Social:Oroch language
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in русский. (August 2024) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
| Oroch | |
|---|---|
| Орочи кэсэни | |
| Native to | Russia |
| Region | Russian Far East |
| Ethnicity | 527 Orochs (2021 census)[1] |
| Extinct | 2008[2] 119 (2021 census)[3] |
Tungusic
| |
| Dialects |
|
| Cyrillic | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | oac |
| Glottolog | oroc1248[4] |
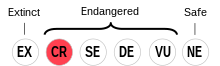 Oroch is classified as Critically Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger. | |
The Oroch language is an extinct language spoken by the Oroch people in Siberia. It is a member of the southern group of the Tungusic languages and is closely related to the Nanai language and Udege language. It was spoken in the Khabarovsk Krai (Komsomolsky, Sovetskaya Gavan, and Ulchsky districts). The language is split into three dialects: Tumninsky, Khadinsky, and Hungarisky. At the beginning of the 21st century, a written form of the language was created. The Russian government and the scientific field disagree on whether the language is living or extinct.[2][5] The last active speaker died in 2008, but there are passive speakers who remember Oroch to varying degrees.[6]
Oroch belongs to the northern subgroup of the Tungusic languages, alongside Udege, its closest relative, and the Ewenic languages.
It is believed that the Oroch language is the closest to Nanai, because a significant group of Nanai (Evenki) origin (Samagirs) joined the Orochs. Until the beginning of the 20th century, some researchers combined the Orochi with the Udege, considering them as close dialects. In the 1930s it was believed that the Udege language could be considered as a single standard language for both ethnic groups.
Extinction
According to the 2002 Census, there were 257 speakers of the Oroch language; however, this is known to be erroneous due to confusion with the similarly-named Orok language. According to the 2010 Census, there were eight speakers. However, according to researchers, by the late 1990s, even the oldest Orochi could only utter a few phrases. The Association of Indigenous Peoples of the Khabarovsk Krai stated that the last fluent speaker of the Oroch language died in 2008. In 2010, this association held a meeting of elderly Orochi, who together were able to remember only about 20 Oroch words, and could not count to ten.[2]
Dialects
The Oroch dialects are (Perekhvalskaya 2022:234):[7]
- Koppi
- Oroch Xadi
- Tumnin
Phonology
Consonants
| Bilabial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | ŋ | |
| Plosive | voiceless | p | t | tʃ | k |
| voiced | b | d | dʒ~ʒ | ɡ | |
| Fricative | voiceless | s | x | ||
| voiced | v | ɣ | |||
| Rhotic | r | ||||
| Lateral | l | ||||
| Approximant | j | ||||
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i iː | u uː ʊ ʊː | |
| Mid | ə əː | ɔ ɔː | |
| Open | æː | a aː |
Oroch has a system of vowel harmony based on the presence or absence of retracted tongue root (RTR).[5]
| Neutral | [–RTR] | [+RTR] |
|---|---|---|
| i iː | u uː | ʊ ʊː ɔ ɔː |
| æː | ə əː | a aː |
Orthography
| А а | Б б | В в | Г г | Д д | Е е | Ё ё | Ж ж |
| З з | И и | Й й | К к | Л л | М м | Н н | Ӈ ӈ |
| О о | П п | Р р | С с | Т т | У у | Ф ф | Х х |
| Ц ц | Ч ч | Ш ш | Щ щ | Ъ ъ | Ы ы | Ь ь | Э э |
| Ю ю | Я я |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Lewis, M. Paul, ed (2015). Ethnologue: Languages of the World (18th ed.). Dallas, Texas: SIL International. https://www.ethnologue.com/18/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Е. В. Перехвальская (2016) (in ru). Язык и общество. Энциклопедия. Moscow: Азбуковник. pp. 339–342/872. ISBN 978-5-91172-129-9. https://iling-ran.ru/library/sociolingva/2016_jazyk_i_obschestvo.pdf.
- ↑ Том 5. «Национальный состав и владение языками». Таблица 7. Население наиболее многочисленных национальностей по родному языку
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds (2017). "Oroch". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. http://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/oroc1248.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Tolskaya, Inna (January 2014). "Oroch Vowel Harmony" (in en). Lingua 138: 128–151. doi:10.1016/j.lingua.2013.10.012. "Oroch, a recently extinct Manchu-Tungusic language".
- ↑ "Перепись населения насчитала в России шесть вымерших и заснувших языков" (in ru). 2024-02-04. https://www.rbc.ru/society/04/02/2024/65bcb9089a794788c65d99b2.
- ↑ Perekhvalskaya, Elena (2022). "From consonant to tone: Laryngealized and pharyngealized vowels in Udihe". in Hölzl, Andreas. Tungusic languages: past and present. Berlin: Language Science Press. pp. 227–263. ISBN 978-3-96110-395-9. OCLC 1356978751.
- ↑ Avrorin (2001)
- ↑ Avrorin & Boldyrev (2001)
Bibliography
- Abramova, G. S. (2002) (in ru). Illustrated Dictionary of the Oroch Language. Saint Petersburg: Drofa.
- Avrorin, V. A. (В. А. Авронин); Boldyrev, B. V. (Б. В. Болдырев) (2001) (in ru). Grammatika orochskogo yazyka. Novosibirsk: SO RAN. ISBN 5-7692-0396-X.
- Альбина Гирфанова (1994). "Орочский язык". Контактологический энциклопедический словарь-справочник: Северный регион. Языки народов Севера, Сибири и Дальнего Востока в контактах с русским языком. М. (1). (in Russian)
External links
| Oroch language test of Wikipedia at Wikimedia Incubator |
| Oroch language test of Wiktionary at Wikimedia Incubator |
 |
