Social:Georgian-Zan languages
| Georgian-Zan | |
|---|---|
| Karto-Zan | |
| Geographic distribution | South Caucasus, Anatolia, Israel |
| Linguistic classification | Kartvelian
|
| Subdivisions |
|
| Glottolog | geor1252[1] |
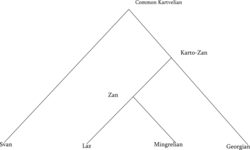
Georgian-Zan languages, also known as Karto-Zan languages is a branch of Kartvelian language family that contains Georgian and Zan languages. Svan language forms the other branch of the Kartvelian family, showing characteristic differences from Karto-Zan group.[2] It has been hypothesized that divergence between Svan and Proto-Kartvelian language goes back as far as 19th century BCE. Georgian and Zan languages on the other hand diversified from Proto-Georgian-Zan language during 7th century BCE.[3] Both languages share common archaic words related to metallurgy and agriculture absent in Svan.
Classification
Karto-Zan languages constitute a branch of the Kartvelian language family. Glottolog internally divides Karto-Zan group in Georgic languages, which contain Georgian and its dialects, Judaeo-Georgian and Old Georgian, and Zan languages constituted by the Mingrelian and Laz languages.[4]
References
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds (2017). "Georgian-Zan". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. http://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/geor1252.
- ↑ (in en) Linguistics. Mouton. 1999. https://books.google.de/books?id=CN1pAAAAIAAJ&q=georgian-zan&dq=georgian-zan&hl=tr&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjOxsftpvTmAhUILFAKHUf-AqgQ6AEIYzAH.
- ↑ (in en) Soviet Anthropology and Archaeology: ISAP Translations from Original Soviet Sources. International Arts and Sciences Press. 1965. https://books.google.de/books?id=HsAjAQAAIAAJ&q=georgian-zan&dq=georgian-zan&hl=tr&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjdgMieofTmAhUNCewKHdrMDcs4ChDoAQgwMAE.
- ↑ "Glottolog 4.1 - Georgian-Zan". https://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/geor1252.
Template:Caucasus-stubTemplate:Language-stub