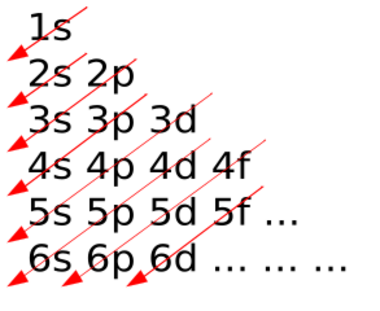
Physics:Wiswesser's rule
The Wiswesser rule gives a simple method to determine the energetic sequence of the atomic subshells [math]\displaystyle{ (n,l) }[/math]. n is the principal quantum number and l is the azimuthal quantum number. The energetic sequence of the subshells characterized by the quantum numbers [math]\displaystyle{ (n,l) }[/math] is the sequence that leads to a monotonically increasing row of function values for the Wiswesser function.
- [math]\displaystyle{ W(n,l) = n + l - \left( \frac{l}{l + 1} \right) }[/math]
For example: if [math]\displaystyle{ n = 2 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ l = 1 }[/math], this corresponds to a 2p-orbital.
If the results of this function for each shell and subshell are ordered, the resulting sequence is: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p...
To illustrate this, the corresponding values of each of these shells can be found in the table below:
| [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ l }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ W(n,l) }[/math] |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 2 | 3.33 |
| 3 | 1 | 3.5 |
| 3 | 2 | 4.33 |
| 4 | 1 | 4.5 |
| 3 | 3 | 5.25 |
| 4 | 2 | 5.33 |
| 5 | 1 | 5.5 |
| 4 | 3 | 6.25 |
| 5 | 2 | 6.33 |
| 6 | 1 | 6.5 |
| 4 | 4 | 7.2 |
| 5 | 3 | 7.25 |
| 6 | 2 | 7.33 |
| 7 | 1 | 7.5 |
| 5 | 4 | 8.2 |
| 6 | 3 | 8.25 |
| 7 | 2 | 8.33 |
We can now clearly see that the Aufbau principle and Wiswesser's Rule come to the same order of filling electron shells.
See also
References