Open Graphics Project
This article needs to be updated. (February 2011) |
| Open Graphics Project | |
|---|---|
| Commercial? | Yes |
| Type of project | Open hardware |
| Website | wiki.opengraphics.org at the Wayback Machine (archived June 9, 2010) |

The Open Graphics Project (OGP) was founded with the goal to design an open-source hardware / open architecture and standard for graphics cards, primarily targeting free software / open-source operating systems. The project created a reprogrammable development and prototyping board and had aimed to eventually produce a full-featured and competitive end-user graphics card.
OGD1
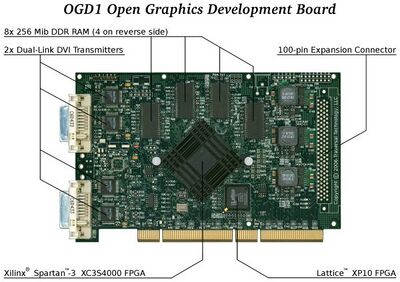
The project's first product was a PCI graphics card dubbed OGD1, which used a field-programmable gate array (FPGA) chip. Although the card did not have the same level of performance or functionality as graphics cards on the market at the time, it was intended to be useful as a tool for prototyping the project's first application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) board, as well as for other professionals needing programmable graphics cards or FPGA-based prototyping boards. It was also hoped that this prototype would attract enough interest to gain some profit and attract investors for the next card, since it was expected to cost around US$2,000,000 to start the production of a specialized ASIC design. PCI Express and/or Mini-PCI variations were planned to follow. The OGD1 began shipping in September 2010,[1] some six years after the project began and 3 years after the appearance of the first prototypes.[2]
Full specifications will be published and open-source device drivers will be released. All RTL will be released. Source code to the device drivers and BIOS will be released under the MIT and BSD licenses. The RTL (in Verilog) used for the FPGA and the RTL used for the ASIC are planned to be released under the GNU General Public License (GPL).
It has 256 MiB of DDR RAM, is passively cooled, and follows the DDC, EDID, DPMS and VBE VESA standards. TV-out is also planned.
Versioning schema
Versioning schema for OGD1 will go like this:
{Root Number} – {Video Memory}{Video Output Interfaces}{Special Options e.g.: A1 OGA firmware installed}
| Field | Example Value | Example Description |
|---|---|---|
| Root number | OGD1P- | OGD1 board with PCI Bus |
| Video memory | 256 | 256 MiB |
| Video outputs, in order, skip any not installed | ||
| First interface | D | Dual-link DVI |
| Second interface | D | Dual-link DVI |
| Third interface | A | Analog video, 75 ohm, VGA compatible |
| Fourth interface | V | TV video |
| Special options, in alphanumeric order, each preceded by a dash | ||
| Factory firmware-RTL | A1 | OGA1 Firmware |
OGD1 components
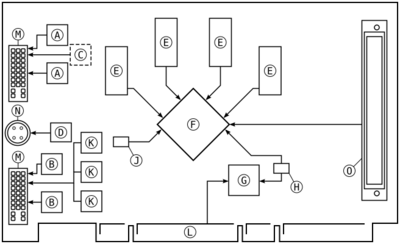
Main components of OGD1 graphics card (shown on the picture)[3]
- A) DVI transmitter pair A
- B) DVI transmitter pair B
- C) 330MHz triple 10-bit DAC (behind)
- D) TV chip
- E) 2x4 256 megabit DDR SDRAM (front, behind)
- F) Xilinx 3S4000 FPGA (main chip)
- G) Lattice XP10 FPGA (host interface)
- H) SPI PROM 1 Mibit
- J) SPI PROM 16 Mibit
- K) 3x 500 MHz DACs (optional)
- L) 64-bit PCI-X edge connector
- M) DVI-I connector A and connector B
- N) S-Video connector
- O) 100-pin expansion bus connector
Divisions/terms related to OGP
- Open Graphics Project (OGP)
- The group of people developing OGA, its written documentation, and its products.
- Open Graphics Architecture (OGA)
- The trade name for open graphics architectures specified by the Open Graphics Project.
- Open Graphics Development (OGD)
- The initial FPGA-based experimentation board used as a test platform for TRV ASICs.
- Traversal Technology (TRV)
- The commercial name for the first ASIC products, based on the Open Graphics Architecture.
- Open Graphics Card (OGC)
- Graphics cards based on TRV chips.
- Open Hardware Foundation (OHF)
- A non-profit corporation whose charter is to promote the design and production of open-source and open-documentation hardware.
Current status
The OGP project failed to gain the necessary funding to produce an ASIC version of its card. The project appears to have been discontinued in 2011.
See also
- Graphics hardware and FOSS
- Open-source hardware
- Open system (computing)
- RISC-V
References
- ↑ "OGD1's Now Available!". http://lists.duskglow.com/open-graphics/2010-September/012160.html.
- ↑ "First Open Graphics board appears". The Inquirer. http://www.theinquirer.net/default.aspx?article=36761.
- ↑ "OGD1 map guide". Open Graphics wiki. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. https://web.archive.org/web/20070927065410/http://wiki.duskglow.com/tiki-page.php?pageName=OGD1_Map_Guide. Retrieved 2006-09-04.
External links
- The official Open Graphics wiki archived at the Wayback Machine June 9, 2010
- Jeremy Andrews (1 March 2006). "Hardware: Open Graphics Development Board Pricing". KernelTrap. http://kerneltrap.org/node/6272. Retrieved 2006-09-04.
- Project VGA – another free graphics core project, aiming at cheaper hardware
- Manticore – an older FPGA-based free graphics core implementation. As of 2009-05-04 no source is available.
- The master thesis "An FPGA-based 3D Graphics System" illustrates very well the design decisions to make, while developing a FPGA-based 3D graphics core.
- The master thesis "A performance-driven SoC architecture for video synthesis" gives a more complete and hands-on approach of some aspects.
 |
