Physics:Isobaric labeling
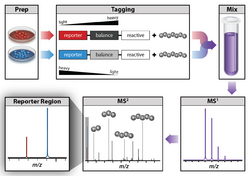
Isobaric labeling is a mass spectrometry strategy used in quantitative proteomics. Peptides or proteins are labeled with chemical groups that have nominally identical mass (isobaric), but vary in terms of distribution of heavy isotopes in their structure. These tags, commonly referred to as tandem mass tags, are designed so that the mass tag is cleaved at a specific linker region upon high-energy collision-induced dissociation (HCD) during tandem mass spectrometry yielding reporter ions of different masses.
The most common isobaric tags are amine-reactive tags.[1] However, tags that react with cysteine residues and carbonyl groups have also been described.[2] These amine-reactive groups go through N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) reactions, which are based around three types of functional groups.[2] Isobaric labeling methods include tandem mass tags (TMT), isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantification (iTRAQ), mass differential tags for absolute and relative quantification, and dimethyl labeling.[1] TMTs and iTRAQ methods are most common and developed of these methods.[1] Tandem mass tags have a mass reporter region, a cleavable linker region, a mass normalization region, and a protein reactive group and have the same total mass.[3]
Workflow
A typical bottom-up proteomics workflow is described by (Yates, 2014).[2] Protein samples are enzymatically digested by a protease to produce peptides. Each digested experimental sample is derivative from a set with a different isotopic variant of the tag. The samples are mixed in typically equal ratios and analyzed simultaneously in one MS run. Since the tags are isobaric and have identical chemical properties, the isotopic variants of the tags appear as a single composite peak at the same m/z value in an MS1 scan with identical liquid chromatography (LC) retention times. During the MS2 analysis and upon fragmentation, each isotopic variant of the tag produces sequence-specific product ions. These product ions are used to determine the peptide sequence and the reporter tags whose abundances reflect the relative ratio of the peptide in the combined samples. The use of MS/MS is required to detect the tags, therefore, unlabeled peptides are not quantified.

Advantages
Explained previously by (Lee, Choe, Aggarwal, 2017).[4] A key benefit of isobaric labeling over other quantification techniques (e.g. label-free) is the multiplex capabilities and thus increased throughput potential. The ability to combine and analyze several samples simultaneously in one LC-MS run eliminates the need to analyze multiple data sets and eliminates run-to-run variation. Multiplexing reduces sample processing variability, improves specificity by quantifying the peptides from each condition simultaneously, and reduces turnaround time for multiple samples. Without multiplexing, information can be missed from run to run, affecting identification and quantification, as peptides selected for fragmentation on one LC-MS/MS run may not be present or of suitable quantity in subsequent sample runs. The current available isobaric chemical tags facilitate the simultaneous analysis of 2 to 11 experimental samples.
Applications
Isobaric labeling has been successfully used for many biological applications including protein identification and quantification, protein expression profiling of normal vs abnormal states, quantitative analysis of proteins for which no antibodies are available and identification and quantification of post-translationally modified proteins.[4]
Availability
There are two types of isobaric tags commercially available: tandem mass tags (TMT) and isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ). Amine-reactive TMT are available in duplex, 6-plex 10-plex, and now 11-plex sets.[5] Amine-reactive iTRAQ are available in 4-plex and 8-plex[6] forms.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Bantscheff, Marcus; Lemeer, Simone; Savitski, Mikhail M.; Kuster, Bernhard (2012-09-01). "Quantitative mass spectrometry in proteomics: critical review update from 2007 to the present" (in en). Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 404 (4): 939–965. doi:10.1007/s00216-012-6203-4. ISSN 1618-2650. PMID 22772140.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Yates, John (2014). "Isobaric Labeling-Based Relative Quantification in Shotgun Proteomics". Journal of Proteome Research 13 (12): 5293–5309. doi:10.1021/pr500880b. PMID 25337643.
- ↑ Thompson, Andrew; Schäfer, Jürgen; Kuhn, Karsten; Kienle, Stefan; Schwarz, Josef; Schmidt, Günter; Neumann, Thomas; Hamon, Christian (2003). "Tandem Mass Tags: A Novel Quantification Strategy for Comparative Analysis of Complex Protein Mixtures by MS/MS" (in en). Analytical Chemistry 75 (8): 1895–1904. doi:10.1021/ac0262560. ISSN 0003-2700. PMID 12713048.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Lee, Kelvin H.; Choe, Leila H.; Aggarwal, Kunal (2006-06-01). "Shotgun proteomics using the iTRAQ isobaric tags" (in en). Briefings in Functional Genomics 5 (2): 112–120. doi:10.1093/bfgp/ell018. ISSN 2041-2649. PMID 16772272. https://academic.oup.com/bfg/article/5/2/112/210770.
- ↑ "Relative quantification of proteins in human cerebrospinal fluids by MS/MS using 6-plex isobaric tags". Anal. Chem. 80 (8): 2921–31. 2008. doi:10.1021/ac702422x. PMID 18312001.
- ↑ "8-plex quantitation of changes in cerebrospinal fluid protein expression in subjects undergoing intravenous immunoglobulin treatment for Alzheimer's disease". Proteomics 7 (20): 3651–60. 2007. doi:10.1002/pmic.200700316. PMID 17880003.
 |
