Software:1000minds
 | |
| Developer(s) | 1000minds Ltd |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 2003 |
| Operating system | Web application |
| Available in | English |
| Type | Decision-making software, Business intelligence, Conjoint analysis, Choice modelling |
| License | Proprietary |
| Website | www |
1000minds is a web application for decision-making[1][2] and conjoint analysis[3][4] supplied by 1000minds Ltd since 2003.[5]
1000minds implements the PAPRIKA method to help organizations, individuals and groups to make decisions based on considering multiple objectives or criteria (i.e. multiple-criteria decision analysis). 1000minds conjoint analysis involves surveying people about their preferences with respect to the relative importance of features or attributes characterizing products or other objects of interest.
In addition, a free consumer-oriented web application based on 1000minds technology to help with 'everyday' decision-making, known as MeenyMo, was released in 2016.[6][7]
Overview
1000minds helps with decisions that involve ranking, prioritizing or choosing between alternatives when multiple objectives or criteria need to be considered simultaneously (i.e. multi-criteria decision making). Depending on the application, budgets or other scarce resources can also be allocated across competing alternatives in pursuit of maximum 'value for money'.[1][2]
The PAPRIKA method is used to determine the relative importance of criteria or attributes and rank alternatives.[8] Invented by Franz Ombler and Paul Hansen at the University of Otago,[9] the PAPRIKA method is based on pairwise comparisons, as illustrated in the accompanying image.
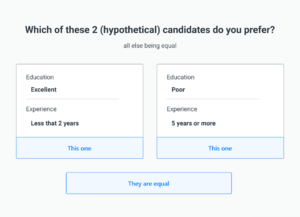
An AI assistant was added to 1000minds in 2023, implementing OpenAI’s GPT-4 technology.[10] The AI assistant suggests criteria and examples of alternatives for the decision at hand; and then the user’s personal preferences or expert knowledge with respect to the relative importance of the criteria are elicited using PAPRIKA, resulting in the alternatives being ranked.
1000minds is also for group decision-making, involving potentially hundreds or thousands of participants – working together or individually with their results aggregated.
1000minds conjoint analysis surveys are for discovering consumers' or other stakeholders' preferences with respect to the relative importance – represented by 'part-worth utilities' or 'weights' – of the features or attributes characterizing products or other objects of interest (i.e. choice modelling, conjoint analysis and discrete choice).
Applications
As well as business, government and non-profit organizations, 1000minds is used for research, as evidenced by the citations below – at over 750 universities and other research organizations worldwide, including for teaching.[11] 1000minds (originally branded as Point Wizard) and several of its applications have won or been a finalist for a number of innovation awards.[10][12][13][14][15][16]
Examples of areas in which 1000minds has been used include the following.
Health
- Prioritising patients for elective (non-urgent) surgery,[17][18][19] rheumatology[20][21][22] and nephrology, geriatrics and gastroenterology[23]
- Identifying criteria for diagnosing and classifying rheumatoid arthritis,[24][25][26] systemic sclerosis,[27][28][29][30][31] gout,[32][33] autoinflammatory disease,[34] cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome,[35][36] dermatomyositis and polymyositis,[37] pediatric post-thrombotic syndrome,[38] systemic lupus erythematosus,[39] Sjögren's syndrome[40][41] and glucocorticoid toxicity[42]
- Measuring patient responses in clinical trials for chronic gout[43][44]
- Testing physical function for patients following hip or knee replacement[45] and educating people with osteoarthritis[46][47][48]
- Developing clinical guidelines for treatment[49][50][51][52]
- Health technology prioritization[53][54][55][56][57][58]
- Prioritizing antibiotic-resistant diseases for R&D[59]
Environment
- Environmental resources management for the ocean[60][61][62]
- Restoration of endangered plant species[63]
- Ecology research ethics[64]
- Sustainable agriculture[65]
Urban planning and waste management
Breeding
Policy-making research
- Monetary policy research[77]
- Retirement income policies research[78]
Management and accounting
- Corporate strategic management[79]
- Measuring business goodwill[80]
Information and communication technology (ICT)
- Cloud computing[81]
- Intelligent transportation systems[82]
Miscellaneous
- Marketing research for mobile banking[83] and fruit juice[84]
- Energy-efficiency decision-making[85][86][87]
- Tourism development[88]
- Evaluating decision-making software[89]
- Research into charitable-giving[90][91]
- Flipped classroom design[92]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weistroffer, H. Roland; Li, Yan (2016). "Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis Software" (in en). Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis. International Series in Operations Research & Management Science. 233. Springer, New York, NY. pp. 1301–1341. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-3094-4_29. ISBN 978-1-4939-3093-7.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Beekman, J. (2020), "2020 Decision analysis software survey", OR/MS Today 47 (6), doi:10.1287/orms.2020.06.04, https://pubsonline.informs.org/magazine/orms-today/2020-decision-analysis-software-survey
- ↑ Smith, K. F. (2011). "The use of conjoint analysis to determine the relative importance of specific traits as selection criteria for the improvement of perennial pasture species in Australia". Crop and Pasture Science 62 (4): 355. doi:10.1071/CP10320.
- ↑ Murphy, Seamus; Cole, Steven M.; Kaminski, Alexander M.; Charo-Karisa, Harrison; Basiita, Rose Komugisha; McDougall, Cynthia; Kakwasha, Keagan; Mulilo, Tabitha et al. (2024). "A gendered conjoint analysis of tilapia trait preference rankings among urban consumers in Zambia: Evidence to inform genetic improvement programs". Aquaculture 591. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2024.741110. Bibcode: 2024Aquac.59141110M.
- ↑ "1000minds Limited". https://app.companiesoffice.govt.nz/companies/app/ui/pages/companies/1284432.
- ↑ Oleson, S. (2016), "Decision analysis software survey", OR/MS Today 43 (5), https://www.informs.org/ORMS-Today/OR-MS-Today-Software-Surveys/Decision-Analysis-Software-Survey
- ↑ Fielding, D.; Hansen, P., eds (August 2016). "Better decision-making!". EcoNZ (37): 7.
- ↑ Hansen, P.; Ombler, F. (2008). "A new method for scoring additive multi-attribute value models using pairwise rankings of alternatives". Journal of Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis 15 (3–4): 87–107. doi:10.1002/mcda.428.
- ↑ Scott, L. (April 2008), "Minds over Matter", North and South: 28–29
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Rae, Sally (23 May 2024). "Otago companies up for Hi-Tech Awards". Otago Daily Times (New Zealand: Allied Press). https://www.odt.co.nz/business/otago-companies-hi-tech-awards.
- ↑ "Research projects – 1000minds" (in en). https://www.1000minds.com/academic/research.
- ↑ "Dunedin's 1000Minds wins award in Sydney" (in en). The National Business Review. 2 May 2007. https://www.nbr.co.nz/article/dunedins-1000minds-wins-award-sydney.
- ↑ "1000Minds". http://consensus.com.au/SoftwareAwards/CSAarchive/CSA2007/1000Minds.htm.
- ↑ "TUANZ announces Innovation Awards finalists". Computerworld New Zealand. 2005.
- ↑ Day, Stacey. "Valid, transparent and fair decision-making processes for access to elective health care • Health Improvement and Innovation Resource Centre" (in en-nz). https://www.hiirc.org.nz/page/17863/valid-transparent-and-fair-decision-making/?tag=healthinnovations&tab=27&contentType=507.
- ↑ Wagstaff, Adam (21 September 2005). "Asian Innovation Awards: contenders stress different ways of thinking". The Asian Wall Street Journal.
- ↑ Hansen, Paul; Hendry, Alison; Naden, Ray; Ombler, Franz; Stewart, Ralph (2012). "A new process for creating points systems for prioritising patients for elective health services". Clinical Governance 17 (3): 200–209. doi:10.1108/14777271211251318.
- ↑ Taylor, William J.; Laking, George (2010). "Value for money – recasting the problem in terms of dynamic access prioritisation". Disability and Rehabilitation 32 (12): 1020–1027. doi:10.3109/09638281003775535. PMID 20380596. https://archive.org/details/sim_disability-and-rehabilitation_2010_32_12/page/1020.
- ↑ Gwynne-Jones, David P.; Iosua, Ella E.; Stout, Kirsten M. (1 May 2016). "Rationing for Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty Using the New Zealand Orthopaedic Association Score: Effectiveness and Comparison With Patient-Reported Scores" (in en). The Journal of Arthroplasty 31 (5): 957–962. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2015.11.022. ISSN 0883-5403. PMID 26944014.
- ↑ Fitzgerald, Avril; Spady, Barbara Conner; DeCoster, Carolyn; Naden, Ray; Hawker, Gillian A.; Noseworthy, Thomas (October 2009). "WCWL Rheumatology Priority Referral Score Reliability and Validity Testing". Arthritis & Rheumatism 60 (Suppl 10): 54. doi:10.1002/art.25137. http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/acrmeeting/abstract.asp?MeetingID=761&id=79687.
- ↑ Fitzgerald, Avril; de Coster, Carolyn; McMillan, Stewart; Naden, Ray; Armstrong, Fraser; Barber, Alison; Cunning, Les; Conner-Spady, Barbara et al. (2011). "Relative urgency for referral from primary care to rheumatologists: The Priority Referral Score". Arthritis Care & Research 63 (2): 231–239. doi:10.1002/acr.20366. ISSN 2151-464X. PMID 20890984.
- ↑ White, Douglas; Solanki, Kamal; Quincey, Vicki; Minett, Andrew; Tam, Gordon; Doube, Alan; Naden, Ray (2015). "Development of a Multidimensional Additive Points System for Determining Access to Rheumatology Services". Journal of Clinical Rheumatology 21 (5): 239–243. doi:10.1097/RHU.0000000000000274. ISSN 1076-1608. PMID 26203827.
- ↑ Noseworthy, T; De Coster, C; Naden, R (2009). "Priority-setting tools for improving access to medical specialists". 6th Health Technology Assessment International Annual Meeting. 38. Singapore. p. S78. http://www.annals.edu.sg/PDF/38VolNo6SupplJun2009/V38N6(Suppl)Final.pdf.
- ↑ Aletaha, Daniel; Neogi, Tuhina; Silman, Alan J.; Funovits, Julia; Felson, David T.; Bingham, Clifton O.; Birnbaum, Neal S.; Burmester, Gerd R. et al. (2010). "2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative". Arthritis & Rheumatism 62 (9): 2569–2581. doi:10.1002/art.27584. ISSN 0004-3591. PMID 20872595.
- ↑ Neogi, Tuhina; Aletaha, Daniel; Silman, Alan J.; Naden, Raymond L.; Felson, David T.; Aggarwal, Rohit; Bingham, Clifton O.; Birnbaum, Neal S. et al. (2010). "The 2010 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: Phase 2 methodological report". Arthritis & Rheumatism 62 (9): 2582–2591. doi:10.1002/art.27580. PMID 20872596.
- ↑ Aletaha, Daniel (2015), "Classification of rheumatoid arthritis", in Emery, Paul, Atlas of Rheumatoid Arthritis, 1, Springer Healthcare, pp. 3–21, doi:10.1007/978-1-907673-91-7_1, ISBN 978-1-907673-90-0
- ↑ Van Den Hoogen, F.; Khanna, D.; Fransen, J.; Johnson, S. R.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Naden, R. P. et al. (2013). "2013 Classification Criteria for Systemic Sclerosis: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Collaborative Initiative". Arthritis & Rheumatism 65 (11): 2737–2747. doi:10.1002/art.38098. PMID 24122180.
- ↑ Van Den Hoogen, F.; Khanna, D.; Fransen, J.; Johnson, S. R.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Naden, R. P. et al. (2013). "2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: An American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative". Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 72 (11): 1747–55. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204424. PMID 24092682.
- ↑ Johnson, S. R.; Naden, R. P.; Fransen, J.; Van Den Hoogen, F.; Pope, J. E.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A.; Matucci-Cerinic, M. et al. (2014). "Multicriteria decision analysis methods with 1000Minds for developing systemic sclerosis classification criteria". Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 67 (6): 706–14. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2013.12.009. PMID 24721558.
- ↑ Pope, Janet E.; Johnson, Sindhu R. (2015). "New Classification Criteria for Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma)". Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America 41 (3): 383–398. doi:10.1016/j.rdc.2015.04.003. ISSN 0889-857X. PMID 26210125.
- ↑ Johnson, Sindhu R. (2015). "New ACR EULAR Guidelines for Systemic Sclerosis Classification". Current Rheumatology Reports 17 (5). doi:10.1007/s11926-015-0506-3. ISSN 1523-3774. PMID 25874345.
- ↑ Neogi, Tuhina; Jansen, Tim L. Th. A.; Dalbeth, Nicola; Fransen, Jaap; Schumacher, H. Ralph; Berendsen, Dianne; Brown, Melanie; Choi, Hyon et al. (2015). "2015 Gout Classification Criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Collaborative Initiative". Arthritis & Rheumatology 67 (10): 2557–2568. doi:10.1002/art.39254. ISSN 2326-5191. PMID 26352873.
- ↑ Vargas-Santos, Ana Beatriz; Taylor, William J.; Neogi, Tuhina (24 June 2016). "Gout Classification Criteria: Update and Implications". Current Rheumatology Reports 18 (7): 46. doi:10.1007/s11926-016-0594-8. PMID 27342957.
- ↑ Haar, Nienke M. ter; Annink, Kim V.; Al-Mayouf, Sulaiman M.; Amaryan, Gayane; Anton, Jordi; Barron, Karyl S.; Benseler, Susanne M.; Brogan, Paul A. et al. (1 May 2017). "Development of the autoinflammatory disease damage index (ADDI)" (in en). Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 76 (5): 821–830. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210092. ISSN 0003-4967. PMID 27811147.
- ↑ Kuemmerle-Deschner, Jasmin B.; Ozen, Seza; Tyrrell, Pascal N.; Kone-Paut, Isabelle; Goldbach-Mansky, Raphaela; Lachmann, Helen; Blank, Norbert; Hoffman, Hal M. et al. (1 June 2017). "Diagnostic criteria for cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome (CAPS)" (in en). Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 76 (6): 942–947. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209686. ISSN 0003-4967. PMID 27707729. http://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1527008/1/Kuemmerle-Deschner_Diagnostic%20criteria.pdf.
- ↑ de Lautour, Hugh; Taylor, William J.; Adebajo, Ade; Alten, Rieke; Burgos-Vargas, Ruben; Chapman, Peter; Cimmino, Marco A.; da Rocha Castelar Pinheiro, Geraldo et al. (May 2016). "Development of Preliminary Remission Criteria for Gout Using Delphi and 1000Minds Consensus Exercises". Arthritis Care & Research 68 (5): 667–672. doi:10.1002/acr.22741. PMID 26414176.
- ↑ Rider, Lisa G.; Aggarwal, Rohit; Pistorio, Angela; Bayat, Nastaran; Erman, Brian; Feldman, Brian M.; Huber, Adam M.; Cimaz, Rolando et al. (1 May 2017). "2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Criteria for Minimal, Moderate, and Major Clinical Response in Juvenile Dermatomyositis" (in en). Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 76 (5): 782–791. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211401. ISSN 0003-4967. PMID 28385804.
- ↑ Avila, M. L.; Brandão, L. R.; Williams, S.; Montoya, M. I.; Stinson, J.; Kiss, A.; Feldman, B. M. (December 2016). "Development of CAPTSure - a new index for the assessment of pediatric postthrombotic syndrome". Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis 14 (12): 2376–2385. doi:10.1111/jth.13530. PMID 27709837.
- ↑ Aringer, M; Dörner, T; Leuchten, N; Johnson, S R (31 May 2016). "Toward new criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus—a standpoint". Lupus 25 (8): 805–811. doi:10.1177/0961203316644338. PMID 27252256.
- ↑ Shiboski, Caroline H.; Shiboski, Stephen C.; Seror, Raphaèle; Criswell, Lindsey A.; Labetoulle, Marc; Lietman, Thomas M.; Rasmussen, Astrid; Scofield, Hal et al. (1 January 2017). "2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for primary Sjögren9s syndrome" (in en). Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 76 (1): 9–16. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210571. ISSN 0003-4967. PMID 27789466.
- ↑ Shiboski, Caroline H.; Shiboski, Stephen C.; Seror, Raphaèle; Criswell, Lindsey A.; Labetoulle, Marc; Lietman, Thomas M.; Rasmussen, Astrid; Scofield, Hal et al. (January 2017). "2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Classification Criteria for Primary Sjögren's Syndrome: A Consensus and Data-Driven Methodology Involving Three International Patient Cohorts". Arthritis & Rheumatology 69 (1): 35–45. doi:10.1002/art.39859. PMID 27785888.
- ↑ Miloslavsky, Eli M.; Naden, Ray P.; Bijlsma, Johannes W. J.; Brogan, Paul A.; Brown, E. Sherwood; Brunetta, Paul; Buttgereit, Frank; Choi, Hyon K. et al. (1 March 2017). "Development of a Glucocorticoid Toxicity Index (GTI) using multicriteria decision analysis" (in en). Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 76 (3): 543–546. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210002. ISSN 0003-4967. PMID 27474764. http://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1508910/.
- ↑ Taylor, W. J.; Singh, J. A.; Saag, K. G.; Dalbeth, N.; MacDonald, P. A.; Edwards, N. L.; Simon, L. S.; Stamp, L. K. et al. (2011). "Bringing It All Together: A Novel Approach to the Development of Response Criteria for Chronic Gout Clinical Trials". The Journal of Rheumatology 38 (7): 1467–70. doi:10.3899/jrheum.110274. PMID 21724718. https://archive.org/details/sim_journal-of-rheumatology_2011-07_38_7/page/1467.
- ↑ Taylor, William J.; Brown, Melanie; Aati, Opetaia; Weatherall, Mark; Dalbeth, Nicola (2013). "Do Patient Preferences for Core Outcome Domains for Chronic Gout Studies Support the Validity of Composite Response Criteria?". Arthritis Care & Research 65 (8): 1259–1264. doi:10.1002/acr.21955. PMID 23335569.
- ↑ Dobson, F.; Hinman, R.S.; Roos, E.M.; Abbott, J.H.; Stratford, P.; Davis, A.M.; Buchbinder, R.; Snyder-Mackler, L. et al. (2013). "OARSI recommended performance-based tests to assess physical function in people diagnosed with hip or knee osteoarthritis". Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 21 (8): 1042–52. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2013.05.002. PMID 23680877.
- ↑ Nicolson, P. J.; French, S. D.; Hinman, R. S.; Hodges, P. W.; Dobson, F. L.; Bennell, K. L. (2014). "Developing key messages for people with osteoarthritis: A delphi study". Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 22: S305–S306. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2014.02.569.
- ↑ French, Simon D.; Bennell, Kim L.; Nicolson, Philippa J. A.; Hodges, Paul W.; Dobson, Fiona L.; Hinman, Rana S. (2015). "What Do People With Knee or Hip Osteoarthritis Need to Know? An International Consensus List of Essential Statements for Osteoarthritis". Arthritis Care & Research 67 (6): 809–816. doi:10.1002/acr.22518. ISSN 2151-464X. PMID 25418120.
- ↑ Aggarwal, Rohit; Rider, Lisa G.; Ruperto, Nicolino; Bayat, Nastaran; Erman, Brian; Feldman, Brian M.; Oddis, Chester V.; Amato, Anthony A. et al. (May 2017). "2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Criteria for Minimal, Moderate, and Major Clinical Response in Adult Dermatomyositis and Polymyositis: An International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies Group/Paediatric Rheu". Arthritis & Rheumatology 69 (5): 898–910. doi:10.1002/art.40064. PMID 28382787.
- ↑ Pinto, Daniel; Danilovich, Margaret K.; Hansen, Paul; Finn, Daniel J.; Chang, Rowland W.; Holl, Jane L.; Heinemann, Allen W.; Bockenholt, Ulf (1 June 2017). "Qualitative Development of a Discrete Choice Experiment for Physical Activity Interventions to Improve Knee Osteoarthritis" (in en). Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 98 (6): 1210–1216.e1. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2016.11.024. ISSN 0003-9993. PMID 28034720.
- ↑ Griffin, D. R.; Dickenson, E. J.; O'Donnell, J.; Agricola, R.; Awan, T.; Beck, M.; Clohisy, J. C.; Dijkstra, H. P. et al. (1 October 2016). "The Warwick Agreement on femoroacetabular impingement syndrome (FAI syndrome): an international consensus statement" (in en). Br J Sports Med 50 (19): 1169–1176. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2016-096743. ISSN 0306-3674. PMID 27629403.
- ↑ Aggarwal, Rohit; Rider, Lisa G.; Ruperto, Nicolino; Bayat, Nastaran; Erman, Brian; Feldman, Brian M.; Oddis, Chester V.; Amato, Anthony A. et al. (1 May 2017). "2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism criteria for minimal, moderate, and major clinical response in adult dermatomyositis and polymyositis" (in en). Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 76 (5): 792–801. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211400. ISSN 0003-4967. PMID 28385805.
- ↑ Rider, Lisa G.; Aggarwal, Rohit; Pistorio, Angela; Bayat, Nastaran; Erman, Brian; Feldman, Brian M.; Huber, Adam M.; Cimaz, Rolando et al. (May 2017). "2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Criteria for Minimal, Moderate, and Major Clinical Response in Juvenile Dermatomyositis: An International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies Group/Paediatric Rheumatology Inter". Arthritis & Rheumatology 69 (5): 911–923. doi:10.1002/art.40060. PMID 28382778.
- ↑ Golan, Ofra; Hansen, Paul; Kaplan, Giora; Tal, Orna (2011). "Health technology prioritization: Which criteria for prioritizing new technologies and what are their relative weights?". Health Policy 102 (2–3): 126–35. doi:10.1016/j.healthpol.2010.10.012. PMID 21071107.
- ↑ Golan, Ofra G; Hansen, Paul (2012). "Which health technologies should be funded? A prioritization framework based explicitly on value for money". Israel Journal of Health Policy Research 1 (1): 44. doi:10.1186/2045-4015-1-44. PMID 23181391.
- ↑ Shmueli, Amir (30 April 2017). "Do the equity-efficiency preferences of the Israeli Basket Committee match those of Israeli health policy makers?". Israel Journal of Health Policy Research 6 (1). doi:10.1186/s13584-017-0145-4. PMID 28469840.
- ↑ Shmueli, Amir; Golan, Ofra; Paolucci, Francesco; Mentzakis, Emmanouil (1 April 2017). "Efficiency and equity considerations in the preferences of health policy-makers in Israel". Israel Journal of Health Policy Research 6 (1): 18. doi:10.1186/s13584-017-0142-7. PMID 28373904.
- ↑ Sullivan, Trudy; Hansen, Paul (1 April 2017). "Determining Criteria and Weights for Prioritizing Health Technologies Based on the Preferences of the General Population: A New Zealand Pilot Study" (in en). Value in Health 20 (4): 679–686. doi:10.1016/j.jval.2016.12.008. ISSN 1098-3015. PMID 28408011.
- ↑ Martelli, Nicolas; Hansen, Paul; van den Brink, Hélène; Boudard, Aurélie; Cordonnier, Anne-Laure; Devaux, Capucine; Pineau, Judith; Prognon, Patrice et al. (1 February 2016). "Combining multi-criteria decision analysis and mini-health technology assessment: A funding decision-support tool for medical devices in a university hospital setting". Journal of Biomedical Informatics 59: 201–208. doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2015.12.002. PMID 26705065.
- ↑ Tacconelli, Evelina; Carrara, Elena; Savoldi, Alessia; Harbarth, Stephan; Mendelson, Marc; Monnet, Dominique L; Pulcini, Céline; Kahlmeter, Gunnar et al. (2017). "Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis". The Lancet Infectious Diseases 18 (3): 318–327. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30753-3. PMID 29276051.
- ↑ Boyd, Philip; Law, Cliff; Doney, Scott (2011). "A Climate Change Atlas for the Ocean". Oceanography 24 (2): 13–6. doi:10.5670/oceanog.2011.42.
- ↑ Chhun, Sophal; Thorsnes, Paul; Moller, Henrik (2013). "Preferences for Management of Near-Shore Marine Ecosystems: A Choice Experiment in New Zealand". Resources 2 (3): 406–438. doi:10.3390/resources2030406. Bibcode: 2013Resou...2..406C.
- ↑ Chhun, Sophal; Kahui, Viktoria; Moller, Henrik; Thorsnes, Paul (2015). "Advancing Marine Policy Toward Ecosystem-Based Management by Eliciting Public Preferences". Marine Resource Economics 30 (3): 261–275. doi:10.1086/681052. ISSN 0738-1360.
- ↑ Graff, P.; McIntyre, S. (2014). "Using ecological attributes as criteria for the selection of plant species under three restoration scenarios". Austral Ecology 39 (8): 907–917. doi:10.1111/aec.12156. Bibcode: 2014AusEc..39..907G.
- ↑ Crozier, G. K. D.; Schulte-Hostedde, A. I. (2014). "Towards Improving the Ethics of Ecological Research". Science and Engineering Ethics 21 (3): 577–94. doi:10.1007/s11948-014-9558-4. PMID 24903671.
- ↑ de Olde, Evelien M.; Moller, Henrik; Marchand, Fleur; McDowell, Richard W.; MacLeod, Catriona J.; Sautier, Marion; Halloy, Stephan; Barber, Andrew et al. (11 May 2016). "When experts disagree: the need to rethink indicator selection for assessing sustainability of agriculture". Environment, Development and Sustainability 19 (4): 1327. doi:10.1007/s10668-016-9803-x.
- ↑ Christofferson, Andrew (2007), "Housing choice in Dunedin", City Planning, District Plan Monitoring Series, Research Report 2007/1, http://www.dunedin.govt.nz/__data/assets/pdf_file/0016/25450/Housing-Choice-in-Dunedin.pdf
- ↑ Moura, Filipe; Cambra, Paulo; Gonçalves, Alexandre B. (2016). "Measuring walkability for distinct pedestrian groups with a participatory assessment method: A case study in Lisbon". Landscape and Urban Planning 157: 282–296. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2016.07.002.
- ↑ Chang, Shoou-Yuh; Gronwald, Frank (1 May 2016). "A Multi-criteria Evaluation of the Methods for Recycling Scrap Tires". The Journal of Solid Waste Technology and Management 42 (2): 145–156. doi:10.5276/JSWTM.2016.145.
- ↑ Byrne, T. J.; Amer, P. R.; Fennessy, P. F.; Hansen, P.; Wickham, B. W. (2011). "A preference-based approach to deriving breeding objectives: Applied to sheep breeding". Animal 6 (5): 778–88. doi:10.1017/S1751731111002060. PMID 22558925.
- ↑ Nielsen, H. M.; Amer, P. R.; Byrne, T. J. (2013). "Approaches to formulating practical breeding objectives for animal production systems". Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section A 64 (1): 2–12. doi:10.1080/09064702.2013.827237. ISSN 0906-4702.
- ↑ Martin-Collado, D.; Byrne, T.J.; Amer, P.R.; Santos, B.F.S.; Axford, M.; Pryce, J.E. (2015). "Analyzing the heterogeneity of farmers' preferences for improvements in dairy cow traits using farmer typologies". Journal of Dairy Science 98 (6): 4148–61. doi:10.3168/jds.2014-9194. ISSN 0022-0302. PMID 25864048.
- ↑ Slagboom, M.; Kargo, M.; Edwards, D.; Sørensen, A. C.; Thomasen, J. R.; Hjortø, L. (2 July 2016). "Herd characteristics influence farmers' preferences for trait improvements in Danish Red and Danish Jersey cows". Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section A 66 (3): 177–182. doi:10.1080/09064702.2016.1277550. ISSN 0906-4702. http://orgprints.org/31388/1/Slagboom%20et%20al.%3B%202017%3B%20Herd%20characteristics%20influence%20farmers%20preferences%20for%20trait%20improvements%20in%20Danish%20Red%20and%20Danish%20Jersey%20cows.pdf.
- ↑ Slagboom, M.; Kargo, M.; Edwards, D.; Sørensen, A.C.; Thomasen, J.R.; Hjortø, L. (1 December 2016). "Organic dairy farmers put more emphasis on production traits than conventional farmers" (in en). Journal of Dairy Science 99 (12): 9845–9856. doi:10.3168/jds.2016-11346. ISSN 0022-0302. PMID 27692711. http://orgprints.org/30149/1/Slagboom_2016_ClusterAnalysis.pdf.
- ↑ Byrne, T.J.; Santos, B.F.S.; Amer, P.R.; Martin-Collado, D.; Pryce, J.E.; Axford, M. (1 October 2016). "New breeding objectives and selection indices for the Australian dairy industry" (in en). Journal of Dairy Science 99 (10): 8146–8167. doi:10.3168/jds.2015-10747. ISSN 0022-0302. PMID 27522425.
- ↑ Smith, K. F.; Fennessy, P. F. (2011). "The use of conjoint analysis to determine the relative importance of specific traits as selection criteria for the improvement of perennial pasture species in Australia". Crop and Pasture Science 62 (4): 355–65. doi:10.1071/CP10320.
- ↑ Smith, K. F.; Ludemann, C.; Lewis, C. D.; Malcolm, B.; Banks, R. G.; Jacobs, J. L.; Fennessy, P. F.; Spangenberg, G. C. (2014). "Estimating the value of genetic gain in perennial pastures with emphasis on temperate species". Crop and Pasture Science 65 (11): 1230. doi:10.1071/CP13384. ISSN 1836-0947.
- ↑ Smith, Christie (2009), "Revealing monetary policy preferences" , Reserve Bank of New Zealand Discussion Paper Series, DP2009/01;
- ↑ Au, Joey; Coleman, Andrew; Sullivan, Trudy (2015). "A Practical Approach to Well-being Based Policy Development: What Do New Zealanders Want from Their Retirement Income Policies?". New Zealand Treasury Working Papers 15 (14). ISBN 978-0-478-43678-5. https://www.treasury.govt.nz/publications/wp/practical-approach-well-being-based-policy-development-what-do-new-zealanders-want-their-retirement-income-policies-wp-15-14.
- ↑ Ruhland, Johannes (2006). "Strategic mobilization: What strategic management can learn from social movement research". Management: Časopis za Teoriju i Praksu Menadžmenta 11 (44): 23–31. http://scindeks.nb.rs/article.aspx?artid=0354-86350644023R.
- ↑ Whiting, Rosalind; Hansen, Paul; Sen, Anindya (2017). "A tool for measuring SMEs' reputation, engagement and goodwill: A New Zealand exploratory study". Journal of Intellectual Capital 18 (1): 170–188. doi:10.1108/JIC-02-2016-0028. ISSN 1469-1930.
- ↑ Isma', Salim Al; ili, N.A.; Li, Mengxiang; Shen, Jun; He, Qiang (2016). "Cloud computing adoption decision modelling for SMEs: a conjoint analysis" (in en). International Journal of Web and Grid Services 12 (3): 296. doi:10.1504/ijwgs.2016.079157. http://ro.uow.edu.au/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=7045&context=eispapers.
- ↑ Mancini, Adriano; Frontoni, Emanuele; Zingaretti, Primo (December 2015). "Embedded Multisensor System for Safe Point-to-Point Navigation of Impaired Users". IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 16 (6): 3543–3555. doi:10.1109/TITS.2015.2489261.
- ↑ Wijland, Roel; Hansen, Paul; Gardezi, Fatima (15 March 2016). "Mobile nudging: Youth engagement with banking apps". Journal of Financial Services Marketing 21 (1): 51–63. doi:10.1057/fsm.2016.1.
- ↑ Lee, Pui Yee; Lusk, Karen; Mirosa, Miranda; Oey, Indrawati (2015). "An attribute prioritization-based segmentation of the Chinese consumer market for fruit juice". Food Quality and Preference 46: 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.foodqual.2015.06.016. ISSN 0950-3293.
- ↑ Karlin, B.; Davis, N.; Sanguinetti, A.; Gamble, K.; Kirkby, D.; Stokols, D. (2012). "Dimensions of Conservation: Exploring Differences Among Energy Behaviors". Environment and Behavior 46 (4): 423–452. doi:10.1177/0013916512467532. https://escholarship.org/uc/item/6xv944gd.
- ↑ Ford, Rebecca; Sumavsk, Ondrej; Clarke, Auren; Thorsnes, Paul (2014). "Personalized Energy Priorities: A User-Centric Application for Energy Advice". Design, User Experience, and Usability. User Experience Design for Everyday Life Applications and Services. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 8519. pp. 542–553. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-07635-5_52. ISBN 978-3-319-07634-8.
- ↑ Ford, Rebecca; Walton, Sara; Stephenson, Janet; Rees, David; Scott, Michelle; King, Geoff; Williams, John; Wooliscroft, Ben (2017). "Emerging energy transitions: PV uptake beyond subsidies". Technological Forecasting and Social Change 117: 138–150. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2016.12.007. https://strathprints.strath.ac.uk/69191/1/Ford_etal_TFSC_2017_Emerging_energy_transitions_PV_uptake.pdf.
- ↑ Romão, João; Machino, Kazuo; Nijkamp, Peter (12 June 2017). "Assessment of wellness tourism development in Hokkaido: a multicriteria and strategic choice analysis". Asia-Pacific Journal of Regional Science 1 (1): 265–290. doi:10.1007/s41685-017-0042-4. Bibcode: 2017AJPRS...1..265R.
- ↑ Mustajoki, Jyri; Marttunen, Mika (2017). "Comparison of multi-criteria decision analytical software for supporting environmental planning processes". Environmental Modelling & Software 93: 78–91. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2017.02.026. Bibcode: 2017EnvMS..93...78M.
- ↑ Hansen, P.; Kergozou, N.; Knowles, S.; Thorsnes, P. (2014). "Developing Countries in Need: Which Characteristics Appeal most to People when Donating Money?". The Journal of Development Studies 50 (11): 1494–1509. doi:10.1080/00220388.2014.925542. http://www.otago.ac.nz/economics/research/otago076647.pdf.
- ↑ Cunningham, Harry; Knowles, Stephen; Hansen, Paul (12 March 2017). "Bilateral foreign aid: how important is aid effectiveness to people for choosing countries to support?". Applied Economics Letters 24 (5): 306–310. doi:10.1080/13504851.2016.1184372. ISSN 1350-4851.
- ↑ Mohammed, Husam Jasim; AL-Dahneem, Ebtehal Abdulmohsin; Hamadi, Abdulmunaam K. (2016). "A comparative analysis for adopting an innovative pedagogical approach of flipped teaching for active classroom learning". Journal of Global Business and Social Entrepreneurship 3: 86–94. ISSN 2462-1714. http://gbse.com.my/22nov16/Paper-9-Done-.pdf.
 |
