Software:Power Plant Simulator & Designer
 | |
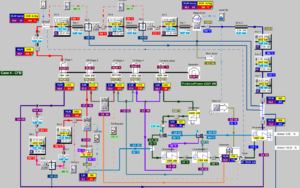 Screenshot PPSD V2020-2 Windows 10 | |
| Developer(s) | KED GmbH (based in Germany][1] |
|---|---|
| Initial release | January 7, 1993 |
| Stable release | PPSD V2020-2
|
| Written in | C++ |
| Operating system |
|
| Platform | x32 and x64 |
| Available in | 3 languages |
| Type | Simulation |
| License | Proprietary software |
| Website | PPSD [2] |
Power Plant Simulator & Designer PPSD is commercial software developed by KED GmbH for modelling thermodynamic cycles and thermodynamic processes and steam generators. PPSD is used mainly for calculation and design of steam generators and power plants.
History
This software was written in 1993 by Grigory Doverman, Ivan Turovsky and Christian Daublebsky von Eichhain as a training simulator for power plants under PC DOS operation system and unique graphical user interface. Later PPSD was adapted for designing of steam generators and heat exchangers, afterwards it was extended to power plants and balance of plants.
Usage
PPSD is applied for the design and calculation of different steam generators [3] with natural circulation, forced circulation and once through with subcritical water and super critical pressure. Also it is possible to design or calculate power plants, cogeneration plants, HRSGs,[4] municipal solid waste and Organic Rankine Cycles. In the last recent versions there were integrated modules for calculating absorption heat pumps for advanced flue gas condensation and District cooling. PPSD is also used for scrutinizing of high temperature corrosion at municipal solid waste incineration.[5] An other use of PPSD is Flow-accelerated corrosion [6] and Natural circulation calculation.[7]
Functional principle
Different components from a component library can be selected an placed as an icon on the graphical user interface. Different components have different icons (e.g. steam turbine, evaporators, condensers, etc.) and can be linked with a connection on the GUI. PPSD has 66 different components and different one phase and two phase working fluids e.g. heat transfer fluid, water/steam, flue gas. The user can change and add working fluids. Also there is a database with different fuels coal, natural gas, oil. In many components there are programmed equations for calculation the heat transfer, heat balance and pressure drop as a function of thermal data and geometrical data. All equations in the model are solved with a special iterative algorithm. During the iteration PPSD accessed the properties of the different working fluids e.g. water steam table IAPWS-IF 97.[8]
The different components can be extended and changed with a visual basic script programming language With the use of object oriented visual basic script programming languages, the scripts can be easily copied to other components.
The user can use different interfaces like MS Excel with VBA for external access to calculation abilities of PPSD, or with Java or C++ to access PPSD calculation abilities form other applications. With this features PPSD can be integrated in a DCS.
Flue-gas condensation heat exchanger design is also possible.
Modes of operation
PPSD have different calculation modes. In the design mode the geometrical and process values are used to calculate the design operation point. In the off design mode the partial load of each component e.g. steam turbine and steam generator base on the design point is calculated and new pressures, temperatures and efficiencys etc. are computed. In dynamic mode transient processes e.g. start-ups, load changes, shedding trips etc. can be calculated as a function of the time. For this the user must insert the energy input as a function of time, valve opening time, PID control values etc.
Interfaces
With the COM- interface the user can have access to all values from external applications, this can be used in DCS[disambiguation needed] for e.g. soot blower control.
Planned features
Different layers, AI Steam Generator Design.
See also
References
- ↑ KED Webpage accessdate=11 April 2020
- ↑ KED Webpage accessdate=11 April 2020
- ↑ HRSG Desing and Operation accessdate=11 April 2020
- ↑ PowerMag accessdate=11 April 2020
- ↑ Korrosion Warnecke accessdate=11 April 2020
- ↑ “DocPlayer” accessdate=11 April 2020
- ↑ “Webpage Technical University Vienna” accessdate=11 April 2020.
- ↑ Website der International Association for the Properties of Water and Steam (engl.)
External links
- webpage of Software Power Plant Simulator & Designer (engl.)
- webpage of International Association for the Properties of Water and Steam (engl.)
- webpage of SienceDirect (engl.)
- webpage of International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (engl.)
- webpage of Technical University of Vienna (ger.)
Literature
- STEAM / its generation and use 42nd ISBN 978-0-9634570-2-8 Library of Congress Catalog Number: 92-74123
- Helmut Effenberger: Dampferzeugung. Springer-Verlag, ISBN 3-540-64175-0
