Physics:Laminar flow
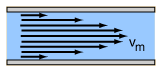
Laminar flow (/ˈlæmɪnər/) is the property of fluid particles in fluid dynamics to follow smooth paths in layers, with each layer moving smoothly past the adjacent layers with little or no mixing.[1] At low velocities, the fluid tends to flow without lateral mixing, and adjacent layers slide past one another smoothly. There are no cross-currents perpendicular to the direction of flow, nor eddies or swirls of fluids.[2] In laminar flow, the motion of the particles of the fluid is very orderly with particles close to a solid surface moving in straight lines parallel to that surface.[3] Laminar flow is a flow regime characterized by high momentum diffusion and low momentum convection.
When a fluid is flowing through a closed channel such as a pipe or between two flat plates, either of two types of flow may occur depending on the velocity and viscosity of the fluid: laminar flow or turbulent flow. Laminar flow occurs at lower velocities, below a threshold at which the flow becomes turbulent. The threshold velocity is determined by a dimensionless parameter characterizing the flow called the Reynolds number, which also depends on the viscosity and density of the fluid and dimensions of the channel. Turbulent flow is a less orderly flow regime that is characterized by eddies or small packets of fluid particles, which result in lateral mixing.[2] In non-scientific terms, laminar flow is smooth, while turbulent flow is rough.
Relationship with the Reynolds number

The type of flow occurring in a fluid in a channel is important in fluid-dynamics problems and subsequently affects heat and mass transfer in fluid systems. The dimensionless Reynolds number is an important parameter in the equations that describe whether fully developed flow conditions lead to laminar or turbulent flow. The Reynolds number is the ratio of the inertial force to the shearing force of the fluid: how fast the fluid is moving relative to how viscous it is, irrespective of the scale of the fluid system. Laminar flow generally occurs when the fluid is moving slowly or the fluid is very viscous. As the Reynolds number increases, such as by increasing the flow rate of the fluid, the flow will transition from laminar to turbulent flow at a specific range of Reynolds numbers, the laminar–turbulent transition range depending on small disturbance levels in the fluid or imperfections in the flow system. If the Reynolds number is very small, much less than 1, then the fluid will exhibit Stokes, or creeping, flow, where the viscous forces of the fluid dominate the inertial forces.
The specific calculation of the Reynolds number, and the values where laminar flow occurs, will depend on the geometry of the flow system and flow pattern. The common example is flow through a pipe, where the Reynolds number is defined as
where:
- DH is the hydraulic diameter of the pipe (m);
- Q is the volumetric flow rate (m3/s);
- A is the pipe's cross-sectional area (m2);
- u is the mean speed of the fluid (SI units: m/s);
- μ is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid (Pa·s = N·s/m2 = kg/(m·s));
- ν is the kinematic viscosity of the fluid, ν = μ/ρ (m2/s);
- ρ is the density of the fluid (kg/m3).
For such systems, laminar flow occurs when the Reynolds number is below a critical value of approximately 2,040, though the transition range is typically between 1,800 and 2,100.[4]
For fluid systems occurring on external surfaces, such as flow past objects suspended in the fluid, other definitions for Reynolds numbers can be used to predict the type of flow around the object. The particle Reynolds number Rep would be used for particle suspended in flowing fluids, for example. As with flow in pipes, laminar flow typically occurs with lower Reynolds numbers, while turbulent flow and related phenomena, such as vortex shedding, occur with higher Reynolds numbers.
Examples

A common application of laminar flow is in the smooth flow of a viscous liquid through a tube or pipe. In that case, the velocity of flow varies from zero at the walls to a maximum along the cross-sectional centre of the vessel. The flow profile of laminar flow in a tube can be calculated by dividing the flow into thin cylindrical elements and applying the viscous force to them.[5]
Another example is the flow of air over an aircraft wing. The boundary layer is a very thin sheet of air lying over the surface of the wing (and all other surfaces of the aircraft). Because air has viscosity, this layer of air tends to adhere to the wing. As the wing moves forward through the air, the boundary layer at first flows smoothly over the streamlined shape of the airfoil. Here, the flow is laminar and the boundary layer is a laminar layer. Prandtl applied the concept of the laminar boundary layer to airfoils in 1904.[6][7]

An everyday example is the slow, smooth and optically transparent flow of shallow water over a smooth barrier.[8]
When water leaves a tap without an aerator with little force, it first exhibits laminar flow, but as acceleration by the force of gravity immediately sets in, the Reynolds number of the flow increases with speed, and the laminar flow of the water downstream from the tap can transition to turbulent flow. Optical transparency is then reduced or lost entirely.
Laminar flow barriers
File:Experimental chamber for studying chemotaxis in response to laminar flow.ogv
Laminar airflow is used to separate volumes of air, or prevent airborne contaminants from entering an area. Laminar flow hoods are used to exclude contaminants from sensitive processes in science, electronics and medicine. Air curtains are frequently used in commercial settings to keep heated or refrigerated air from passing through doorways. A laminar flow reactor (LFR) is a reactor that uses laminar flow to study chemical reactions and process mechanisms. A laminar flow design for animal husbandry of rats for disease management was developed by Beall et al. 1971 and became a standard around the world[9] including in the then-Eastern Bloc.[10]
See also
- Hagen–Poiseuille equation
- Shell balance
- Wake turbulence
- Water current
References
- ↑ Streeter, V.L. (1951-1966) Fluid Mechanics, Section 3.3 (4th edition). McGraw-Hill
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Geankoplis, Christie John (2003). Transport Processes and Separation Process Principles. Prentice Hall Professional Technical Reference. ISBN 978-0-13-101367-4. http://www.pearsonhighered.com/educator/product/Transport-Processes-and-Separation-Process-Principles-Includes-Unit-Operations/9780131013674.page.
- ↑ Noakes, Cath; Sleigh, Andrew (January 2009). "Real Fluids". An Introduction to Fluid Mechanics. University of Leeds. http://www.efm.leeds.ac.uk/CIVE/CIVE1400/Section4/laminar_turbulent.htm.
- ↑ Avila, K.; Moxey, D.; de Lozar, A.; Avila, M.; Barkley, D.; Hof, B. (July 2011). "The Onset of Turbulence in Pipe Flow". Science 333 (6039): 192–196. doi:10.1126/science.1203223. PMID 21737736. Bibcode: 2011Sci...333..192A.
- ↑ Nave, R. (2005). "Laminar Flow". HyperPhysics. Georgia State University. http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/pfric.html.
- ↑ Anderson, J. D. (1997). A History of Aerodynamics and Its Impact on Flying Machines. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-66955-3. https://books.google.com/books?isbn=0521669553.
- ↑ Rogers, D. F. (1992). Laminar flow analysis. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-41152-1. https://books.google.com/books?isbn=0521411521.
- ↑ ((sovereign578)) (5 November 2016). "Laminar Flow in Nature" (in en). https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uaqKFeqRLik.
- ↑ Faith, Robert E.; Hessler, Jack R. (2006). "10. Housing and Environment". The Laboratory Rat (2 ed.). Amsterdam Boston: American College of Laboratory Animal Medicine (AP). p. 304/pp. 304–337/xvi+912. ISBN 978-0-08-045432-0. OCLC 162569241. ISBN 9780120749034 ISBN 0120749033
- ↑ Trávníček, J.; Mandel, L. (1979). "Gnotobiotic techniques". Folia Microbiologica (Czechoslovak Society for Microbiology (Springer)) 24 (1): 6–10. doi:10.1007/bf02927240. ISSN 0015-5632. PMID 374207.
External links
- 3mtr High laminar Flow Waterfall, 1:01 m:s, 2016 on YouTube
- Build a laminar flow nozzle for $15, 8:07 m:s, 2008 on YouTube
- Laminar flow of a small stream, 2016 on YouTube
- A fountain in Chicago, 2014 on YouTube
- Reversible laminar flow demonstrated with blue and green corn syrup, 2007 on YouTube
- Laminar flow in a pipe, 2006 on YouTube
 |
