Medicine:Juvenile nephronophthisis
| Juvenile nephronophthisis | |
|---|---|
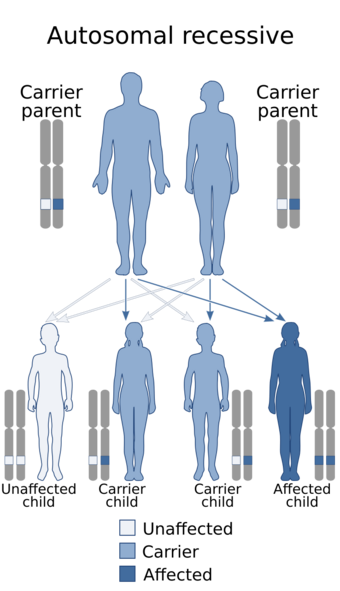 | |
| Juvenile nephronophthisis is inherited via an autosomal recessive manner |
Juvenile nephronophthisis is the juvenile form of nephronophthisis that causes end stage kidney disease around the age of 13; infantile nephronophthisis and adolescent nephronophthisis cause ESKD around the ages of 1 and 19, respectively.
Signs and symptoms
Typically, the signs and symptoms of juvenile nephronophthisis are limited to the kidneys. They include polyuria, polydipsia, weakness, and fatigue.[1] Anemia, growth retardation, no hypertension. Proteinuria and hematuria are usually absent. Polyuria is resistant to vasopressin. When other organ systems are affected, symptoms can include situs inversus, heart abnormalities, and liver fibrosis. Juvenile nephronophthisis can also be associated with other rare disorders, including Senior–Løken syndrome and Joubert syndrome.[1]
Pathophysiology
Juvenile nephronophthisis causes fibrosis and scarring of the kidneys, which accounts for the symptoms observed. The kidneys also often have corticomedullary cysts.[1]
- Inability to conserve sodium because of defect of tubules leading to polyuria and polydipsia.
- Anemia is attributed to a deficiency of erythropoietin production by failing kidneys.
- Growth retardation, malaise and pallor are secondary to anemia.
- No hypertension as nephronophthisis is a salt-losing enteropathy.
Diagnosis
Ultrasonography shows bilateral small kidneys with loss of corticomedullary junction and multiple cysts only in the medulla. Cysts may only be seen if they are large enough, they are rarely visible early in disease.[citation needed]
Differential diagnosis
Patients with medullary cystic disease present with similar features as juvenile nephronophthisis but they can be differentiated by:
- Absence of growth retardation.
- Age of presentation is third or fourth decade.
- Hypertension may occur (in JN, hypertension is not seen).
In polycystic kidney disease, there is bilateral enlargement of kidneys (small kidneys in JN).
Treatment
The only option is renal transplant.
Epidemiology
It is the most common genetic cause of end stage kidney disease (kidney failure) in childhood and adolescence.[citation needed]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Nephronophthisis". http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/nephronophthisis. Retrieved 2015-07-25.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |

