Medicine:Gottron's sign
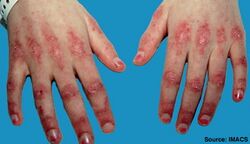
Gottron's sign is a pathognomonic cutaneous manifestation associated with dermatomyositis (DM), which is an inflammatory disorder affecting the skin and muscles.[1] The primary lesion of dermatomyositis appears as a violaceous, macular erythema with a symmetric distribution, which may progress and become poikilodermatous (atrophic with telangiectasia and pigmentary changes) and indurated (as a result of mucin deposition).[2]
Gottron's papules
Gottron's papules are violaceous erythematous papules that commonly occur overlying the dorsal interphalangeal (DIP) or metacarpophalangeal joints (MCP), as well as the elbows or knee joints. They are found in approximately 70 percent of patients diagnosed with dermatomyositis.[2][3][4][5][6]
Gottron's sign
Gottron's sign are erythematous or violaceous macules or plaques overlying the elbows and/or knees and are considered to be less specific finding for DM.[7] They follow the same symmetric distribution pattern as Gottron’s papules but do not appear in the interphalangeal spaces. This is a contrasting dermatologic distribution pattern to what is observed in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.[2][8][5][6]
Differential diagnosis
Source:[6]
| Primary dermatomyositis | Secondary dermatomyositis | Not dermatomyositis |
|---|---|---|
| Classic adult dermatomyositis | Drug induced (dtatins, NSAID, chemotherapeutics, antibiotics) | Lupus |
| Paraneoplastic dermatomyositis | Infection induced (HIV, HSV) | Lichen planus |
| Amyopathic dermatomyositis | Psoriasis | |
| Juvenile dermatomyositis | Polymorphous light eruption | |
| "overlap syndrome" dermatomyositis | Granuloma annulare | |
| Dermatitis (contact, seborrheic, atopic) | ||
| Trauma-induced knuckles |
References
- ↑ "Dermatomyositis - About the Disease - Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center" (in en). https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/6263/dermatomyositis.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 Koler, Ric Anthony; Montemarano, Andrew (2001-11-01). "Dermatomyositis" (in en-US). American Family Physician 64 (9): 1565–1573. PMID 11730311. https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2001/1101/p1565.html.
- ↑ "UpToDate". https://www.uptodate.com/contents/polymyositis-dermatomyositis-and-other-forms-of-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathy-beyond-the-basics/print.
- ↑ "Gottron Papules: A Key Sign of an Autoimmune Muscle Disease" (in en). https://archive.is/nTuT0.
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.0 5.1 "Adult-onset dermatomyositis | DermNet" (in en). https://dermnetnz.org/topics/adult-onset-dermatomyositis.
- ↑ Jump up to: 6.0 6.1 6.2 BSc, Heather M. Babcock; PhD, Mohammed S. Osman MD; Md, Tiffany Kwok; Md, Stephen Chihrin; MSc, Stephanie O. Keeling MD; Mph, Sumit R. Majumdar MD (2013). "The Pathognomonicity of Gottron's Sign" (in en). Canadian Journal of General Internal Medicine 8 (1). doi:10.22374/cjgim.v8i1.97. ISSN 2369-1778. https://cjgim.ca/.
- ↑ Marvi, Umaima; Chung, Lorinda; Fiorentino, David F (2012). "Clinical Presentation and Evaluation of Dermatomyositis". Indian Journal of Dermatology 57 (5): 375–381. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.100486. ISSN 0019-5154. PMID 23112358.
- ↑ Marvi, Umaima; Chung, Lorinda; Fiorentino, David F (2012). "Clinical Presentation and Evaluation of Dermatomyositis". Indian Journal of Dermatology 57 (5): 375–381. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.100486. ISSN 0019-5154. PMID 23112358.
 |