Medicine:Oxycephaly
From HandWiki
| Oxycephaly | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Turricephaly,[1] Acrocephaly, Hypsicephaly,[1] Oxycephalia,[1] Steeple head,[1] Tower head,[1] Tower skull, High-head syndrome, Turmschädel,[2] |
 | |
| Symptoms | Pointy head |
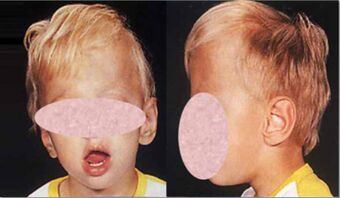
Oxycephaly is a type of cephalic disorder where the top of the skull is pointed or conical due to premature closure of the coronal suture plus any other suture, like the lambdoid,[3] or it may be used to describe the premature fusion of all sutures.[2] It should be differentiated from Crouzon syndrome. Oxycephaly is the most severe of the craniosynostoses.
Presentation
Common associations
It may be associated with:[4]
- 8th cranial nerve lesion
- Optic nerve compression
- Intellectual disability
- Syndactyly
Diagnosis
Treatment
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Mosby's Medical Dictionary (8th ed.). Elsevier. 2009. http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/oxycephaly. Retrieved 24 August 2013.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Bodian, Martin (May 6, 1950). "Oxycephaly.". Journal of the American Medical Association 143 (1): 15–8. doi:10.1001/jama.1950.02910360017006. PMID 15415226.
- ↑ "oxycephaly". TheFreeDictionary. http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/oxycephaly.
- ↑ Weerakkody, Yuranga; Goel, Ayush. "Oxycephaly". Radiopaedia.org. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/oxycephaly.
Further reading
- NINDS Overview
- Ebenezer, Roy (1960). "Craniostenosis or oxycephaly". Indian Journal of Ophthalmology 8 (3): 77–80. ISSN 0301-4738. PMID 13819157. http://www.ijo.in/article.asp?issn=0301-4738;year=1960;volume=8;issue=3;spage=77;epage=80;aulast=Ebenezer.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |


