Social:Naukan Yupik language
| Naukan Yupik | |
|---|---|
| Нывуӄаӷмистун Nuvuqaghmiistun | |
| Native to | Russia |
| Region | Bering Strait region (or Chukchi Peninsula) |
| Ethnicity | 450 Naukan people (2010)[1] |
Native speakers | 60, 13% of ethnic population (2010)[2] |
Eskimo–Aleut
| |
Early forms | Proto-Eskimo–Aleut
|
| Cyrillic | |
| Official status | |
Official language in |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | ynk |
| Glottolog | nauk1242[3] |
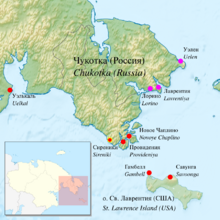 Naukan Yupik settlements (magenta dots) | |
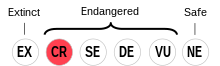 East Cape Yupik is classified as Critically Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger | |
Naukan Yupik language[4] or Naukan Siberian Yupik language (Naukan Yupik: Нывуӄаӷмистун; Nuvuqaghmiistun) is a critically endangered Eskimo language spoken by c. 70 Naukan persons (нывуӄаӷмит) on the Chukotka peninsula. It is one of the four Yupik languages, along with Central Siberian Yupik, Central Alaskan Yup'ik and Pacific Gulf Yupik.
Linguistically, it is intermediate between Central Siberian Yupik and Central Alaskan Yup'ik.[5]
Morphology
Chart example of the oblique case:
| Case | singular | dual | plural |
|---|---|---|---|
| Locative | mi | ˠni | ni |
| Abl. / Instr. | məˠ | ˠnəˠ | nəˠ |
| Allative | mun | ˠnun | nun |
| Vialis | kun | ˠkun | təkun |
| Aequalis | tun | ˠtun | tətun |
The non-possessed endings in the chart may cause a base-final 'weak' ʀ to drop with compensatory gemination in Inu. Initial m reflects the singular relative marker. The forms with initial n (k or t) are combined to produce possessed oblique with the corresponding absolutive endings in the 3rd person case but with variants of the relative endings for the other persons.
In proto-Eskimo, the ŋ is often dropped within morphemes except when next to ə. ŋ is also dropped under productive velar dropping (the dropping of ɣ,ʀ, and ŋ between single vowels), and "ana" goes to "ii" in these areas.
Numerals
- ataasiq
- maalghut
- pingayut
- sitamat
- tallimat
- aghvinelek
- maalghugneng aghvinelek
- pingayuneng aghvinelek
- qulngughutngilnguq
- qulmeng
- atghanelek
- maalghugneng atghanelek
- pingayuneng atghanelek
- akimiaghutngilnguq
- akimiaq
- akimiaq ataasimeng
- akimiaq maalghugneng
- akimiaq pingayuneng
- yuinaghutngilnguq
- yuinaq
Notes
- ↑ Naukan Yupik at Ethnologue (19th ed., 2016)
- ↑ Naukan Yupik at Ethnologue (23rd ed., 2020)
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds (2017). "Naukan Yupik". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. http://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/nauk1242.
- ↑ Jacobson 2005
- ↑ Jacobson 2005, p. 150
References
- Jacobson, Steven A. (2005), "History of the Naukan Yupik Eskimo dictionary with implications for a future Siberian Yupik dictionary", Études/Inuit/Studies 29 (1–2), http://www.erudit.org/revue/etudinuit/2005/v29/n1-2/013937ar.pdf
- Fortescue, M. D.; Jacobson, S. A.; Kaplan, L. D. (1994), Comparative Eskimo dictionary: With Aleut cognates, Fairbanks: Alaska Native Language Center
| Naukan Yupik language test of Wikipedia at Wikimedia Incubator |
 |