Medicine:Fleischer ring
| Fleischer ring | |
|---|---|
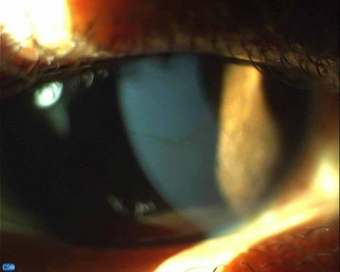 | |
| Fleischer ring in keratoconus, by Mahmoud et al., 2022.[1] | |
| Differential diagnosis | keratoconus |
Fleischer rings are pigmented rings in the peripheral cornea, resulting from iron deposition[2] in basal epithelial cells, in the form of hemosiderin.[3] They are usually yellowish to dark-brown, and may be complete or broken.[4] The rings are best seen using the slit lamp under cobalt blue filter.[4]
They are named for Bruno Fleischer.[5]
Fleischer rings are indicative of keratoconus,[6] a degenerative corneal condition that causes the cornea to thin and change to a conic shape.
Confusion with Kayser-Fleischer rings
Some confusion exists between Fleischer rings and Kayser-Fleischer rings. Kayser-Fleischer rings are caused by copper deposits in descemet's membrane of cornea, and are indicative of Wilson's disease, whereas Fleischer rings are caused by iron deposits in basal epithelial cells. One example of a medical condition that can present with Fleischer rings is keratoconus.
See also
- Hudson–Stahli line
- Limbal ring
References
- ↑ Mahmoud, Mohamed Magdy Ibrahim; Hamdy, Alaa Mohamed; Mohamed, Ashraf Bori; Diaa El Din, Yasmine Ahmed (2022-07-01). "An Updated Overview of Keratoconus Management: Review Article". The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (Egypts Presidential Specialized Council for Education and Scientific Research) 88 (1): 2777–2780. doi:10.21608/ejhm.2022.241951. ISSN 2090-7125.
- ↑ "Cornea & External Diseases-Keratoconus Fleischer's Ring". http://dro.hs.columbia.edu/fleischer.htm.
- ↑ "Definition: Fleischer's ring from Online Medical Dictionary". http://cancerweb.ncl.ac.uk/cgi-bin/omd?Fleischer%27s+ring.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Fleischer's Ring | Columbia Ophthalmology". 2021-01-12. https://www.columbiaeye.org/education/digital-reference-of-ophthalmology/cornea-external-diseases/degenerations/fleischers-ring.
- ↑ Fleischer, B (1906). "Über Keratokonus und eigenartige Pigmentbildung in der Kornea". Münchener medizinische Wochenschrift 53: 625–626.
- ↑ "Secondary keratoconus with corneal epithelial iron ring similar to Fleischer's ring". Japanese Journal of Ophthalmology 44 (4): 381–6. 2000. doi:10.1016/S0021-5155(00)00179-9. PMID 10974294.
 |
