Medicine:Johnson–McMillin syndrome
From HandWiki
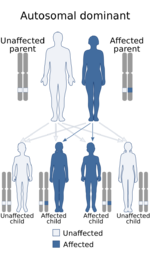
Johnson–McMillin syndrome, also known as Johnson neuroectodermal syndrome, is a neuroectodermal syndrome characterized by conductive hearing loss and alopecia, microtia, conductive hearing loss, anosmia/hyposmia, and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.[2][3]
See also
- List of cutaneous conditions
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 "OMIM Entry - % 147770 - JOHNSON NEUROECTODERMAL SYNDROME". https://www.omim.org/entry/147770.
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. pp. 831. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ↑ Abdel-Meguid, N; Gebril, OH; Abdelraouf, ER; Shafie, MA; Bahgat, M (2014). "Johnson-McMillin Microtia Syndrome: New Additional Family.". J Family Med Prim Care 3 (3): 275–8. doi:10.4103/2249-4863.141639. PMID 25374870.
External links
 |