Social:Yugh language
| Yugh | |
|---|---|
| Sym Ket, Yug | |
| Дьук Ďuk | |
| Pronunciation | yug |
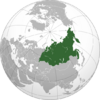
| Native to | Russia |
| Region | Yenisei River |
| Ethnicity | 7 Yughs (2020) |
| Extinct | 1972[1] 2–3 nonfluent speakers (1991)[2][3] 3 (2020)[4] |
Dené–Yeniseian?
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | yug |
yug | |
| Glottolog | yugh1239[5]yugh1240 additional bibliography[6] |
 Map of pre-contact Yeniseian languages. | |
 Yug is classified as Extinct by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger (2010) | |

Yugh (/ˈjuːɡ/ YOOG; Yug) is a Yeniseian language, closely related to Ket, formerly spoken by the Yugh people, one of the southern groups along the Yenisei River in central Siberia.[7] It went extinct by 1972.[1] It was once regarded as a dialect of the Ket language, which was considered to be a language isolate, and was therefore called Sym Ket or Southern Ket; however, the Ket considered it to be a distinct language. By the early 1990s there were only two or three nonfluent speakers remaining,[2] and the language was virtually extinct. The 2002 census recorded 19 ethnic Yugh in all of Russia.[8] In the 2010 census, only one ethnic Yugh was counted, also stating their proficiency in Yugh,[9] while in the 2020 census, 7 ethnic Yugh were counted,[10] 2 of them stating that they were speakers of Yugh.[4]
Phonology
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i [i] | ɨ [ɨ] | u [u] |
| Close-mid | e [e] | ə [ə] | o [o] |
| Open-mid | ɛ [ɛ] | ʌ [ʌ] | ɔ [ɔ] |
| Open | a [a] |
Consonants
| Labial | Alveolar | Alveolo-
Palatal |
Palatalized | Velar | Uvular | Laryngeal/ Pharyngeal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plosive | voiceless | p [p] | t [t] | tʼ [tʲ] | k [k] | (q [q]) | ʔ [ʔ] | |
| voiced | b [b] | d [d] | dʼ [dʲ] | g [g] | ||||
| Fricative | voiceless | f [f] | s [s] | š [ʃ] | šʼ [ʃʲ] | χ [χ] | ||
| voiced | (v [v]) | z [z] | ž [ʒ] | žʼ [ʒʲ] | [ɣ] | (R [ʁ]) | ||
| Affricate | (c [t͡s]) | čʼ [t͡ʃ] | ||||||
| Nasal | m [m] | n [n] | nʼ [nʲ] | ŋ [ŋ] | ||||
| Trill | [r] | |||||||
| Lateral | l [l] | lʼ [lʲ] | ||||||
| Approximant | j [j] | |||||||
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Vajda, Edward (2024-02-19), Vajda, Edward, ed., "8 The Yeniseian language family", The Languages and Linguistics of Northern Asia (De Gruyter): pp. 365–480, doi:10.1515/9783110556216-008, ISBN 978-3-11-055621-6, https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/9783110556216-008/html, retrieved 2024-06-26
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Yugh language at Ethnologue (15th ed., 2005)
- ↑ Kibrik, Aleksandr E. (March 1991). "The Problem of Endangered Languages in the USSR" (in en). Diogenes 39 (153): 67–83. doi:10.1177/039219219103915305. ISSN 0392-1921. https://www.cambridge.org/core/product/identifier/S0392192100322519/type/journal_article.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Том 5. «Национальный состав и владение языками». Таблица 7. Население наиболее многочисленных национальностей по родному языку
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds (2017). "Yugh". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. http://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/yugh1239.
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds (2017). "Yugh (Retired)". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. http://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/yugh1240.
- ↑ Vajda, Edward J.. "The Ket and Other Yeniseian Peoples". http://pandora.cii.wwu.edu/vajda/ea210/ket.htm.
- ↑ 2002 Russian census data
- ↑ 2010 Russian census data
- ↑ Том 5. «Национальный состав и владение языками». Таблица 1. Национальный состав населения
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Werner, Heinrich (1997). Das Jugische (sym-ketische). Veröffentlichungen der societa uralo-altaica. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz. ISBN 978-3-447-03999-4. https://theswissbay.ch/pdf/Books/Linguistics/Mega%20linguistics%20pack/Paleosiberian/Yeniseian/Yugh%3B%20Das%20Jugische%20%28Werner%29.pdf.
References
- Vajda, Edward J. (2002). Yeniseian Peoples and Languages: A History of Yeniseian Studies with an Annotated Bibliography and a Source Guide. Curzon Press. ISBN 0-7007-1290-9.
External links
- Yugh basic lexicon at the Global Lexicostatistical Database
- Yugh at the Vanishing Peoples / Languages database
 |