Social:Luilang language
| Luilang | |
|---|---|
| Ketagalan | |
| Native to | Taiwan |
| Region | Banqiao area, New Taipei City |
| Ethnicity | Ketagalan |
| Extinct | mid-20th century[1] |
Austronesian
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | kae |
kae.html | |
| Glottolog | keta1243[2] |
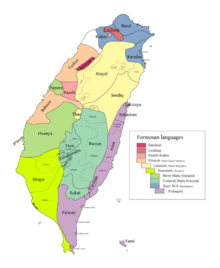 Luilang is the northernmost of the four red areas in the map. | |
Luilang, or ambiguously Ketagalan (Ketangalan, Tangalan; Chinese: 凱達格蘭語; pinyin: Kǎidágélányǔ), was a Formosan language spoken south of modern-day Taipei in northern Taiwan by one of several peoples that have been called Ketagalan. The language probably went extinct in the mid-20th century and it is very poorly attested.
Location
According to oral tradition, the Luilang people originally inhabited four villages near Taipei: Luili (雷里, Leili), Siulang (秀朗, Xiulang), Bulisiat (務裡薛, Wulixue) and Liau-a (了阿, Liao'a). These merged under the combined name Luilang (雷朗, Leilang), and later migrated to their current location in Outer Oat-a (外挖仔庄, Waiwazizhuang) in the 18th century.[3]
Name
The name 'Ketagalan' is used by Ethnologue and Glottolog for the Luilang language. However, that name is ambiguous, originally referring to all of plains tribes of northern Taiwan. There has been argument in the literature as to whether it is better applied to Luilang, to the south and west of Taipei, or to Basay, to the east. 'Luilang' is an ancestral village name, and so unambiguous for the language southwest of Taipei, whereas 'Basay' is the endonym of the language to the east, and also unambiguous.[3]
Numerals
The numerals of Luilang are rather divergent. For instance, the Basay language has numerals 5–10 that are cognate with Proto-Malayo-Polynesian, which Luilang does not. Forms recorded by Guérin (using French transcription), Ino (using Japanese transcription) and Ogawa are:[4][5]
| source | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xiulang? (Guérin 1868) | saka | tsusa | toulou | souvad | laleup | tsouloup | patsouo-ana | patouloun | sateuna | isit |
| Xiulang (Ino 1896) | saka | tsusa | tooru | sma | naru | tsuro | yinai | tonai | satoronai | |
| Xiulang (Ino 1897) | saka | tsusa | tooru | seva | rārup | tserup | senai | patoorunai | satoorunai | irip |
| Luilang (Ogawa 1944) | sa(ka) | tsusa | tuḷu | suva | (na)lup | (na)tsulup | innai | patulunai | satulunai | isit |
| Ketangalan[6] | tsa | Lusa | tsʰu: | špat | tsima | anum | pitu | watsu | siwa | Labatan |
Notes
- ↑ Luilang at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds (2017). "Ketangalan". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. http://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/keta1243.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Tsuchida, Shigeru. 1985. Kulon: Yet another Austronesian language in Taiwan?. Bulletin of the Institute of Ethnology, Academia Sinica 60. 1-59.
- ↑ Laurent Sagart (2004) The Higher Phylogeny of Austronesian and the Position of Tai-Kadai
- ↑ Li, Jen-kuei and Masayuki Toyoshima (eds). 2006. comparative vocabulary of Formosan languages and dialects, by Naoyoshi Ogawa. Asian and African lexicon series 49. Institute for Languages and cultures of Asia and Africa, Tokyo University of Foreign Studies.
- ↑ "The Numbers List". https://www.zompist.com/numbers.shtml.
References
- Li, Paul Jen-kuei (1992). "Táiwān píngpǔzú de zhǒnglèi jíqí xiānghù guānxì 台灣平埔族的種類及其相互關係". in Li, Paul Jen-kuei (in zh). Selected Papers on Formosan Languages. 2. Taipei: Institute of Linguistics, Academia Sinica.
- Inō, Kanori 伊能嘉矩 (2012) (in zh). Píngpǔzú diàochá lǚxíng: Yīnéng jiājǔ "Táiwān tōngxìn" xuǎnjí. Taibei Shi: Yuanliu. ISBN 9789573268932.
 |
