylglycosaminuria
- Battaglia Neri syndrome
- Börjeson–Forssman–Lehmann syndrome
- Chromosome 6q deletion syndrome
- Coarse face - hypotonia - constipation
- Congenital hypothyroidism
- Dandy–Walker malformation (with mental retardation basal ganglia disease and seizures)
- Dyggve–Melchior–Clausen syndrome
- Fucosidosis type 1
- Fucosidosis type II
- Gangliosidosis generalized GM1 (type 1)
- Gangliosidosis GM1 (type 3)
- GM1 gangliosidosis
- Goldberg syndrome
- Hyde-Forster-Mccarthy-Berry syndrome
- Hyper IgE (Job Syndrome)
- Hypomelanosis of Ito
- I cell disease
- Immunodeficiency due to defect in MAPBP-interacting protein
- Infantile sialic acid storage disorder
- Mannosidosis (alpha B lysosomal)
- McCune–Albright syndrome
- Mental retardation (X-linked - epilepsy - progressive joint contractures - typical face)
- Mental retardation (X-linked Raynaud type)
- Miescher's syndrome
- Morquio syndrome
- Morquio syndrome type A
- Morquio syndrome type B
- MPS 3 C
- MPS 3 D
- Mucolipidosis III
- Mucopolysaccharidosis type 2 Hunter syndrome- mild form
- Mucopolysaccharidosis type 2 Hunter syndrome- severe form
- Mucopolysaccharidosis type 3
- Mucopolysaccharidosis type 6
- Mucopolysaccharidosis type 7 Sly syndrome
- Mucopolysaccharidosis type I Hurler syndrome
- Mucopolysaccharidosis type I Hurler/Scheie syndrome
- Mucopolysaccharidosis type I Scheie syndrome
- Multiple endocrine abnormalities - adenylyl cyclase dysfunction
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B
- Neuraminidase deficiency (type II juvenile form)
- Nodulosis–arthropathy–osteolysis syndrome
- Nonkeratan-sulfate-excreting Morquio syndrome
- Pituitary tumors (adult)
- Sialidosis type II (congenital)
- Sialidosis type II (infantile)
- Sialuria syndrome
- Simpson–Golabi–Behmel syndrome
- Simpson–Golabi–Behmel syndrome - type 1 (SGBS1)
- Skeletal dysplasia - coarse facies - mental retardation
- Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia (genevieve type)
- Sulfatidosis juvenile (Austin type)
- Winchester syndrome
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Kagalwala, T. Y.; Bharucha, B. A.; Khare, R. D.; Kumta, N. B. (1 November 1988). "Diagnostic approach to coarse facies". The Indian Journal of Pediatrics 55 (6): 861–870. doi:10.1007/BF02727817. PMID 3235137.
- ↑ "Causes of Coarse facial features". WrongDiagnosis.com. 2010-11-18. http://www.wrongdiagnosis.com/symptoms/coarse_facial_features/causes.htm. Retrieved 2011-01-03.
External links
 |

