Social:Mingrelian language
| Mingrelian | |
|---|---|
| მარგალური ნინა Template:Tlit | |
| Native to | Georgia |
| Region | Mingrelia Abkhazia |
| Ethnicity | Mingrelians |
Native speakers | 345,530 (2015)Template:Ethnologue24 does not exist |
| Georgian script | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | xmf |
| Glottolog | ming1252[1] |
 | |
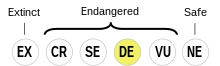 Mingrelian is classified as Definitely Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger | |
File:WIKITONGUES- Valerian speaking Mingrelian.webm
The Mingrelian or Megrelian language (მარგალური ნინა margaluri nina) is a Kartvelian language spoken in Western Georgia (regions of Mingrelia and Abkhazia), primarily by the Mingrelians. Mingrelian has historically been only a regional language within the boundaries of historical Georgian states and then modern Georgia, and the number of younger people speaking it has decreased substantially, with UNESCO designating it as a "definitely endangered language".[2]
Distribution and status

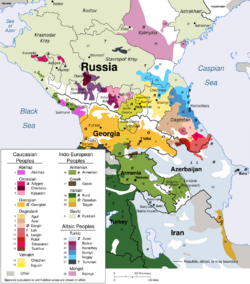
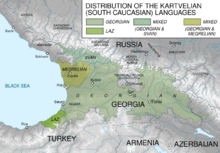
No reliable figure exists for the number of native speakers of Mingrelian, but it is estimated to be between 300,000 and 500,000. Most speakers live in the Mingrelia (or Samegrelo and formerly Odishi) region of Georgia, which comprises the Odishi Hills and the Colchis Lowlands, from the Black Sea coast to the Svan Mountains and the Tskhenistskali River. Smaller enclaves existed in Abkhazia,[3] but the ongoing civil unrest there has displaced many Mingrelian speakers to other regions of Georgia. Their geographical distribution is relatively compact, which has helped to promote the transmission of the language between generations.
Mingrelian is generally written in the Georgian alphabet, but it has no written standard or official status. Almost all speakers are bilingual; they use Mingrelian mainly for familiar and informal conversation, and Georgian (or, for expatriate speakers, the local official language) for other purposes.
History
Mingrelian is one of the Kartvelian languages. It is closely related to Laz, from which it has become differentiated mostly in the past 500 years, after the northern (Mingrelian) and southern (Laz) communities were separated by Turkic invasions. It is less closely related to Georgian, the two branches having separated in the first millennium BC or earlier, and even more distantly related to Svan, which is believed to have branched off in the 2nd millennium BC or earlier.[4] Mingrelian is mutually intelligible only with Laz.
Some linguists refer to Mingrelian and Laz as Zan languages.[5] Zan had already split into Mingrelian and Laz variants by early modern times, however, and it is not customary to speak of a unified Zan language today.
The oldest surviving texts in Mingrelian date from the 19th century, and are mainly items of ethnographical literature. The earliest linguistic studies of Mingrelian include a phonetic analysis by Aleksandre Tsagareli (1880), and grammars by Ioseb Kipshidze (1914) and Shalva Beridze (1920). From 1930 to 1938 several newspapers were published in Mingrelian, such as Kazakhishi Gazeti, Komuna, Samargalosh Chai, Narazenish Chai, and Samargalosh Tutumi. More recently, there has been some revival of the language, with the publication of a Mingrelian–Georgian dictionary by Otar Kajaia, a Mingrelian-German dictionary by Otar Kajaia and Heinz Fähnrich, and books of poems by Lasha Gakharia, Edem Izoria, Lasha Gvasalia, Guri Otobaia, Giorgi Sichinava, Jumber Kukava, and Vakhtang Kharchilava, journal Skani, Mingrelian Wikipedia, as well as books and magazines published by Jehovah's Witnesses.[6]
Phonology
Vowels
Mingrelian has five vowel phonemes /i ɛ a ɔ u/. The Zugdidi-Samurzaqano dialect has a sixth /ə/ which is the result of assimilation of /i/ and /u/.
| Front | Back | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| unrounded | rounded | ||
| High | i [i] ი | (ə [ə]) ჷ | u [u] უ |
| Mid | e [ɛ] ე | o [ɔ] ო | |
| Low | a [ɑ] ა | ||
Consonants
The consonant inventory of Mingrelian contains series of aspirated and ejective consonants that contrast with voiced consonants. The inventory and is almost identical to that of Laz, Georgian, and Svan. The table below shows the consonants of Mingrelian in romanized script, phonetic symbols from the IPA, and in Mkhedruli script.
| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m [m] მ | n [n] ნ | |||||
| Plosive | voiced | b [b] ბ | d [d] დ | g [ɡ] გ | |||
| aspirated | p [pʰ] ფ | t [tʰ] თ | k [kʰ] ქ | ||||
| ejective | p̌ [pʼ] პ | ţ [tʼ] ტ | ǩ [kʼ] კ | qʼ [qʼ] ყ | ɔ [ʔ] ჸ | ||
| Affricate | voiced | ž [d͡z] ძ | dj [d͡ʒ] ჯ | ||||
| aspirated | ʒ [t͡sʰ] ც | ç [t͡ʃʰ] ჩ | |||||
| ejective | ǯ [t͡sʼ] წ | č [t͡ʃʼ] ჭ | |||||
| Fricative | voiced | v [v] ვ | z [z] ზ | j [ʒ] ჟ | ɣ [ɣ] ღ | ||
| voiceless | s [s] ს | ş [ʃ] შ | x [x] ხ | h [h] ჰ | |||
| Trill | r [r] რ | ||||||
| Approximant | l [l] ლ | y [j] ჲ | |||||
Phonetic processes
Vowel reduction
Certain pairs of vowels reduce to single vowels:[clarification needed]
- ae and ai → ee → e
- ao, oa and oo → aa → a
- ou → uu → u
In Zugdidi-Samurzaqano dialect the vowels i and u also often reduce to ə.
Pre-consonant change of velar g
Before consonants, g → r.
Positional change of uvular q' sound
In word-initial prevocalic and intervocalic positions, q' → ʔ. Before the consonant v, q' → ɣ/ǩ.
Regressive assimilation of consonants
The common types are:
- voicing/devoicing of voiceless/voiced consonants before voiced/voiceless ones (respectively).
- glottalization of consonants before the glottalized ones and the glottal stop.
Progressive dissimilation
If the stem contains r then the suffixes -ar and -ur transform to -al and -ul, e.g. xorga (Gaghma Pirveli Khorga, the village)→ xorg-ul-i ("Khorgan"). The rule is not valid if in the stem with r an l appears later, e.g. marṫvili ("Martvili", the town) dj marṫvil-ur-i (adj. "Martvilian")
In a stem with voiceless affricates or voiceless sibilants, a later ǯ is deaffricated to d, e.g. orcxondji dj orcxondi "comb", ç̌andji dj ç̌andi "fly (insect)", isindji dj isindi "arrow", etc.
The transformation of l
- in all dialects of Mingrelian, before consonants l → r.
- in the Martvili subdialect in word-initial prevocalic position, l → y → ∅ and in intervocalic position l → ∅ [further explanation needed]
Intervocalic deletion of v
Between the vowels the organic[clarification needed] v disappears, e.g. xvavi (Geo. "abundance, plenty") → *xvai → xvee (id.), mṭevani (Geo. "raceme") → ţiani (id.), etc.
Phonetic augmentation n
Before the stops and affricates, an inorganic[clarification needed] augmentation n may appear (before labials n → m).
Mingrelian orthography
Mingrelian is written in the Georgian Mkhedruli script. The spelling using the Mkhedruli script uses symbols not used in Georgian : ⟨ჲ ჷ ჸ⟩ to represent /j ə ʔ/, respectively. The Mkhedruli script was used in Mingrelian publications from 1866 to 1906, from 1930 to 1939, in 1966, and has been used from 1995 on.
One book in Mingrelian was printed in the Cyrillic script in 1899 using the alphabet shown below. Slightly different Cyrillic orthographies were used in several printed texts from 1887 to 1903. The 1887 version had several Cyrillic letters in unusual phonetic values: я [dz], ѣ [h].
The Latin script column shows romanizations used by linguists.
| Mkhedruli | Mingrelian Latin | Mingrelian Cyrillic | IPA transcription |
|---|---|---|---|
| ა | a | а | ɑ |
| ბ | b | б | b |
| გ | g | г | ɡ |
| დ | d | д | d |
| ე | e | е | ɛ |
| ვ | v | в | v |
| ზ | z | з | z |
| თ | t | ꚋ | t |
| ი | i | і | i |
| კ | ǩ | к | kʼ |
| ლ | l | л | l |
| მ | m | м | m |
| ნ | n | н | n |
| ჲ | y | ј | j |
| ო | o | о | ɔ |
| პ | p̌ | п | pʼ |
| ჟ | zh | ж | ʒ |
| რ | r | р | r |
| ს | s | с | s |
| ტ | ṫ | т | tʼ |
| უ | u | у | u |
| ჷ | ƨ | ѵ | ə |
| ფ | p | ҧ | p |
| ქ | k | ӄ | k |
| ღ | ǧ | ҕ | ɣ |
| ყ | q̌ | k | qʼ |
| ჸ | ɔ | ɣ | ʔ |
| შ | ş / sh | ш | ʃ |
| ჩ | ç / ch | ч | t͡ʃ |
| ც | ʒ / ts | ц | t͡s |
| ძ | dz | ӡ | d͡z |
| წ | ǯ / tz | ҵ | t͡sʼ |
| ჭ | ç̌ | ꚓ | t͡ʃʼ |
| ხ | x | х | x |
| ჯ | dj | џ | d͡ʒ |
| ჰ | h | һ | h |
Grammar
Dialects
The main dialects and subdialects of Mingrelian are:
- Zugdidi-Samurzakano or Northwest dialect
- Jvari
- Senaki-poti or Southeast dialect
- Martvili-Bandza
- Abasha
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination | მარგალური edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia |
Famous speakers
- Lavrenti Beria, Soviet leader Joseph Stalin's chief of secret police
- Konstantine Gamsakhurdia, one of the most influential Georgian writers of the 20th century
- Zviad Gamsakhurdia, first president of post-Soviet Georgia
- Antisa Khvichava, claimed world's oldest person (purportedly 132 years old at the time of her death in 2012).[7]
- Khvicha Kvaratskhelia, Georgian footballer
- Ilia Topuria, Spanish and Georgian mixed martial artist
References
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds (2017). "Mingrelian". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. http://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/ming1252.
- ↑ "UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger". http://www.unesco.org/culture/languages-atlas/en/atlasmap/language-id-1057.html.
- ↑ "Georgia". First paragraph, third sentence. https://2009-2017.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/5253.htm. "The United States supports Georgia’s sovereignty and territorial integrity within its internationally recognized borders, and does not recognize the Abkhazia and South Ossetia regions of Georgia, currently occupied by Russia, as independent."
- ↑ Schulze, Wolfgang (2009). "Languages in the Caucasus". http://wschulze.userweb.mwn.de/lgxcauc.pdf.
- ↑ "K2olxuri Ena (Colchian Language)" (DOC). http://www.icgl.org/articles/ReviewofColchian.doc.
- ↑ "იეჰოვაშ მოწმეეფიშ გიშაშკუმალირი ბიბლიური წიგნეფი დო ჟურნალეფი". https://www.jw.org/xmf/%E1%83%9E%E1%83%A3%E1%83%91%E1%83%9A%E1%83%98%E1%83%99%E1%83%90%E1%83%AA%E1%83%98%E1%83%94%E1%83%A4%E1%83%98/.
- ↑ Dzhindzhikhashvili, Misha (8 July 2010). "Georgia Claims it Has World's Oldest Person, 130". Yahoo! News. Associated Press. https://news.yahoo.com/s/ap/20100708/ap_on_re_eu/eu_georgia_oldest_person.
Further reading
- Amirejibi, Rusudan (2006). Kʻolkhuri (Megrul-Lazuri) Ena. Gamomcʻemloba "Universali". ISBN 99940-61-43-7. https://www.tsu.ge/data/image_db_innova/Kolxuri_GEO.pdf.
- Beridze, Shalva (1920). Megruli (Iveriuli) Ena.
- Broers, Laurence (2012). "'Two Sons of One Mother'. Nested Identities and Centre-Periphery Politics in Post-Soviet Georgia". When the Elephant Broke Out of the Zoo. A Festschrift for Donald Rayfield. Stanford Slavic Studies. 39. ISBN 9781572010888.
- Kʻajaia, Otʻar (2001–2002). Megrul-kʻartʻuli lekʻsikoni. Gamomcʻemloba "Nekeri", Tʻbilisi. OCLC 50676816.
- Kipshidze, Ioseb (1914). Grammatika mingrelʹskogo (iverskogo) i͡azyka. https://archive.org/details/GrammatikaMingrelskogoiverskogoJazyka.
- Kʻobalia, Alio; Čʻuxua, Merab; Kʻobalia, Nana (2010). Megruli Leksikʻoni. Gamomcʻemloba Artanuji. ISBN 9789941421143.
- Tsargareli, Aleksandre (1880). Megrelʹskie ėti͡udy, Analiz fonetiki megrelʹskogo i͡azyka.
External links
- TITUS Caucasica: Megrelisch (in German)
- Otar Kajaia's Megrelian-Georgian dictionary at TITUS.
- Megrelian Project at Lund University, Sweden
- Article on the situation in 2017 from OpenDemocracy
- Rusudan Gersamia's and Irina Lobzhanidze's Megrelian Online Converter at CML, Georgia
Template:Languages of Georgia (country)
Template:Georgia (country) topics
 |