Social:Knowledge transfer

Knowledge transfer refers to transferring an awareness of facts or practical skills from one entity to another.[1] The particular profile of transfer processes activated for a given situation depends on (a) the type of knowledge to be transferred and how it is represented (the source and recipient relationship with this knowledge) and (b) the processing demands of the transfer task.[2] From this perspective, knowledge transfer in humans encompasses expertise from different disciplines: psychology, cognitive anthropology, anthropology of knowledge, communication studies and media ecology.[3][4]
Overview
Because of the rapid development of strategies for promoting wider information use during the "information age", a family of terms – knowledge transfer, learning, transfer of learning, and knowledge sharing – are often used interchangeably or as synonyms. While the concepts of knowledge transfer, learning, and transfer of learning are defined in closely related terms, they are different notions. According to conventional usage in psychology, Transfer of Learning occurs in people when they apply already learned information, strategies, and skills to a new situation or context. Another concept of learning is attributed to all animals and even certain plants.[5] Learning in humans starts before birth.[6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14] According to cognitive psychology, learning begins from unaware[15] and, even before birth during pregnancy,[16] from non-perceptual processes of distinguishing sensory stimuli.[17][18][19][20] In contrast to both above, knowledge transfer is a process in humans that requires intention from both sides: to share facts or skills from one side and acquire new knowledge from another (see the definition of knowledge transfer).[21]
The most significant difficulties exist with separating the terms knowledge transfer and knowledge sharing. According to Paulin and Suneson (2012), their distinction is based on different representations of the relationship between knowledge and its context by different authors.[22] Scientists who use the term knowledge transfer intend knowledge as an object without regard to the context; they amplify the enablers, suppress disabling conditions, and overcome obstacles, including the barriers, if they want to create good conditions for knowledge flow.[22] Scholars who believe that knowledge is something that is constructed in a social context and which cannot be separated from the context (or the individual) use knowledge sharing and focus more on the development of "space" or "environment" to better fit individuals who need to develop personal knowledge with the help of those who have already developed it.[22] Another approach suggests that knowledge sharing is a subset of knowledge transfer.[23] Knowledge sharing refers to a linear (unidirectional) process using a personalization strategy.[23] Knowledge transfer is a non-linear (bidirectional) process that may also proceed unidirectionally (as those linear in Knowledge sharing). According to Tangaraja and colleagues (2016), the essential peculiarity of knowledge transfer is that it is distinguished by the strategy used.[23] Indeed, the meaning of the word transfer implies the aim since the dictionary defines it as the process "to move someone or something from one place, vehicle, person, or group to another".[24] In contrast, sharing refers to "having or using something simultaneously as someone else" without targeting.[25]
The brief overview of related fields of knowledge introduces the main concepts that scholars consider when studying the current topic.
In cognitive anthropology, scholars tend to study patterns of shared knowledge. Cognitive anthropology is concerned with what people from different groups know and how that implicit knowledge changes how people perceive and relate to the world around them.[26] This discipline attempts to understand the impact of culture on developing the cognitive schema – a culturally specific mental structure responsible for an active organization of past experiences, implying activation of the whole.[27][28] Cognitive anthropologists strive to identify and systematize certain essential aspects of culture to understand how these peculiarities affect knowledge transfer.[29] Because the cognitive schemas on the same issue may differ in different cultures, the particularities of knowledge transfer in different environments are essential.
In psychology, knowledge transfer is also based on the notion of cognitive schema and involves essential processes of Assimilation and Accommodation.[30] Assimilation refers to an interpretation of new information within the framework of existing cognitive schema. It is the reuse of existing schemata to fit the new information.[30] Accommodation refers to making minor changes to acquired knowledge to create a new schema for that knowledge to cope with things that do not fit existing schemas.[30] In terms of psychology, knowledge transfer relates to the transformability of the transferred knowledge for assimilating by existing cognitive schemas and the translatability of the source practice for creating the new cognitive schema in the accommodation.[1]
In communication studies, basic concepts like "sender", "receiver", "message", "channel", "signal", "encoding", "decoding", "noise", "feedback", and "context", appear in different models, which are classified in many ways. Models of communication adhere to the main properties of any model: Mapping (emulating something existing in objective reality); Reduction (including only attributes that appear relevant to the model's creator or user); Pragmatism (not relating unambiguously to its original).[31] Communication studies recognize two main categories of models for describing knowledge transfer.[32] The linear direction category presents a unidirectional process in which messages flow from the communicator to the audience.[32] Conversely, the non-linear category is multi-directional: messages are sent back and forth between participants.[32]
In organizational theory, knowledge transfer is the practical problem of transferring knowledge from one part of the organization to another. Like knowledge management, knowledge transfer seeks to organize, create, capture or distribute knowledge and ensure its availability for future users. It is considered to be more than just a communication problem. If it were merely that, then a memorandum, an e-mail or a meeting would accomplish the knowledge transfer. Knowledge transfer is more complex because:
- knowledge resides in organizational members, tools, tasks, and their subnetworks[33] and
- much knowledge in organizations is tacit or hard to articulate.[34]
The subject has been taken up under the title of knowledge management since the 1990s. The term has also been applied to the transfer of knowledge at the international level.[35][36]
In business, knowledge transfer now has become a common topic in mergers and acquisitions.[37] It focuses on transferring technological platforms, market experience, managerial expertise, corporate culture, and other intellectual capital that can improve the companies' competence.[38] Since technical skills and knowledge are very important assets for firms' competence in the global competition,[39] unsuccessful knowledge transfer can have a negative impact on corporations and lead to expensive and time-consuming M&A not creating values to the firms.[40]
History
Knowledge transfer between humans is a practice that likely dates back to the "Great Leap Forward" in behavioral modernity about 80,000 years ago, with the origin of speech initiating as far back as 100,000 BCE.[41] Many scholars agree that modern human behavior can be characterized by abstract thinking, planning depth, symbolic behavior (e.g., art, ornamentation), music and dance, exploitation of large game, and blade technology, among others – "a set of traits that have come to be accepted as indicators of behavioral modernity"[42][43]
The scientific study of knowledge transfer began in the first half of the twentieth century, focusing mainly on innovation adoption by individuals.[44] In 1943, Ryan and Gross (1943) recognized the diffusion of innovation as an essential social process where interpersonal contact may play a pivotal role.[45]
The period since 1945 has been characterized as the information age that increased motivation to develop strategies for promoting its wider use.[44] After the Second War, three principal demands encouraged academic research on the topic: (a) a desire for rapid technological change to stimulate more significant economic growth; (b) a desire to enhance the transfer of technology emerging from defence and space-related research; and (c) a desire to promote the adoption of innovations in health, education, and human services.[44] Numerous research studies tested different strategies of knowledge distribution: print materials, films, videotapes, audiocassettes, consultation, organization development, technical assistance, network arrangements, training conferences and workshops, and participant observation.[44] In 1991, Backer (1991) proposed six crucial points for knowledge utilization:
- Interpersonal contact: To get an innovation used in new settings, there needs to be direct, personal contact between the source and recipient;[44]
- Planning and conceptual foresight: a thought-out plan for how the innovation will be adopted in a new setting;[44]
- Outside consultation on the change process;[44]
- User-oriented transformation of information: what is known about an innovation needs to be translated to the recipient;[44]
- Individual and organizational championship: influential staff members and organizational leaders express enthusiasm for its adoption;[44]
- Potential user involvement: everyone who will have to live with the results of an organizational change needs to be involved in planning for innovation adoption.[44]
During the first years after its reemergence, the notion of Knowledge transfer was usually treated in line with the notion of the knowledge-based theory of the firm.[46][47] One of the most commonly cited authors here was Szulanski, who in numerous books and articles had developed the notion of knowledge transfer, especially regarding intra-firm knowledge. His early work clearly stated that knowledge is regarded as a firm's stock.[48] Szulanski's doctoral dissertation ("Exploring internal stickiness: Impediments to the transfer of best practice within the firm") proposed that knowledge transfer within a firm is inhibited by factors other than a lack of incentive. How well knowledge about best practices remains broadly accessible within a firm depends upon the nature of that knowledge, from where (or whom) it comes, who gets it, and the organizational context within which any transfer occurs. "Stickiness" is a metaphor that comes from the difficulty of circulating fluid around an oil refinery (including effects of the fluid's native viscosity). It is worth noting that his analysis does not apply to scientific theories, where a different set of dynamics and rewards apply.[48]
Argote and Ingram (2000) defined knowledge transfer as "the process through which one unit (e.g., group, department, or division) is affected by the experience of another"[33] (p. 151). They further pointed out the transfer of organizational knowledge (i.e., routine or best practices) can be observed through changes in the knowledge or performance of recipient units. Even though the benefits of knowledge transfer are well known, the effectiveness of the process varies considerably.[33] The transfer of organizational knowledge, such as best practices, can be quite difficult to achieve.
Modern theories
Knowledge transfer can lead to a number of outcomes for organizations, including: greater decision making, improved customer relations,[49] innovation performance, financial performance, transfer effectiveness, transfer efficiency, patent, new product development, and technological leadership.[49][50] The growing body of literature shows two sets of research on knowledge transfer.[49] One set of studies focus on understanding the individual level and extending to group dynamics, e.g. aiming to better understand trust, respect, relationships, self-efficacy.[49] The second set of studies focus on the organizational level, e.g. discussing cultural aspects, structure, rewards and recognition, policy norms, training, relations.[49]
- Evolutionary theory of innovation: The theory concerns the external local network embeddedness, stating that subsidiaries' relational embeddedness with the external local network is essential for developing local innovations.[51] It highlights the role of previous reverse knowledge transfers in functional areas; the transformation of local into global innovations is more likely to happen due to these previous reverse knowledge transfers.[51] Reverse knowledge transfers indicate internal embeddedness, which is essential for transforming local innovation into global innovation. The theory argues that subsidiaries' relational embeddedness with the external local network is positively associated with local innovation.[51]
- Institutional theory: The theory argues that the benefits firms can derive from innovation offshoring depend on the institutional environment at home. It explores institutions that facilitate reverse knowledge transfer or institutional arbitrage with respect to innovation-related activities.[52]
- Internationalization theory: The theory concerns firm-level and country-level antecedents of R&D internationalization strategies (the knowledge flow between the foreign and home locations), focusing on differences between enterprises in emerging and advanced economies. It argues that Home-base-exploiting strategies are mostly driven by firm-level factors. Home-base-augmenting strategies are mostly driven by country-level factors.[53]
- Knowledge-based view of firm: This study investigates the role of a strong subsidiary leadership and entrepreneurial culture in the promotion of marketing knowledge inflows and their consequences on the subsidiary's ability to develop new products when moderated by the tacitness of knowledge.[54] It argues that subsidiaries' strong leadership support and entrepreneurial culture are fundamental mechanisms that foster marketing knowledge inflows from both the headquarters and peer subsidiaries. Moreover, marketing knowledge inflows enhance the focal subsidiary's innovation abilities. Tacit knowledge exerts contradictory moderating effects on the transfers of marketing knowledge, carrying distinct implications for a subsidiary's knowledge management.[54]
- Organization learning theory: The theory contributes to knowledge about the positive impact of knowledge inflows on the innovation of an organizational unit by studying the role of knowledge outflows during knowledge transfer.[55] This paper argues that knowledge outflows influence innovation through a self-learning mechanism and a fairness assessment mechanism and play a unique and important role in team innovation. A theoretical model examines the distinct and synergistic effects of total and balanced knowledge flows on employees' innovative behavior in an organizational unit.[55]
- Resource based view: This is the study on impact of managerial top-down knowledge transfer on a middle manager's individual ambidexterity and decision performance. Top-down managerial knowledge inflow benefits middle manager strategic decision making and short- and long-term performance.[56]
- Social capital theory: The study analyses the importance of different knowledge management practices to promote organizational innovation in multinational companies. It concerns the links among internationalization, reverse knowledge transfer, social capital, and organizational innovation.[57] Internalization does not directly affect organizational innovation but indirectly through the transfer of knowledge from external subsidiaries to headquarters. This knowledge and others from internal and external social capital are essential for developing innovations.[57]
- Social network theory: The theory combines research in international business with social theory, showing that subsidiaries that extensively draw on external knowledge sources are also more likely to generate knowledge outflows to local firms.[58] It argues that this may be explained by the subsidiaries' willingness to build the trust that facilitates the establishment of reciprocal knowledge linkages.[58]
- Upper echelon theory: The theory concerns antecedents of innovation performance for the subsidiaries of multinational enterprises (MNEs) using the microfoundations approach. The ability of foreign subsidiaries to generate innovation plays an increasingly important role in enhancing the performance of MNEs. The study suggests that the international experience of the top management team of a subsidiary and its CEO's industry experience positively affect subsidiary innovation.[59]
Three related concepts are "knowledge utilization", "research utilization" and "implementation", which are used in the health sciences to describe the process of bringing a new idea, practice or technology into consistent and appropriate use in a clinical setting.[60] The study of knowledge utilization/implementation (KU/I) is a direct outgrowth of the movement toward evidence-based medicine and research concluding that health care practices with demonstrated efficacy are not consistently used in practice settings.
Knowledge transfer within organisations and between nations also raises ethical considerations particularly where there is an imbalance in power relationships (e.g. employer and employee) or in the levels of relative need for knowledge resources (such as developed and developing worlds).[61]
Knowledge transfer includes, but encompasses more than, technology transfer.
Mechanisms
Message
Translation of knowledge implies the decontextualization and contextualization of knowledge which the entity possess in explicit and tacit forms (also see the Section "Overview"). Explicit knowledge is an awareness of facts or skills that can be readily articulated, conceptualized, codified, formalized, stored and accessed. Tacit knowledge can be defined as skills, ideas and experiences that are possessed by people but are not codified and may not necessarily be easily expressed.[62] According to Professor Nonaka (2009), the distinction between explicit and tacit knowledge suggests four basic patterns for translating knowledge where they interact in a spiral manner.[63]
- from tacit to tacit knowledge
- from tacit to explicit knowledge
- from explicit to explicit knowledge
- from explicit to tacit knowledge.[63]
The transfer of knowledge can be viewed as the transmission of a chain of small, interchangeable, semantic units. A Knowledge Transfer Unit was defined as the smallest amount of information that can be accurately communicated.[64]
Channels
Communication studies systematize our understanding of the communication process by introducing models of communication that describe different modalities of message exchange (see also the section "Overview"). In the case of explicit knowledge, all models are reduced to the simple scheme. A source (a sender in terms of communication studies) encodes information as a message and sends it to the recipient (a receiver) through a channel. The recipient needs to decode the message to understand the initial idea and provides some form of feedback. In both cases, the third player is the noise that may interfere and distort the message.[65] The two modes of knowledge transfer – the linear (a unidirectional process) and non-linear (a multi-directional) – encompass a set of different configurations of models.
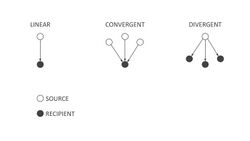
For instance, according to Sailer and colleagues (2021), based on the number of sources and recipients, all types of knowledge transfer can be reduced to 3 subtypes, namely: linear, divergent, and convergent. Linear knowledge transfer occurs when there is one source and one recipient (e.g. when one person explains a specific topic to someone else). Divergent knowledge transfer occurs when there is one source and multiple recipients (e.g. when a team leader outlines specific tasks for the team). Convergent knowledge transfer occurs when one recipient acquires information from different sources. A typical example of convergent knowledge transfer is when a patient receives information about a condition from several doctors. Convergent knowledge transfer is especially efficient in producing in-depth knowledge of a specific topic.[64]
A 2009 survey of MIT professors found the following channels for knowledge transfer in order of importance:[66]
- formal consulting;
- publications (journal and conference papers);
- hiring former students by industry;
- research collaboration;
- co-supervising students;
- patents and licenses;
- informal conversations;
- conference presentations.
The transfer of tacit knowledge has yet to be studied.
Procedure
Given the contributions of key theorists[1][44] (see the above sections), a guide to the knowledge transfer process may be generalized in the following translation procedure:
1) The first stage aims at establishing the transfer design considering multiple actors, their different interests, perceptions, and interpretations in shaping translations that the existing theory suggests:[1]
- Identifying the knowledge holders within the organization
- Motivating them to share
- Exploring and formulating the difference in the source and recipient contexts,[1] for designing (a) the similarity between the source and recipient (whether translation is possible or not), and (b) the SWOT analysis of the translation
- Understanding what is known about an innovation needs to be translated to the recipient to create User-oriented transformation of information[44]
- Decontextualizing the knowledge obtained from knowers[1]
- Contextualizing the transferring knowledge by translating an abstract representation into concrete materialized practices in the recipient context[1]
- Designing a sharing mechanism to facilitate the transfer by planning and conceptual foresight: a thought-out plan for how the innovation will be adopted in a new setting[44]
- Identifying influential staff members and organizational leaders in the recipient organization that express enthusiasm for the new knowledge adoption (individual and organizational championship)[44]
- Involving potential users: everyone who will have to live with the results of an organizational change needs to be involved in planning for innovation adoption[44]
2) The second stage forms the transfer design rules based on the activity in the first stage:[1]
- Establishing a direct, personal contact between the source and recipient[44]
- Identifying the best mode of translation from the range: the reproducing mode, the modifying mode, and the radical mode[1]
- Executing the transfer plan
3) The third stage aims at studying what a difference the translation makes:[1]
- Measuring to ensure the transfer
- Applying the knowledge transferred
- Monitoring and evaluating
Between public and private domains
With the move of advanced economies from a resource-based to a knowledge-based production,[67] many national governments have increasingly recognized "knowledge" and "innovation" as significant driving forces of economic growth, social development, and job creation. In this context the promotion of 'knowledge transfer' has increasingly become a subject of public and economic policy. However, the long list of changing global, national and regional government programmes indicates the tension between the need to conduct 'free' research – that is motivated by interest and by private sector 'short term' objectives – and research for public interests and general common good.[68]
The underlying assumption that there is a potential for increased collaboration between industry and universities is also underlined in much of the current innovation literature. In particular the Open Innovation approach to developing business value is explicitly based on an assumption that Universities are a "vital source for accessing external ideas". Moreover, Universities have been deemed to be "the great, largely unknown, and certainly underexploited, resource contributing to the creation of wealth and economic competitiveness."[69]
Universities and other public sector research organisations (PSROs) have accumulated much practical experience over the years in the transfer of knowledge across the divide between the domains of publicly produced knowledge and the private exploitation of it. Many colleges and PSROs have developed processes and policies to discover, protect and exploit intellectual property (IP) rights, and to ensure that IP is successfully transferred to private corporations, or vested in new companies formed for the purposes of exploitation. Routes to commercialization of IP produced by PSROs and colleges include licensing, joint venture, new company formation and royalty-based assignments.
Organisations such as AUTM in the US, the Institute of Knowledge Transfer in the UK, SNITTS in Sweden and the Association of European Science and Technology Transfer Professionals in Europe have provided a conduit for knowledge transfer professionals across the public and private sectors to identify best practice and develop effective tools and techniques for the management of PSRO/college produced IP. On-line communities of practice for knowledge transfer practitioners are also emerging to facilitate connectivity (such as The Global Innovation Network[70] and the knowledge Pool).
Business-University Collaboration was the subject of the Lambert Review in the UK in 2003.
Neuro-education seeks to improve quality of didactic methods and reduce the so called research practice gap.[71]
In the knowledge economy
With the production factors of the knowledge economy having broadly reshaped and supplanted those of prior economic models,[72] researchers have characterized the management and processing of organizational knowledge as vital to organizational success, with knowledge transfer in particular playing a key role in the practice of technology sharing, personnel transfers, and strategic integration.[73]
Knowledge transfer can also be achieved through investment programme, both intentionally and unintentionally in the form of skills, technology, and "tacit knowledge" including management and organisational practices. For example, foreign investment in African countries have shown to provide some knowledge transfer.[74]
As a competitive advantage in firm
Knowledge, and especially knowledge transfer, has emerged as a key resource in the post-industrial era.[75] This makes it an important resource for creating a sustainable competitive advantage. The resource-based view (RBV) emphasizes knowledge as a main source of competitive advantage. Knowledge transfer thus becomes a rare, valuable, imperfectly imitable and also non-substitutable strategic axis for organizations.[76] Moreover, according to the knowledge-based vision (KBV), the more knowledge an organization has, the more it will be able to learn new knowledge, so the competitive advantage based on knowledge will be sustainable over time.[77]
In organizations, knowledge is regularly passed on by employees to each other. Subsequently, organization resources are increased and/or updated, which allows employees to improve and adjust their practices.[76][78] The acquisition of skills by employees is closely linked to the organization's performance, which is mainly the result of the skills accumulated and put into practice by employees.[79]
One of the remarkable effects of knowledge transfer is the increase in profits and the development of competitive advantage. In a few words, a competitive advantage is the possibility for an organization to strengthen its core competencies by using knowledge from outside. For this, three elements have been defined to measure it:[76]
- Knowledge transfer contributes to the development of research and development capabilities;
- Knowledge transfer provides the opportunity to replace old technologies with new ones;
- Knowledge transfer contributes to reducing research and development time.
These three elements are possible when the organization possesses skills that are equal to or superior to those of its competitors, which allows it to gain a competitive advantage. In these situations, the transfer of knowledge acts on the evolution and in particular on the development of the basic knowledge already acquired by the organization. This acquisition manifests itself in the improvement of the organization's performance and therefore in the gain of a competitive advantage.[80]
In landscape ecology
By knowledge transfer in landscape ecology, means a group of activities that increase the understanding of landscape ecology with the goal of encouraging application of this knowledge. Five factors will influence knowledge transfer from the view of forest landscape ecology: the generation of research capacity, the potential for application, the users of the knowledge, the infrastructure capacity, and the process by which knowledge is transferred (Turner, 2006).
Platforms
A recent trend is the development of online platforms aiming to optimize knowledge transfer and collaboration.[81][82][83] Information technology (IT) systems are common computer platforms/systems that try to help organizations and people to share information and knowledge.[84] IT systems can store, share and collect knowledge that is important to the organization. In practice, the need for IT systems or knowledge management systems is often strategic.[85] Different knowledge management systems and platforms can provide big advantages for data systems looking to identify, transfer, share and display important metrics.[85] Different knowledge transfer platforms are tools to share knowledge faster and more efficiently. The main idea is to help people work productively with data and knowledge.
- Knowledge management systems (KMS) are computer-based systems designed to assist organizations with managing knowledge related actions. This usually involves for example: document administration, cooperation or social networking. Some of the most commonly used knowledge management systems are Microsoft SharePoint, Confluence and Documentum.[86][87]
- Learning management systems (LMS) are software applications, which aid with management, delivery and inspection of educational courses and training programs. They can be used in workplaces to back online or combined learning and trace learning outcomes. Among these systems are Blackboard or Moodle, although companies may use different systems such as Google Classroom, Second Life, Edmondo or others, if they are correctly adapted for the needs of the company.[88][89]
- Enterprise social networks (ESN) refer to specific social media platforms explicitly designed for usage within organizations. These platforms usually involve features such as instant, direct messaging and file sharing. ESNs are widely considered a form of knowledge management technology to gather their collective intelligence and improve productivity. Commonly used platforms are Microsoft Teams, Yammer or Slack.[90][91]
- Video conferencing tools have become increasingly popular as a tool to simplify knowledge transfer. The growth in popularity of video conferencing is mainly due to growing trend of remote work and online learning. The value of video conferencing for knowledge transfer comes from instantaneous communication, cooperation and feedback between team members. The usage of video conferencing tools is usually accompanied by the usage of other previously mentioned knowledge transfer platforms. Among these platforms belong Zoom, Microsoft Teams, Google Meet, Skype, Cisco Webex and others.[92][93]
- Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) platforms have been found to be effective due to their potential to create engaging experiences. These technologies allow real-world scenario simulations and interaction with digital objects. The engaging way in which these processes are conducted has been found to lead to improved work and learning outcomes. The usage of VR and AR is enabled by VR and AR headsets. Oculus Quest 2, Microsoft HoloLens, Google Glass and ZSpace are all among the examples for virtual and augmented reality headsets. These headsets run on various operating systems, some of which are specifically developed for the headsets, while others are modified versions of regular operating systems used by other smart devices.[94][95][96]
Challenges
Factors that complicate knowledge transfer include:
- The inability to recognize and articulate "compiled" or highly intuitive competencies – tacit knowledge idea[34]
- Different views on explicitness of knowledge[97]
- Geography or distance[98]
- Limitations of information and communication technologies (ICTs)[99]
- Lack of a shared/superordinate social identity[100]
- Language
- Areas of expertise
- Internal conflicts (for example, professional territoriality)
- Generational differences
- Union-management relations
- Incentives
- Problems with sharing beliefs, assumptions, heuristics and cultural norms.
- The use of visual representations to transfer knowledge (knowledge visualization)
- Previous exposure or experience with something
- Misconceptions
- Faulty information
- Organizational culture non-conducive to knowledge sharing (the "Knowledge is power" culture)
- Motivational issues, such as resistance to change and power struggles[101]
- Lack of trust
- Capabilities of the receptor to interpret and absorb knowledge[101]
- Context of the knowledge (tacit, context-specific knowledge)[101]
- Inability to detect the opportunity of knowledge sharing
Everett Rogers pioneered diffusion of innovations theory, presenting a research-based model for how and why individuals and social networks adopt new ideas, practices and products. In anthropology, the concept of diffusion also explores the spread of ideas among cultures.
Practices
- Mentorship
- Guided experience
- Simulation
- Guided experimentation
- Work shadowing
- Paired work
- Community of practice
- Narrative transfer
- Practices
Incorrect usage
Knowledge transfer is often used as a synonym for training. Furthermore, information should not be confused with knowledge, nor is it, strictly speaking, possible to "transfer" experiential knowledge to other people.[102] Information might be thought of as facts or understood data; however, knowledge has to do with flexible and adaptable skills – a person's unique ability to wield and apply information. This fluency of application is in part what differentiates information from knowledge. Knowledge tends to be both tacit and personal; the knowledge one person has is difficult to quantify, store, and retrieve for someone else to use.
Knowledge transfer (KT) and knowledge sharing (KS) are sometimes used interchangeably or are considered to share common features. Since some knowledge management researchers assume that these two concepts are rather similar and have overlapping content, there is often confusion, especially among researchers and practitioners, about what a certain concept means. For this reason, terms such as KS and KT get used incorrectly without any respect to their real meaning and these meanings can change from paper to paper.[23]
See also
- Communities of practice
- Customer knowledge
- Explicit knowledge
- Ignorance management
- Industrial knowledge theft
- Information society
- Institutional memory
- Instructional theory
- Knowledge management
- Knowledge tagging
- Knowledge translation
- Media richness theory
- Technology brokering
- Technology transfer
- Transfer of learning
- Value presentation
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 Kjell Arne Røvik (2016). "Knowledge Transfer as Translation: Review and Elements of an Instrumental Theory." International Journal of Management Reviews, Vol. 18, 290–310 (2016) DOI: 10.1111/ijmr.12097
- ↑ Timothy J. Nokes (2009). "Mechanisms of knowledge transfer," Thinking & Reasoning, 15:1, 1–36, DOI: 10.1080/13546780802490186
- ↑ Argote, Linda; Ingram, Paul (May 2000). "Knowledge Transfer: A Basis for Competitive Advantage in Firms". Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 82 (1): 150–169. doi:10.1006/obhd.2000.2893. ISSN 0749-5978. https://doi.org/10.1006/obhd.2000.2893.
- ↑ Szulanski, Gabriel (May 2000). "The Process of Knowledge Transfer: A Diachronic Analysis of Stickiness". Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 82 (1): 9–27. doi:10.1006/obhd.2000.2884. ISSN 0749-5978. https://doi.org/10.1006/obhd.2000.2884.
- ↑ Karban, R. (2015). "Plant Learning and Memory." In: Plant Sensing and Communication. Chicago and London: The University of Chicago Press, pp. 31–44, [1] Archived 2022-12-31 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ OECD (2007). Understanding the Brain: The Birth of a Learning Science. OECD Publishing. p. 165. ISBN 978-92-64-02913-2.
- ↑ Chapter 2: The Montessori philosophy. From Lillard, P. P. Lillard (1972). Montessori: A Modern Approach. Schocken Books, New York.
- ↑ Castiello, U.; Becchio, C.; Zoia, S.; Nelini, C.; Sartori, L.; Blason, L.; D'Ottavio, G.; Bulgheroni, M.; Gallese, V. (2010). "Wired to be social: the ontogeny of human interaction." PloS one, 5(10), p.e13199.
- ↑ Kisilevsky, B.C. (2016). "Fetal Auditory Processing: Implications for Language Development? Fetal Development." Research on Brain and Behavior, Environmental In uences, and Emerging Technologies,: 133–152.
- ↑ Lee, G.Y.C.; Kisilevsky, B.S. (2014). "Fetuses respond to father's voice but prefer mother's voice after birth." Developmental Psychobiology, 56: 1–11.
- ↑ Hepper, P.G.; Scott, D.; Shahidullah, S. (1993). "Newborn and fetal response to maternal voice." Journal of Reproductive and Infant Psychology, 11: 147–153.
- ↑ Lecanuet, J.P.; Granier‐Deferre, C.; Jacquet, A.Y.; Capponi, I.; Ledru, L. (1993). "Prenatal discrimination of a male and a female voice uttering the same sentence." Early development and parenting, 2(4): 217–228.
- ↑ Hepper P. (2015). "Behavior during the prenatal period: Adaptive for development and survival." Child Development Perspectives, 9(1): 38–43. DOI: 10.1111/cdep.12104.
- ↑ Jardri, R.; Houfflin-Debarge, V.; Delion, P.; Pruvo, J-P.; Thomas, P.; Pins, D. (2012). "Assessing fetal response to maternal speech using a noninvasive functional brain imaging technique." International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience, 2012, 30: 159–161. doi:10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2011.11.002.
- ↑ Tomasello, M. (2019). Becoming human: A theory of ontogeny. Cambridge, Massachusetts, US: Harvard University Press.
- ↑ Val Danilov I (2024). "Child Cognitive Development with the Maternal Heartbeat: A Mother-Fetus Neurocognitive Model and Architecture for Bioengineering Systems". In: Ben Ahmed M, Boudhir AA, Abd Elhamid Attia HF, Eštoková A, Zelenáková M (eds) Information Systems and Technological Advances for Sustainable Development. DATA 2024. Lecture Notes in Information Systems and Organisation, vol 71. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-75329-9_24
- ↑ Val Danilov, I. (2024). "Shared Intentionality Before Birth: Emulating a Model of Mother-Fetus Communication for Developing Human-Machine Systems." In: Arai, K. (eds) Intelligent Systems and Applications. IntelliSys 2023. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 824. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-47715-7_5
- ↑ Val Danilov, Igor (2023-02-17). "Theoretical Grounds of Shared Intentionality for Neuroscience in Developing Bioengineering Systems". OBM Neurobiology 7 (1): 156. doi:10.21926/obm.neurobiol.2301156. https://www.lidsen.com/journals/neurobiology/neurobiology-07-01-156.
- ↑ Val Danilov, Igor (2023). "Shared Intentionality Modulation at the Cell Level: Low-Frequency Oscillations for Temporal Coordination in Bioengineering Systems". OBM Neurobiology 7 (4): 1–17. doi:10.21926/obm.neurobiol.2304185. https://www.lidsen.com/journals/neurobiology/neurobiology-07-04-185.
- ↑ Val Danilov I. (2023). "Low-Frequency Oscillations for Nonlocal Neuronal Coupling in Shared Intentionality Before and After Birth: Toward the Origin of Perception." OBM Neurobiology 2023; 7(4): 192; doi:10.21926/obm.neurobiol.2304192.https://www.lidsen.com/journals/neurobiology/neurobiology-07-04-192
- ↑ Nonaka, Ikujiro; Takeuchi, Hirotaka (1995-05-18). The Knowledge-Creating Company. Oxford University PressNew York, NY. ISBN 978-0-19-509269-1. https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780195092691.001.0001.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 Paulin, D., & Suneson, K. (2012). "Knowledge transfer, knowledge sharing and knowledge barriers–three blurry terms in KM." Electronic Journal of Knowledge Management, 10(1), pp82-92. Available online.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 23.3 Tangaraja, G., Mohd Rasdi, R., Abu Samah, B. & Ismail, M. (20 April 2016). "Knowledge sharing is knowledge transfer: a misconception in the literature". Journal of Knowledge Management 20 (4): 653–670. doi:10.1108/jkm-11-2015-0427. ProQuest 1826809483. http://psasir.upm.edu.my/id/eprint/54677/1/Knowledge%20sharing%20is%20knowledge%20transfer.pdf. Retrieved 20 December 2019.
- ↑ Cambridge dictionary. "Knowledge transfer". Retrieved 2 February 2024. https://dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/knowledge-transfer
- ↑ Cambridge dictionary. "Sharing". Retrieved 2 February 2024. https://dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/share?q=sharing
- ↑ D'Andrade, Roy (1995). The Development of Cognitive Anthropology, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- ↑ Schacter, D. L., & Kihlstrom, J. F. (1989). "Functional amnesia." Handbook of neuropsychology, 3, 209–231.
- ↑ Kamppinen, M. (1993). "Cognitive schemata." In Consciousness, Cognitive Schemata, and Relativism: Multidisciplinary Explorations in Cognitive Science (pp. 133–168). Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands.
- ↑ Tyler, Stephen A. (1969). Cognitive anthropology : readings. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston. ISBN 0-03-073255-7. OCLC 22714.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 30.2 Piaget, Jean. 1963. The Origins of Intelligence in Children. Translated by M. Cook. New York: Norton.
- ↑ Herbert Stachowiak (1973). Allgemeine Modelltheorie, S. 131–133. The Internet Archive, retrieved 30 January 2024.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 Narula, Uma (2006). Handbook of Communication Models, Perspectives, Strategies. Atlantic Publishers & Dist. ISBN 9788126905133.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 33.2 Argote, L.; Ingram, P. (2000). "Knowledge transfer: A Basis for Competitive Advantage in Firms". Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 82 (1): 150–169. doi:10.1006/obhd.2000.2893.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 Nonaka, I.; Takeuchi, H. (1995). The Knowledge-Creating Company. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-509269-1. https://archive.org/details/knowledgecreatin00nona.
- ↑ "Languages create barrier in scientific knowledge transfer – The Economic Times". The Economic Times. 2016-12-30. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/science/languages-create-barrier-in-scientific-knowledge-transfer/articleshow/56258399.cms.
- ↑ "INTERNATIONAL KNOWLEDGE TRANSFER – Investigations of European Practices". https://ec.europa.eu/research/innovation-union/pdf/ikt_expert_report.pdf.
- ↑ Rosenkranz, Stephanie; Schmitz, Patrick W. (1999). "Know-how disclosure and incomplete contracts". Economics Letters 63 (2): 181–185. doi:10.1016/S0165-1765(99)00038-5. ISSN 0165-1765. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0165176599000385.
- ↑ Fong Boh, Wai; Nguyen, T.T.; Xu, Yun (2013-02-15). "Knowledge transfer across dissimilar cultures". Journal of Knowledge Management 17 (1): 29–46. doi:10.1108/13673271311300723. ISSN 1367-3270.
- ↑ Calipha, Rachel; Brock, David M.; Rosenfeld, Ahron; Dvir, Dov (2018-08-20). "Acquired, transferred and integrated knowledge: a study of M&A knowledge performance". Journal of Strategy and Management 11 (3): 282–305. doi:10.1108/jsma-07-2017-0049. ISSN 1755-425X.
- ↑ Ng, Artie W.; Chatzkel, Jay; Lau, K.F.; Macbeth, Douglas (2012-07-20). "Dynamics of Chinese emerging multinationals in cross-border mergers and acquisitions". Journal of Intellectual Capital 13 (3): 416–438. doi:10.1108/14691931211248963. ISSN 1469-1930.
- ↑ Miyagawa, Shigeru; Ojima, Shiro; Berwick, Robert C.; Okanoya, Kazuo (2014-06-09). "The integration hypothesis of human language evolution and the nature of contemporary languages". Frontiers in Psychology 5: 564. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00564. ISSN 1664-1078. PMID 24936195.
- ↑ Mcbrearty, Sally; Brooks, Alison S. (2000-11-01). "The revolution that wasn't: a new interpretation of the origin of modern human behavior". Journal of Human Evolution 39 (5): 453–563. doi:10.1006/jhev.2000.0435. ISSN 0047-2484. PMID 11102266. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0047248400904354. Retrieved 2022-11-21.
- ↑ Henshilwood, Christopher S.; Marean, Curtis W. (2003-12-01). "The Origin of Modern Human Behavior: Critique of the Models and Their Test Implications". Current Anthropology 44 (5): 627–651. doi:10.1086/377665. ISSN 0011-3204. PMID 14971366. https://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/10.1086/377665. Retrieved 2022-11-21.
- ↑ 44.00 44.01 44.02 44.03 44.04 44.05 44.06 44.07 44.08 44.09 44.10 44.11 44.12 44.13 44.14 44.15 Backer T.E. (1991) "Knowledge utilization. Knowledge: Creation, Diffusion, Utilization." Knowledge 12(3), 225–240.
- ↑ Ryan B. & Gross N. (1943). "The diffusion of hybrid corn seed in two Iowa communities." Rural Sociology 8(1), 15–24.
- ↑ Grant, R. M. (1996) "Toward a knowledge-based theory of the firm," Strategic Management Journal, Vol 17, pp 109–122.
- ↑ Kogut, B.; Zander, U. (1992) "Knowledge of the Firm, Combinative Capabilities, and the Replication of Technology," Organization Science, Vol 3, No. 3, pp 383–397
- ↑ 48.0 48.1 Szulanski, Gabriel (1996). "Exploring internal stickiness: Impediments to the transfer of best practice within the firm". Strategic Management Journal 17: 27–43. doi:10.1002/smj.4250171105.
- ↑ 49.0 49.1 49.2 49.3 49.4 Amitabh Anand, Birgit Muskat, Andrew Creed, Ambika Zutshi, Anik o Csepregi (2021). "Knowledge sharing, knowledge transfer and SMEs: evolution, antecedents, outcomes and directions." Personnel Review, Emerald Publishing Limited, 0048-3486 DOI: 10.1108/PR-05-2020-0372.
- ↑ Shiwangi Singh; Sanjay Dhir (2023). "Knowledge transfer and innovation in multinationals: a review of the literature using SCM-TBFO framework." An International Journal, Emerald Publishing Limited 1463–5771 DOI:10.1108/BIJ-07-2022-0485.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 51.2 Isaac, V. R., Borini, F. M., Raziq, M. M., & Benito, G. R. (2019). "From local to global innovation: The role of subsidiaries' external relational embeddedness in an emerging market." International Business Review, 28(4), 638–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibusrev.2018.12.009
- ↑ Rosenbusch, N., Gusenbauer, M., Hatak, I., Fink, M. and Meyer, K.E. (2019), "Innovation offshoring, institutional context and innovation performance: a meta-analysis," Journal of Management Studies, Vol. 56 No. 1, pp. 203–233. https://doi.org/10.1111/joms.12407
- ↑ Urbig, D., Procher, V.D., Steinberg, P.J. and Volkmann, C. (2022). "The role of firm-level and country- level antecedents in explaining emerging versus advanced economy multinationals' R&D internationalization strategies," International Business Review, Vol. 31 No. 3, 101954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibusrev.2021.101954
- ↑ 54.0 54.1 Crespo, C.F., Crespo, N.F. and Curado, C. (2022). "The effects of subsidiary's leadership and entrepreneurship on international marketing knowledge transfer and new product development" International Business Review, Vol. 31 No. 2, p. 101928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibusrev.2021.101928
- ↑ 55.0 55.1 Lai, J., Lui, S.S. and Tsang, E.W. (2016). "Intrafirm knowledge transfer and employee innovative behavior: the role of total and balanced knowledge flows," Journal of Product Innovation Management, Vol. 33 No. 1, pp. 90–103. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12262
- ↑ Torres, J.P., Drago, C. and Aqueveque, C. (2015) "Knowledge inflows effects on middle managers' ambidexterity and performance," Management Decision, Vol. 53 No. 10, pp. 2303–2320. https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-04-2015-0133
- ↑ 57.0 57.1 Jimenez-Jimenez, D., Martınez-Costa, M. and Sanz-Valle, R. (2014). "Knowledge management practices for innovation: a multinational corporation's perspective," Journal of Knowledge Management, Vol. 18 No. 5, pp. 905–918. https://doi.org/10.1108/JKM-06-2014-0242
- ↑ 58.0 58.1 Perri, A. and Andersson, U. (2014). "Knowledge outflows from foreign subsidiaries and the tension between knowledge creation and knowledge protection: evidence from the semiconductor industry," International Business Review, Vol. 23 No. 1, pp. 63–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibusrev.2013.08.007
- ↑ Nuruzzaman, N., Gaur, A.S. and Sambharya, R.B. (2019). "A microfoundations approach to studying innovation in multinational subsidiaries," Global Strategy Journal, Vol. 9 No. 1, pp. 92–116. https://doi.org/10.1002/gsj.1202
- ↑ Greenhalgh, T.; Robert, G.; Macfarlane, F.; Bate, P.; Kyriakidou, O. (2004). "Diffusion of innovations in service organizations: Systematic review and recommendations". Milbank Quarterly 82 (4): 581–629. doi:10.1111/j.0887-378x.2004.00325.x. PMID 15595944.
- ↑ Harman, C.; Brelade, S. (2003). "Doing the Right Thing in a Knowledge Transfer". Knowledge Management Review 6 (1): 28–31.
- ↑ Polanyi, Michael. 1966. The Tacit Dimension. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 4.
- ↑ 63.0 63.1 Nonaka, I. (2009). "The knowledge-creating company." In The economic impact of knowledge (pp. 175–187). Routledge.
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 Sailer, Martin H. M.; Georgiev, Yuriy; Mitov, Gergo; Guentchev, Marin (2021-12-18). "A memory-based structural model for knowledge management and transfer". Knowledge Management Research & Practice 20 (4): 654–660. doi:10.1080/14778238.2021.2015263. ISSN 1477-8238. https://doi.org/10.1080/14778238.2021.2015263.
- ↑ Ruben, Brent D. (2001). "Models Of Communication". In Schement, Jorge Reina (ed.). Encyclopedia of Communication and Information. Macmillan Reference USA. ISBN 9780028653860.
- ↑ Agrawal, A.; Henderson, R. (2009). Putting patents in context: Exploring knowledge transfer from MIT. 2009. Economic Institutions of Strategy Advances in Strategic Management. 26/13-37. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.48.1.44.14279 Retrieved 03.02.2024 https://dspace.mit.edu/bitstream/handle/1721.1/3957/IB_Putting+Patents.pdf?sequence=2
- ↑ OECD (1999), Managing national innovation systems, OECD publications service, Paris
- ↑ H.Rubin, Tzameret (2014). "The Achilles Heel of a Strong Private Knowledge Sector: Evidence from Israel". The Journal of Innovation Impact 7: 88–99. http://nimbusvault.net/publications/koala/inimpact/papers/inkt14-011.pdf. Retrieved 2016-12-23.
- ↑ Holland, G. (1999). "Foreword". in Gray, H.. University and the creation of wealth. Open University Press.
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ "The research-practice gap". Association for Computing Machinery – Advancing Computing as a Science & Profession. http://interactions.acm.org/archive/view/july-august-2010/the-research-practice-gap1.
- ↑ Drucker, Peter F. (Winter 1999). "Knowledge-worker productivity: the biggest challenge". California Management Review 41 (2): 79–84. doi:10.2307/41165987. http://genderi.org/pars_docs/refs/63/62938/62938.pdf. Retrieved 2021-07-16.
- ↑ Inkpen, Andrew C.; Dinur, Adva (1 Aug 1998). "Knowledge Management Processes and International Joint Ventures". Organization Science 9 (4): 454–468. doi:10.1287/orsc.9.4.454. https://pubsonline.informs.org/doi/abs/10.1287/orsc.9.4.454. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ↑ Calabrese, Linda. "Chinese investment and knowledge transfer in Africa". https://degrp.odi.org/publication/chinese-investment-and-knowledge-transfer-in-africa/.
- ↑ Jose Maria Corella; Isabel de Val Pardo (2001). Sistemas de Salud – Diagnostico y Planificacion
- ↑ 76.0 76.1 76.2 Shu-HsienLiao; Ta-Chien Hu (2007). "Knowledge transfer and competitive advantage on environmental uncertainty: An empirical study of the Taiwan semiconductor Industry" Elsevier
- ↑ H. Zack (1999). "Managing codified knowledge" Sloan Management Review (40) pp. 45–58 http://web.cba.neu.edu/~mzack/articles/kmarch/kmarch.htm
- ↑ Eva Maria Pertusa Ortega; Laura RiendaGarcia (2005). "Génération et transfert de connaissances par la structure organisationnelle" Cairn, La Revue des Sciences de Gestions, pp. 73–80 https://www.cairn.info/revue-des-sciences-de-gestion-2005-3-page-73.htm
- ↑ Lyles, Marjorie A.; Salk, Jane E. (1996). "Knowledge Acquisition from Foreign Parents in International Joint Ventures: An Empirical Examination in the Hungarian Context". Journal of International Business Studies 27 (5): 877–903. doi:10.1057/palgrave.jibs.8490155.
- ↑ Cohen, Wesley M.; Levinthal, Daniel A. (1990). "Absorptive Capacity: A New Perspective on Learning and Innovation". Administrative Science Quarterly 35 (1): 128–152. doi:10.2307/2393553.
- ↑ Schmidt, Danilo Marcello; Böttcher, Lena; Wilberg, Julian; Kammerl, Daniel; Lindemann, Udo (2016-01-01). "Modeling Transfer of Knowledge in an Online Platform of a Cluster". Procedia CIRP. 26th CIRP Design Conference 50: 348–353. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2016.05.036. ISSN 2212-8271.
- ↑ Birkenmeier, Beat; Ulmer, Dominik (August 2002). Development of a central Knowledge Transfer Platform in a highly decentralised environment. euroCRIS. ISBN 9783933146847. https://dspacecris.eurocris.org/handle/11366/140. Retrieved 2019-05-25.
- ↑ nczyzcpa (2013-09-29). "Lodz Knowledge Transfer Platform". https://ec.europa.eu/growth/tools-databases/regional-innovation-monitor/support-measure/lodz-knowledge-transfer-platform.
- ↑ Gurteen, David (February 1999). "Creating a Knowledge Sharing Culture". Knowledge Management Magazine 2 (5). http://www.providersedge.com/docs/km_articles/Creating_a_K-Sharing_Culture_-_Gurteen.pdf. Retrieved 2023-05-11.
- ↑ 85.0 85.1 Rothberg, Helen N.; Erickson, G. Scott (2017-02-13). "Big data systems: knowledge transfer or intelligence insights?". Journal of Knowledge Management 21 (1): 92–112. doi:10.1108/jkm-07-2015-0300. ISSN 1367-3270. http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/jkm-07-2015-0300.
- ↑ Yeo, R. K., & Ning, Y. (2019). Investigating the use of SharePoint as a knowledge management tool in Singapore government agencies. Journal of Librarianship and Information Science, 51(4), 1164–1174.
- ↑ Mamakou, X., & Skalkos, D. (2019). A comparative analysis of knowledge management systems: Documentum, SharePoint and Confluence. International Journal of Business and Economic Affairs, 4(3), 20–29.
- ↑ Elangovan, M., & Priya, R. (2021). An exploratory study of Blackboard and Moodle for online teaching and learning in higher education. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 18(1), 28. doi:10.1186/s41239-021-00274-7
- ↑ Pusiri, T., & Tongurai, C. (2021). Comparative study of blackboard and moodle for e-learning in higher education. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Education, 14(2), 61–69.
- ↑ Grajales III, F. J., Sheps, S., Ho, K., Novak-Lauscher, H., & Eysenbach, G. (2014). Social media: A review and tutorial of applications in medicine and health care. Journal of medical Internet research, 16(2), e13.
- ↑ Crampton, J. W. (2019, October 24). Yammer vs. Teams: What's the Difference? CMSWire.com. https://www.cmswire.com/digital-workplace/yammer-vs-teams-whats-the-difference/
- ↑ Ahmed, I. (2021). Videoconferencing in the time of COVID-19. Journal of Chemical Education, 98(5), 1261–1262.
- ↑ Nair, R., & Prakash, B. (2021). A Comparative Study of Zoom, Skype, Webex, Google Meet, and Microsoft Teams during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Educational Technology Systems, 49(1), 130–151. doi:10.1177/0047239520966713
- ↑ Díaz-González, L., Guerrero, L. A., Aedo, I., & García-Rodríguez, A. (2019). The potential of virtual reality and augmented reality for commercial training. IEEE Technology and Engineering Management Review, 7, 68–78.
- ↑ Honein-AbouHaidar, G. N., Nabhani-Gebara, S., & Vyas, A. (2019). A review of virtual, augmented, and mixed reality for public health. Frontiers in public health, 7, 194.
- ↑ Giannotti, V. A., Vasilakakos, T., Monaci, M., & Tsiailas, T. (2019). The use of virtual reality in anatomy teaching. Journal of education and health promotion, 8, 185.
- ↑ Dubickis, M.; Gaile-Sarkane, E. (2017). "Tacit vs Explicit Knowledge Dichotomy: State-of-the-Art Review for Technology Transfer Purposes". Financial Environment and Business Development. Eurasian Studies in Business and Economics. 4. pp. 423–433. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-39919-5_31. ISBN 978-3-319-39918-8.
- ↑ Galbraith, C. S. (1990). "Transferring core manufacturing technologies in high-technology firms". California Management Review 32 (4): 56–70. doi:10.2307/41166628.
- ↑ Roberts, Joanne (2000). "From Know-how to Show-how: Questioning the Role of Information and Communication Technologies in Knowledge Transfer". Technology Analysis & Strategic Management 12 (4): 429–443. doi:10.1080/713698499.
- ↑ Kane, A. A.; Argote, L.; Levine, J. (2005). "Knowledge transfer between groups via personnel rotation: Effects of social identity and knowledge quality". Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 96 (1): 56–71. doi:10.1016/j.obhdp.2004.09.002.
- ↑ 101.0 101.1 101.2 Nieves, Julia; Osorio, Javier (2013). "The role of social networks in knowledge creation". Knowledge Management Research & Practice 11 (1): 62–77. doi:10.1057/kmrp.2012.28. ISSN 1477-8238.
- ↑ Stake, Robert E. (2005). "Qualitative Case Studies". in Denzin, Norman K.. The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Research. Thousand Oaks: Sage. pp. 456.
Further reading
- Fan, Y (1998). "The Transfer of Western Management to China: Context, Content and Constraints". Management Learning 29 (2): 201–221. doi:10.1177/1350507698292005. http://bura.brunel.ac.uk/handle/2438/1305.
- Argote, L. et al. (2000). "Knowledge Transfer in Organizations: Learning from the Experience of Others", Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 82(1) (May): 1–8
- Castells, M. (1996). Conclusion, The Rise of the Network Society. The Information Age: Economy, Society & Culture, Volume 1. (pp. 469–478). Oxford: Blackwell
- Leonard, D.; and Swap, W. (2005) Deep Smarts: How to cultivate and transfer enduring business wisdom, HBSP. ISBN 1-59139-528-3
- Lipphardt, Veronika / Ludwig, David: Knowledge Transfer and Science Transfer, European History Online, Mainz: Institute of European History, 2011, retrieved: January 11, 2012
- Shaw, M. (2001). "Integrating Learning Technologies: The social-cultural, pragmatic and technology design contexts", Teaching and Learning with Technology, (6)
- Trautman, Steve (2006). "Teach What You Know: A Practical Leader's Guide to Knowledge Transfer" , Addison-Wesley
- Davenport, Thomas H.; and Prusak, Laurence (2000). Working Knowledge: How Organizations Manage What They Know, Boston Massachusetts, Harvard Business School Press
- Turner, (2006). Knowledge Transfer in Forest Landscape Ecology: A Primer. In: Forest landscape ecology, transferring knowledge to practice. Perera. A.H., Buse, L.J. and Crow, T.R. (Eds), New York, Springer, 1–2.
External links
- Project of knowledge transfer of the CIPRA "Future in the Alps"
- "Knowledge Transfer Study – 2 Year study project for the European Commission"
- Learn MERN and improve your Knowledge"
 |
