Medicine:Idiopathic CD4+ lymphocytopenia
| Idiopathic CD4+ lymphocytopenia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Immunodeficiency 13 |
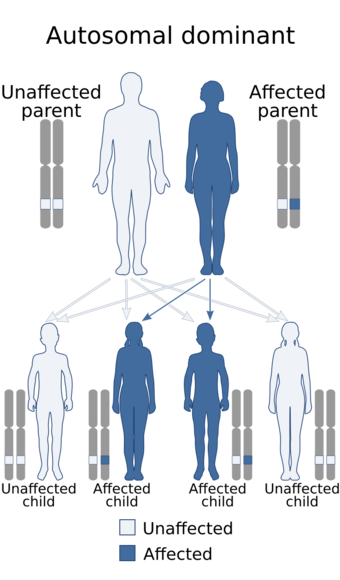 | |
| Idiopathic CD4+ lymphocytopenia is inherited via autosomal dominant manner[1] | |
| Specialty | Immunology |
Idiopathic CD4+ lymphocytopenia (ICL) is a rare medical syndrome in which the body has too few CD4+ T lymphocytes, which are a kind of white blood cell.[2] ICL is sometimes characterized as "HIV-negative AIDS", though, in fact, its clinical presentation differs somewhat from that seen with HIV/AIDS.[3] People with ICL have a weakened immune system and are susceptible to opportunistic infections, although the rate of infections is lower than in people with AIDS.[4]
Cause
The cause of ICL, like all idiopathic conditions, is unknown. It does not appear to be caused by a transmissible agent, such as a virus.[5] It is widely believed that there is more than one cause.[6][non-primary source needed]
Pathophysiology
The loss of CD4+ T cells appears to be through apoptosis.[4][7] The accelerated deaths of the T cells is likely driven by crosslinking T cell receptors.[7]
Diagnosis
The mandatory criteria for diagnosis of idiopathic CD4+ lymphocytopenia include:[8]
- Low numbers of CD4+ cells, on two or more measurements over at least six weeks:
- CD4 cell count less than 300 cells per microliter, or
- Less than 20% of T lymphocytes are CD4+
- Laboratory evidence of lack of HIV infection
- Absence of any alternative explanation for the CD4 lymphocytopenia
A one-time finding of low CD4+ cells is usually associated with a recent infection and resolves on its own.[7] Alternative explanations for the low CD4 counts include conditions such as blood cancers (aleukemia), treatment with chemotherapy, immunosuppressive medications, or other medications that suppress or kill T cells, infections, and problems with blood production.[2][9][non-primary source needed]
All criteria must be fulfilled for a diagnosis of ICL. In addition, if these findings are present but combined with other significant findings, such as anemia or thrombocytopenia, then other diagnoses must be considered[citation needed].
Treatment
Fludarabine-based hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has shown to be a feasible treatment for ICL.[10][non-primary source needed]
Prognosis
In contrast to the CD4+ cell depletion caused by HIV, in general, patients with idiopathic CD4 lymphocytopenia have a good prognosis.[6][11][12][13][non-primary source needed] The decline in CD4+ T-cells in patients with ICL is generally slower than that seen in HIV-infected patients.[3] The major risk to people with ICL is unexpected infections, including cryptococcus, atypical mycobacterial and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PCP). The condition may also resolve on its own.[14]
ICL sometimes precedes and may be the first signal of several blood cancers. ICL patients have developed primary effusion lymphoma,[15][non-primary source needed][16] primary leptomeningeal lymphoma,[9] diffuse large cell lymphoma,[17][non-primary source needed] MALT lymphoma,[18] and Burkitt's lymphoma,[19] among others.
ICL may indirectly trigger autoimmune diseases. It has been associated with several cases of autoimmune disease Sjögren syndrome.[4][20]
Because all of the reported autoimmune diseases and lymphomas involve B cells, one hypothesis proposes that ICL's narrow T cell repertoire predisposes the immune system to B cell disorders.[4]
Epidemiology
ICL is a very rare disease.[2] In 1993, a total of 47 confirmed cases were reported in a survey sponsored by the Centers for Disease Control.[21]
References
- ↑ "OMIM Entry - # 615518 - IMMUNODEFICIENCY 13; IMD13" (in en-us). https://omim.org/entry/615518.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Idiopathic CD4 lymphocytopenia". Curr Opin Rheumatol 18 (4): 389–95. July 2006. doi:10.1097/01.bor.0000231908.57913.2f. PMID 16763460.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Idiopathic CD4 lymphocytopenia and opportunistic infection--an update". FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 54 (3): 283–9. December 2008. doi:10.1111/j.1574-695X.2008.00490.x. PMID 19049641.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "Idiopathic CD4+ lymphocytopenia and Sjogren syndrome". Arch. Ophthalmol. 123 (7): 1012. July 2005. doi:10.1001/archopht.123.7.1012-a. PMID 16009850.
- ↑ Online Medical Dictionary entry on T-lymphocytopenia
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Idiopathic CD4+ T-lymphocytopenia--four patients with opportunistic infections and no evidence of HIV infection". N. Engl. J. Med. 328 (6): 393–8. February 1993. doi:10.1056/NEJM199302113280604. PMID 8093636.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 "Apoptotic depletion of CD4+ T cells in idiopathic CD4+ T lymphocytopenia". J. Clin. Invest. 97 (3): 672–80. February 1996. doi:10.1172/JCI118464. PMID 8609222.
- ↑ UpToDate article on "Techniques and interpretation of measurement of the CD4 cell count in HIV-infected patients", by John G. Bartlett. Accessed 30 Oct 2006.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "Primary leptomeningeal lymphoma in a patient with concomitant CD4+ lymphocytopenia". Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 88 (3): 339–42. March 2002. doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)62019-4. PMID 11926631.
- ↑ Hamidieh, A. A.; Pourpak, Z.; Hamdi, A.; Nabavi, M.; Ghavamzadeh, A. (2013). "Successful fludarabine-based hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in a pediatric patient with idiopathic CD4+ lymphocytopenia". Pediatric Transplantation 17 (4): E109–11. doi:10.1111/petr.12086. PMID 23581828.
- ↑ "Acquired immunodeficiency without evidence of infection with human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2.". Lancet 340 (8814): 273–4. 1992. doi:10.1016/0140-6736(92)92359-N. PMID 1353194.
- ↑ "Idiopathic CD4+ T-lymphocytopenia--immunodeficiency without evidence of HIV infection.". N Engl J Med 328 (6): 380–5. 1993. doi:10.1056/NEJM199302113280602. PMID 8093634.
- ↑ "Idiopathic CD4+ T-lymphocytopenia--an analysis of five patients with unexplained opportunistic infections.". N Engl J Med 328 (6): 386–92. 1993. doi:10.1056/NEJM199302113280603. PMID 8093635.
- ↑ "Idiopathic CD4+ lymphocytopenia: natural history and prognostic factors". Blood 112 (2): 287–294. July 2008. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-12-127878. PMID 18456875.
- ↑ "Human herpes virus 8-negative primary effusion lymphoma with BCL6 rearrangement in a patient with idiopathic CD4 positive T-lymphocytopenia". Haematologica 93 (1): e21–3. January 2008. doi:10.3324/haematol.12085. PMID 18166773.
- ↑ "PEL, Kaposi's sarcoma HHV8+ and idiopathic T-lymphocitopenia CD4+". Clin Ter 158 (2): 151–5. 2007. PMID 17566517.
- ↑ "Diffuse large cell lymphoma and t(8;22) (q24;q11) in a patient with idiopathic CD4+ T-lymphopenia". Leuk. Lymphoma 41 (3–4): 421–3. April 2001. doi:10.3109/10428190109057998. PMID 11378556.
- ↑ "[Multifocal MALT lymphoma and acute cytomegalovirus gastritis revealing CD4 lymphopenia without HIV infection]" (in fr). Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 23 (1): 132–6. January 1999. PMID 10219614.
- ↑ "[Idiopathic CD4+ T-lymphocytopenia terminating in Burkitt's lymphoma]" (in ja). Rinsho Ketsueki 38 (7): 599–603. July 1997. PMID 9267164.
- ↑ "CD4+ T-lymphocytopenia--a frequent finding in anti-SSA antibody seropositive patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome". J. Rheumatol. 31 (4): 726–8. April 2004. PMID 15088298. http://www.jrheum.com/subscribers/04/04/726.html.
- ↑ "Unexplained opportunistic infections and CD4+ T-lymphocytopenia without HIV infection. An investigation of cases in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control Idiopathic CD4+ T-lymphocytopenia Task Force.". N Engl J Med 328 (6): 373–9. 1993. doi:10.1056/NEJM199302113280601. PMID 8093633.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |

