Physics:Optical window
From HandWiki
The meaning of this term depends on the context.
Natural sciences
Objects are often transparent to some wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum, but not others. A "window" is a group of wavelengths that will pass through an object (the wavelengths which are not blocked by the object). An optical window is one which includes the wavelengths humans can see (visible light).
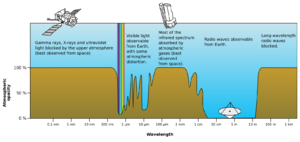
- In planetary sciences, the atmosphere is transparent to visible light, meaning that sunlight mostly passes through the atmosphere and is absorbed by the ground (see Rayleigh scattering). The ground then warms up and heats the atmosphere from below. The sun's energy escapes back into space through the infrared window. The atmosphere is not transparent but 100% opaque to many wavelengths (see diagram). The wavelengths in which it is transparent are called "window"s.
- In astronomy, the concept is similar. The optical window is the optical portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that passes through the atmosphere all the way to the ground. Most electromagnetic radiation wavelengths are blocked by the atmosphere, so this is like a window that lets through only a narrow selection of what is out there, though the sun is particularly active in the passed wavelengths. It is called "optical" because the wavelengths we can see are all in this range. The window runs from around 300 nanometers (ultraviolet-B) at the short end up into the range the eye can use, roughly 400–700 nm and continues up through the visual infrared to around 1100 nm, which is in the near-infrared range. There are also infrared and "radio windows" that transmit some infrared and radio waves. The radio window runs from about one centimeter to about eleven-meter waves.[1]
- In medical physics, the optical window is the portion of the visible and infrared spectrum where living tissue absorbs relatively little light. This window runs approximately from 650 to 1200 nm. At shorter wavelengths, light is strongly absorbed by hemoglobin in blood, while at longer wavelengths water strongly absorbs infrared light.
Technology
A window through which optical measurements are made.
- In optics, it means an optical material that allows light into an optical instrument (usually at least mechanically flat, sometimes optically flat, depending on resolution requirements) piece of transparent (for a wavelength range of interest, not necessarily for visible light). A window is usually parallel and is likely to be anti-reflection coated, at least if it is designed for visible light. An optical window may be built into a piece of equipment (such as a vacuum chamber) to allow optical instruments to view inside that equipment.
- For UV/VIS spectroscopy, these types of windows are usually made from glass or fused silica. In IR spectroscopy, there is a wide range of materials from Barium Fluoride (BaF2), Germanium (Ge), Zinc Selenide (ZnSe) and Sapphire that transmit light into the far infrared. These windows are either built into circular or rectangular configurations.[2]
See also
- Infrared (atmospheric) window
- Optical window in biological tissue
- Radio window
References
- ↑ Beer, Tom (January 1975) (Hardcover. 170 pgs.). The aerospace environment. Taylor & Francis Ltd. pp. 26. ISBN 978-0-85109-021-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=uqo9AAAAIAAJ&pg=PA26&dq=optical+window&cd=15#v=onepage&q=optical%20window&f=false.
- ↑ The Ultimate Guide to Optical Windows optical windows
 |
